Starlink’s satellite network is disrupting radio astronomers by creating unwanted electromagnetic radiation (UEMR), known as “radio noise.”
More on the news
- Starlink currently has over 6,300 satellites orbiting Earth at around 550 km altitude.
- These satellites provide high-speed internet to remote areas with limited access.
- The work of radio astronomers is disrupted by interference from satellites.

About Starlink satellites
- It is a large constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
- Developed by: SpaceX, led by Elon Musk.
- Purpose: Provide global high-speed internet, especially in remote and underserved areas.
- Applications: Rural internet, disaster zones, military applications, and potential support for 5G networks.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is the Space Internet?
- It is defined as the international connection that relies on satellites orbiting the earth.
- These satellites send and receive signals that connect to the internet service providers (ISPs).
- It routes the signals to users’ internet modems.
- It aims to provide internet access globally especially in remote areas.
|
- Starlink’st-Generation Satellites:
- The first-generation Starlink satellites:
- It was launched as part of the initial phase of SpaceX’s satellite internet constellation.
- These satellites operate in low Earth orbit (LEO) to provide internet connectivity.
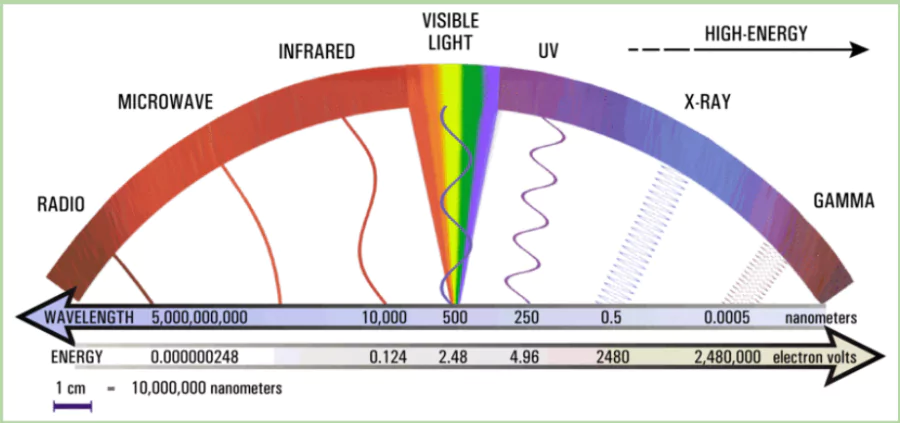
Radio waves
- These are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies.
- They can be naturally produced or artificially generated.
- Key Applications:
- Communication: Used for radio broadcasting, mobile phones, and satellite communication.
- Radar: Essential for navigation and weather tracking.
- Networking: Enables wireless internet and other data transmission.
|
-
- Second-Generation Satellites:
- Starlink’s second-generation satellites emit UEMR 32 times brighter than the first generation.
- It has also worsened the problem despite efforts to reduce radio leaks.
Benefits of Starlink Satellites
- Global Coverage: Brings internet access to remote and underserved areas, reducing the digital gap.
- Low Latency: Provides low latency (20-40 ms) because of the satellites’ low Earth orbit which make it good for real-time activities like video calls and online gaming.
- Quick Setup: Can be set up faster than traditional ground-based networks which makes it ideal for emergencies and disaster zones.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Limitations
- Limited coverage: starlink satellites are not suitable for crowded cities due to its high demand and its infrastructure.
- Radio Pollution: It can interfere with radio signals which can make its study hard for that period.
- Visibility: These satellites are highly reflective and visible which can disrupt astronomical observations.
Need for Regulations on Satellite Emissions
- Increasingly bright satellites: Starlink’s new generation of satellites is significantly brighter than the previous one, despite efforts to reduce radio frequency interference (RFI).
- Growing number of satellites: The number of satellites in orbit is expected to increase dramatically in the coming years which can exacerbate the problem of RFI.
- Lack of regulations: Currently, there are no specific regulations governing satellite emissions.
Space Internet Projects in Low Earth Orbit
- One Web: It is a global satellite internet project.
- It uses a large constellation of satellites in Low Earth Orbit to offer internet services.
- It also aims to provide services in rural and remote areas with limited internet options.
- Project Kuiper: It is Amazon’s initiative to provide satellite based internet service globally.
- Similar to one web, it aims to offer services in rural and remote areas with limited internet options.
|
-
- There is only voluntary cooperation between satellite operators and astronomers.
- Need for regulation: To minimize the impact of satellite emissions on astronomical observations, regulations are necessary to set limits on RFI levels and ensure compliance.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Radio Astronomy
- Radio astronomy observes space objects using radio waves, which are longer than visible light.
- Radio telescopes detect these radio waves, unlike regular telescopes that detect light.
- Bright light can make it hard to see objects, and the same happens with radio waves when satellites interfere.
- The radio waves from satellites overwhelm telescopes which make it hard for scientists to study space properly.
|
![]() 21 Sep 2024
21 Sep 2024

