Montelukast
|
Context:
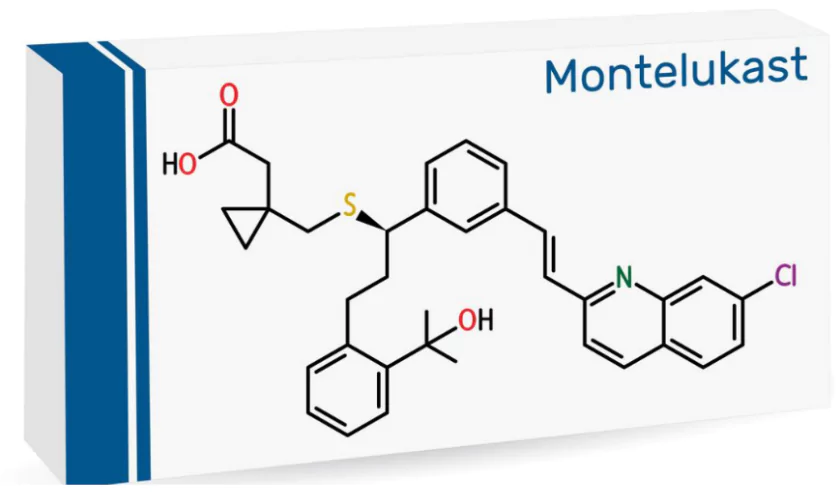
While caution is being exercised everywhere, the sale of Montelukast drugs in India is unregulated and seems to be increasing exponentially.
About Montelukast:
- Refers: An orally dosed drug to prevent wheezing, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and coughing caused by asthma, and also used to prevent breathing difficulties during exercise.
- Classification: Montelukast is not an antihistamine.
-
- Antihistamines are common drugs that can be purchased without a prescription and are used to treat short-lived allergic reactions, like a sneezing fit or an itch.
- Availability: It is readily available as a film-coated tablet, chewable tablet, or oral granules and syrup (for kids) under different brand names.
- Approval: It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1998 and marketed under the brand name ‘Singulair’.
- It was approved for treating chronic asthma and prophylaxis and the prevention of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
- It is also approved to relieve seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis symptoms.
|
YUDH ABHYAS-2024

|
Context:
Recently, the 20th edition of India-USA Joint Military Exercise YUDH ABHYAS-2024 was held at Foreign Training Node in Mahajan Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan.
About Exercise YUDH ABHYAS:
- Annual Joint Exercise: It has been held annually since 2004, alternating between India and the USA.
- Aim: To enhance joint military capability of both sides to undertake counter terrorism operations in a sub conventional scenario under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
Significance:
- Share Best Practices: It will enable both sides to share best practices in tactics, techniques and procedures of conducting joint operations.
- Interoperability: It will facilitate developing interoperability, bonhomie and camaraderie between the two armies.
- Enhance Cooperation: The joint exercise will also enhance defence cooperation, further augmenting bilateral relations between the two friendly nations.
- Counter Terrorism: Prepare a joint exercise to a terrorist action, joint planning and combined field training exercises that simulate real-world counter-terror missions.
Joint Exercises of India-USA:
- Military Training: Yudh Abhyas, Vajra Prahar and Exercise Tiger Triumph
- Exercise Tiger Triumph is the first tri-service military exercise between the two countries.
- Its 1st edition was held in 2019.
- Air Forces: Cope India
- Naval Exercise (along with Japan): Malabar
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR): In September 2022, the QUAD countries (US, India, Japan and Australia) signed the “Guidelines for the Quad Partnership on HADR in the Indo-Pacific”.
|
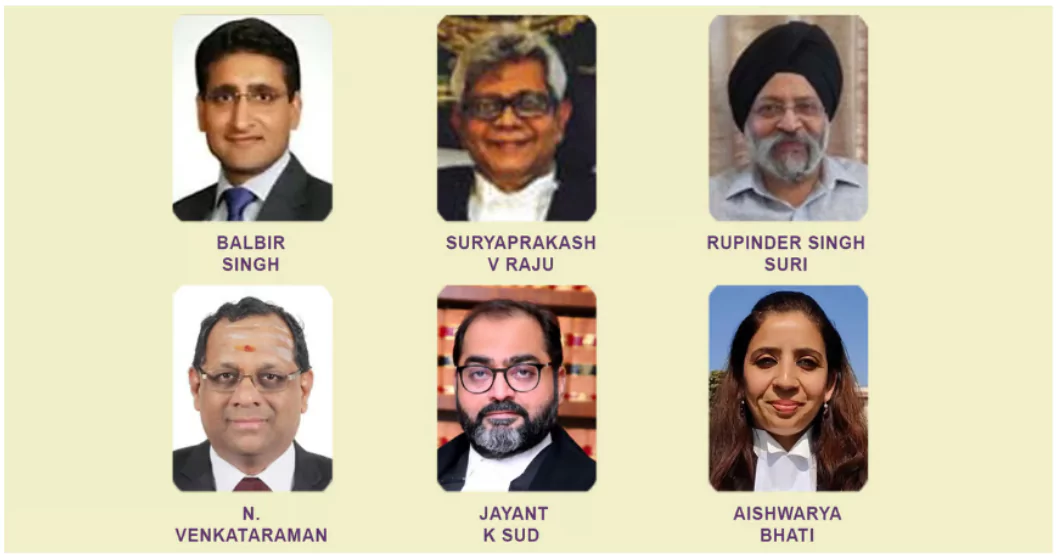
Additional Solicitor Generals

