India’s External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar highlighted the importance of BRICS for multipolarity and global diversity in the BRICS Foreign Ministers Meeting on the sidelines of UNGA79.
- The meeting was convened by Brazilian Foreign Minister Mauro Vieira.
- Agenda: The focus of the discussion was on reforming multilateralism and strengthening development, Sustainable Development Goals, addressing debt, promoting fair trade, and poverty alleviation
About BRICS Group
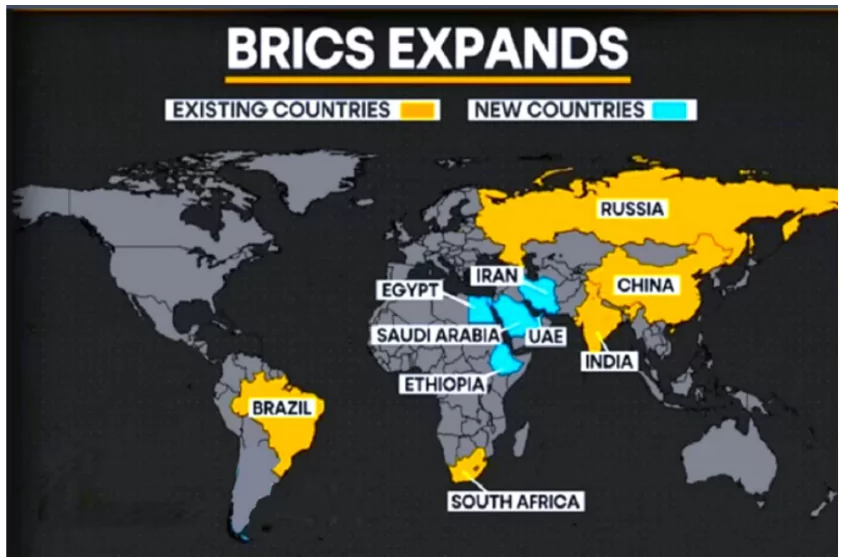
- BRICS is an acronym for the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies namely,
- Members: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa
- South Africa joined the group in 2010
- Coined by: It is coined in 2001 by economist Jim O’Neill to represent the four rapidly growing economies of Brazil, Russia, India, and China
- Origin: The group was formalised as BRIC during the 1st BRIC Foreign Ministers’ Meeting, which met on the sidelines of the General Debate of the UN Assembly in New York City 2006
- 1st BRIC Summit: The 1st BRIC summit was held in Yekaterinburg, Russia on 16 June 2009.
- Expansion: The 2023 summit of BRICS in Johannesburg accepted 5 new countries ie. , Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia and the UAE from 1st january 2024
- BRICS Summit 2024: It will be hosted by Russia in Kazan from October 22 to 24, 2024.
- Agenda: To promote partnership and cooperation within the framework of the association on three key tracks – politics and security, the economy and finance, and cultural and humanitarian ties.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Significance
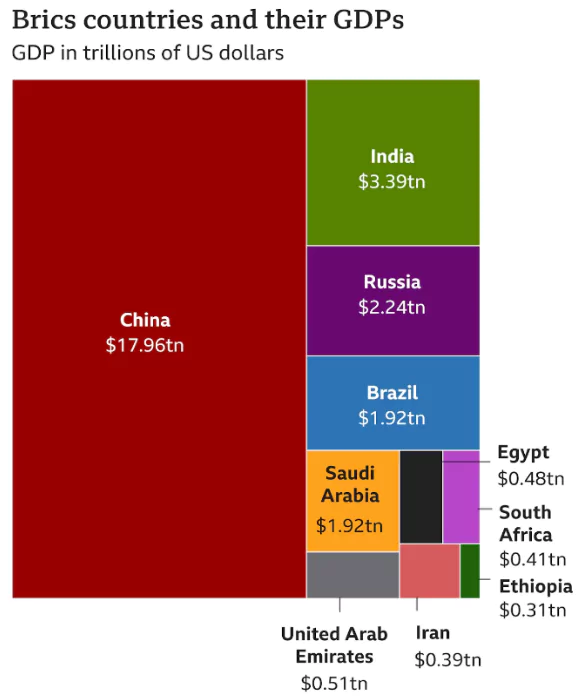
- Representation: BRICS countries together host 41% of the global population, with a combined GDP of around $25.85 trillion , representing about 24% of the world’s total economic output and cover 29 percent of the planet’s land resource.
