The Centre is planning to allocate Rs 6,000 crore to promote precision farming.
- There is a provision of introducing a Smart Precision Horticulture Programme under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) scheme.

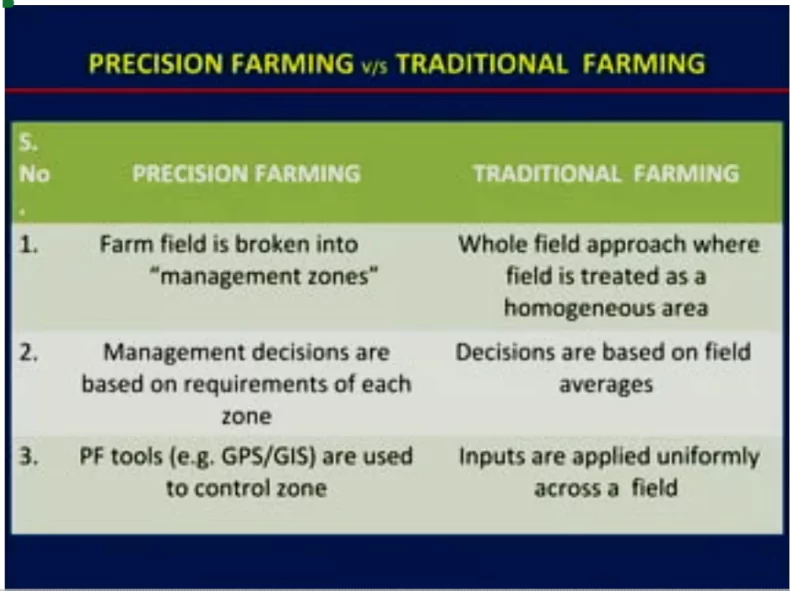
What is precision farming?
- Precision agriculture (PA) is a modern farming approach that focuses on using smart technologies like Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), drones, and data analytics.
- It uses mapping systems, GPS, satellite imagery, sensors, and remote sensing technologies.
- Key Goal: To create a decision-support system for whole farm management.
- optimise resource usage
- Improve quality yields
- preserving natural resources.
- About Smart Precision Horticulture Programme
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Precision farming technologies
- Global Positioning System: GPS uses satellites and helps farmers in creating accurate maps of their fields.
- Grid sampling: It is a method of collecting soil at a regular interval to check its properties.
- This technique helps farmers in understanding soil variations, PH levels, nutrients, moisture across the field.
- Variable-rate technology: This is a technique in which all inputs such as seed, fertilisers, and water are applied at a varied rate.
- It helps farmers in over and under application of inputs in the field.
|
-
- It is an initiative of the Union Ministry of Agriculture.
- The programme will cover 15,000 acres of land from 2024-25 to 2028-29.
- It aims to benefit around 60,000 farmers.
- Precision Farming Development Centres (PFDCs)
- The Centre has set up 22 PFDCs to test and modify farming technologies according to local conditions.
- These PFDCs are located in State/Central Agricultural Universities, ICAR Institutes, and IITs across several states, including Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Odisha, Rajasthan, West Bengal, UP, and more.

Challenges of Precision Farming
- High Costs: Tools like GPS and drones are expensive, making them unaffordable for many farmers.
- Lack of Standardization: There are no common rules for data collection, which complicates the effective use of precision farming.
- Connectivity Issues: Reliable internet is needed for real-time data sharing, but rural areas often lack strong connections.
- Environmental Concerns: Misuse of technology can harm the environment which leads to issues like soil damage and water shortages.
Other key initiatives for agriculture
-
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
- AIF, launched during COVID-19, provides loans for infrastructure projects in smart and precision agriculture.
- Farmers, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Primary Agricultural Credit Societies, and Self-Help Groups (SHGs) are eligible for loans with a 3% interest subvention.
- Funding is available for technological solutions like:
- Farm/harvest automation
- Drones
- Specialised sensors
- Blockchain and AI
- Remote sensing and IoT in agriculture.
-
International Collaboration
- The government is looking to partner with countries like the Netherlands and Israel that are known for using advanced technology in farming through centers of excellence.
- Over the next five years, the plan is to set up 100 Centres of Excellence (CoEs) to promote modern farming methods.
- So far, 32 CoEs have already been created in 14 states under the Indo-Israel Agriculture Project.
-
Support for States and UTs
-
- Funds are provided to states/UTs for projects using AI and machine learning under schemes like the National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture.
|
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
![]() 17 Sep 2024
17 Sep 2024