|
Context: Recently, the government has appointed six senior advocates as Additional Solicitor Generals (ASGs) to represent it in the Supreme Court.
Additional Solicitor General of India:
- Role
- The Addl. SGI is a law officer who assists the SGI and the Attorney General of India.
- The SGI and Addl. SGIs advise the government and represent the Union of India in legal matters.
- Appointment
- The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC), headed by the Prime Minister, recommends and officially appoints the SGI and Addl. SGIs.
- The proposal for appointment is usually made by the Joint Secretary or Law Secretary in the Department of Legal Affairs.
- Status: The SGI and Addl. SGIs are statutory posts, unlike the Attorney General of India’s Constitutional post.
- Governing rules: The Addl. SGI is governed by the Law Officers (Conditions of Service) Rules, 1987.
Solicitor General of India
- The Solicitor General is a subordinate office to the Attorney General of India. He is the secondary law officer of the country.
- Assistance: The Solicitor General is assisted by Additional Solicitor Generals, who represent the Union of India across courts.
- Constitutional Position: While the Attorney General of India is a constitutional office, the Solicitor General of India and Additional Solicitor Generals are statutory offices, appointed by the Appointment Committee of the Cabinet.
|
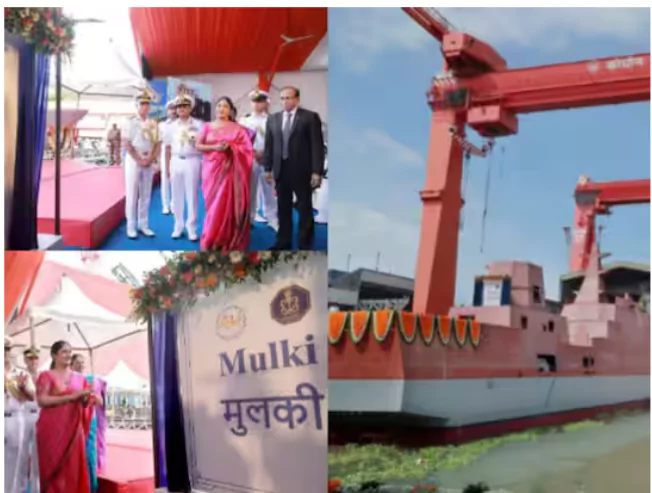
INS Malpe and INS Mulki