- International Cooperation: BRICS countries are influential members of leading international organisations and agencies, including the UN, the G20, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Group of 77.
- Global South: The BRICS was a grouping of emerging economies which are not fully aligned with western systems and institutions and thus represented the global south into developing their own parallel order for their own development.
- Alternative Financial Architecture: BRICS through the New Development Bank (NDB) promotes economic progress in less developed countries without the debilitating conditionalities of the support imposed by the World Bank and IMF
About Multipolarity
- The international system is characterized by the distribution of power and Multipolarity is a system where there are three or more great powers active in the international scene.
- A multipolar system doesn’t require three powers of equal size; it just requires that significant power is concentrated in more than two states.
BRICS and Emerging Multipolarity
- Representing Global South: BRICS provides an alternative framework for the Global South to be represented in the critical deliberations shaping global agendas, trade regulations, and other consequential international matters.
- Financial Autonomy and Equity: The BRICS nations has initiated discussions to de-dollarize intra-BRICS transactions, a step towards financial equity and autonomy.
- The idea is to trade between the “R5,” denoting the currencies of the BRICS countries, (the Brazilian Real, the Russian Ruble, the Indian Rupee, the Chinese Renminbi, and the South African Rand)
- BRICS Expansion: The 5 new members of the BRICS will expand the bloc’s reach into pivotal new region ie. Africa with the inclusion of Ethiopia and Egypt and MIddle- East Asia with inclusion of Iran and UAE and Saudi Arabia
- Energy Strategic Advantage: The expanded BRICS bloc now controls close to half of the global energy production with Russia, Saudi Arabia, Brazil, Iran and UAE in its ambit. Also with China and India ( the largest consumer countries) also a part, a synergy is created within the bloc, where members’ energy demands can be substantially met by intra-bloc supply
- Petrodollars: For the BRICS+ nations, trading oil in petrodollars will not only bolster their foreign currency reserves but also provide them with bargaining leverage on the global stage posing a considerable challenge to the dollar’s hegemony in the Global South.
- Showing Solidarity: The BRICS nations’ non compliance with western-led economic and financial sanctions against Russia by offering trade diversion and other relief has weakened the effectiveness of US-led sanctions as a tool for advancing economic and geopolitical interests.
|
Challenges
- Geographical Cohesion: The BRICS countries are geographically dispersed with each residing in different corners of the globe thus limiting their cooperation and bargaining power on only specific matters.
- Example: Regional grouping like African Union or ASEAN works with more synergy as they have a stake in regional development.
- Lack of a Common Point: BRICS countries came together on the plank of engaging in only economy and Trade without having any shared history, culture, or language or political structure among them.
- Collective Decisions: BRICS, unlike groups like EU or ASEAN, is not characterized by collective decision making and does not seem to function as a bloc in traditional sense.
- Economic Asymmetries: The economic domination of China in the bloc has established China centered intra-BRICS trade relations leading to capturing of markets by China originated products.
- Perception as Anti West: The presence of China, Russia and now Iran in the grouping and also its stated goal of providing an alternative financial and governing architecture can be perceived as an attempt to challenge the western dominated rules based order.
- Expansion Strategy: BRICS’s expansion strategy is not clearly defined and was announced without a concrete policy to guide the group’s future expansion. Also there can be a clash between the democratic and non-democratic political ideologies leading to more divergences within the group in the future.
- Competing Political Interest: The BRICS group host regional rivals with competing political and economic interest like China v/s India and now Saudi Arabia v/s Iran. Such competition could risk derail the cooperation within the group and may lead to fragmentation within the group.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Way Forward
- Strengthen Cooperation: BRICS nations must strengthen macroeconomic policy coordination amongst themselves and multilateral cooperation by engaging within frameworks such as the G20, WTO, World Bank, and International Monetary Fund to improve global economic governance.
- Diversification: BRICS expansion has provided its members with opportunities to diversify their partnerships in energy sector (6 top oil producers in the group), enabling technology transfer, advancing space research, and strengthening the BRICS’ New Development Bank (NDB)
- Build New Institutions: The BRICS with the recent addition of members is an expanding body which requiring new BRICS institution like a Secretariat and BRICS currency union which will to govern the future direction of the body.
- Focus on People-to-people Cooperation: The BRICS group should also focus on building people to people ties as it lacks any common cultural and historical link. This can be done by encouraging tourism via the BRICS Visa or building BRICS educational institutions.
![]() 28 Sep 2024
28 Sep 2024