|
Context: The Indian navy launched the fourth and fifth ships, Malpe and Mulki, of the 8 Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft project.
- INS Malpe and INS Mulki are two of the latest indigenously designed and built Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Watercrafts (ASWSWCs) developed for the Indian Navy.
- These vessels are the fourth and fifth ships in the series of ASWSWCs commissioned by the Navy.
- Constructed by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- The contract for eight such vessels was signed between the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and CSL on April 30, 2019.
- Classified as the Mahe Class, these ships will eventually replace the Abhay Class ASW Corvettes currently in service.
- Features:
-
- The ships are designed for a range of operations, including anti-submarine warfare in coastal waters, mine-laying, sub-surface surveillance, search and rescue, and low-intensity maritime missions.
- Measuring 78 meters in length, 11.36 meters in width, and with a draught of 2.7 meters, these vessels displace around 900 tonnes.
- They can reach speeds of up to 25 knots and have a range of 1,800 nautical miles.
- Fitted with state-of-the-art, indigenously developed SONAR systems for underwater detection,
- Also equipped with lightweight torpedoes, anti-submarine warfare rockets, a close-in weapon system, and remote-controlled guns for enhanced operational capability.
|
Financial Action Task Force (FATF)

|
Context: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is expected to release its report on India’s mutual evaluation, which was adopted at its June 2024 plenary in Singapore, on September 19.
About FATF
- FATF is an intergovernmental organization established in 1989 out of a G-7 meeting of developed nations in Paris.
- Secretariat: Located at the OECD headquarters in Paris, it supports the substantive work of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) membership and global network.
- Evolution of Mandate: Originally formed to combat money laundering, it expanded its mandate after the 9/11 attacks to include efforts against terrorist financing.
- Later, efforts to counter the financing of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) were added in 2012.
- Weapons of mass destruction (WMD) are weapons that can cause massive destruction and loss of human life on a large scale.
- Grey and Black Lists
- Grey List: Includes countries considered safe havens for supporting terror funding and money laundering, serving as a warning.
- Black List: Comprises Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs) supporting such activities.
- Sessions and Decision-Making:Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Plenary is the decision-making body, meeting three times per year to discuss Mutual Evaluation Reports (MERs) of countries.
- Countries with major deficiencies in their Anti-Money Laundering/Combating the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) regimes are listed under “jurisdictions under increased monitoring” (grey list) or “high-risk jurisdictions” (black list).
- Membership: Currently, a 40-member body representing major financial centres globally.
- Includes two regional organisations: the European Commission and the Gulf Cooperation Council.
- India’s Association: India joined as an observer in 2006 and became a full member in 2010.
- Additionally, India is part of its regional partners, the Asia Pacific Group (APG) and the Eurasian Group (EAG).
- India’s Status: “Regular follow-up” category (includes France, Italy, Russia, and the UK)
- Observers: There are 31 international and regional organisations which are Associate Members or Observers of the FATF and participate in its work.
- Organisations with observer status include the Asian Development Bank (ADB), International Monetary Fund (IMF), Interpol, and the World Bank, among others.
- Mutual Evaluation Report:
- It is an assessment of a country’s measures to combat money laundering and the financing of terrorism and proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
- Evaluation Team: The reports are peer reviews, where members from different countries assess another country.
- Without prejudice: The mutual evaluation report is without prejudice to the status or justification that led to the designation of an entity as a terrorist or terrorist group or organisation.
- Mutual Evaluations have two main components
- Effectiveness
- Technical compliance
|
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)

|
Context: The Centre has relaxed the “automatic exclusion” criteria under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G).
More in news:
- Newly Eligible Households:
- Families owning two-wheelers, motorised fishing boats, refrigerators, and landline phones.
- Households earning up to Rs 15,000 per month.
- Additional Key Exclusion Criteria:
- Households with pucca roofs and/or pucca walls.
- Households living in homes with more than two rooms.
About Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G):
- Objective: Provide pucca houses with basic amenities to rural families who are homeless or living in kutcha or dilapidated houses.
- Beneficiaries: Identified using the Socio-Economic and Caste Census (SECC) 2011.
- Flagship mission by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD), implemented by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- Cost Sharing:
- 60:40 ratio between the Centre and states for plain areas.
- 90:10 ratio for Northeastern states, Himalayan states, and J&K.
- 100% cost borne by Centre for other UTs.
- Features:
-
- Financial Assistance:
- Beneficiaries receive up to Rs 1.2 lakh in plains.
- Up to Rs 1.3 lakh in hilly states, difficult areas, and tribal/backward districts under the Integrated Action Plan (IAP).
- Construction: Beneficiaries construct houses with government technical assistance.
- Convergence with other schemes: Encourages coordination with schemes like Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) and MGNREGA for toilet construction and wage employment.
|
![]() 11 Sep 2024
11 Sep 2024