Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun have won the Nobel Prize for Medicine 2024 for “the discovery of microRNA and its role in post-transcriptional gene regulation”.
About Nobel Prize
- Categories: Nobel Prize is a set of five international prizes awarded annually in Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace.
- Origin :The Nobel Prize was established by the will of Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite.
- First awarded in 1901 on the 5th anniversary of the death of Alfred Nobel.
- In 1968, a sixth prize was introduced in Economic Sciences (Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences) but is not officially called a Nobel Prize.
- Venue: The prizes are awarded by the Nobel Foundation in Stockholm, Sweden.
- The Peace Prize is awarded in Oslo, Norway.
- Eligibility: It can only be awarded to individuals except for the peace prize that can be conferred on individuals or institutions.
- A maximum of 3 individuals can share a prize.
Notable Awards in Medicine
- James D. Watson is a Nobel Prize-winning scientist for his work on DNA and genetics.
- The 2023 Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded to Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman for their work on messenger Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA).
Nobel Prize and India
- Rabindranath Tagore was the first non-European and Indian to receive a Nobel Prize in 1913 for Literature.
- India’s first Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman in 1930 for his work on the scattering of light and the discovery of the Raman Effect.
Also Read: Nobel Prize 2024 Winners List
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is MicroRNA (miRNA)?
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a class of small, non-coding RNA molecules that regulates gene expression in cells by binding to messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and blocking them from making proteins.
- Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are molecules that do not encode proteins.
Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun
- Both Ambros and Ruvkun are American biologists.
- Ambros currently works at the Programme in Molecular Medicine at the University of Massachusetts in the U.S.
- Ruvkun is a professor of genetics at the Harvard Medical School and researches microRNA and RNA interference mechanisms at the Ruvkun Lab at Massachusetts General Hospital.
- Their research revealed a new class of tiny RNA molecules critical for regulating gene activity, essential for multicellular organisms’ development and function.
- This breakthrough, first made in the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans.
|
-
- Examples include miRNAs, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), and transfer RNAs (tRNAs).
- Composition: miRNAs are approximately 21 to 24 nucleotides long, much smaller than messenger RNAs (mRNAs), which carry instructions for protein synthesis.
- Their small size allows them to bind to specific target mRNAs.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Discovery of MicroRNAs
- miRNAs were first discovered in Caenorhabditis elegans, a nematode worm, by Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun in 1993.
- miRNAs are found in cells and in the bloodstream.
Significance of MicroRNAs
- Role in biological processes :They are significant for different biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune response.
- Biological Regulation: They also regulate cholesterol metabolism and are involved in cardiomyopathies and stroke.
- Role in pregnancy: MicroRNAs contribute to pregnancy development by regulating steps like trophoblast differentiation, embryo implantation, and maternal-foetal immune tolerance.
- Disease Implications: Alteration in miRNA expression can lead to changes in the gene expression profile, contributing to many human disorders.
- Abnormal expression of miRNA has been linked to many human cancers.
- Mutations in genes coding for microRNAs have been found in humans, causing conditions such as congenital hearing loss, eye and skeletal disorders
- Applications: A single micro-RNA can regulate the expression of many genes, and alternatively a single gene can also be controlled by multiple micro-RNAs.
- This leads to fine tuning of different types of cells despite similar genetic information.
- Understanding them is the first step towards further research.
How do miRNAs Control Gene Expression?
- miRNAs control gene expression by binding to mRNA in the cell cytoplasm.
- Instead of being quickly translated into protein, the marked mRNA is either destroyed and its components recycled or preserved for later translation.
- If the level of a specific miRNA is underexpressed (abnormally low), the protein it regulates may be overexpressed (unusually high level in the cell).
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Production and Cycle of MicroRNA
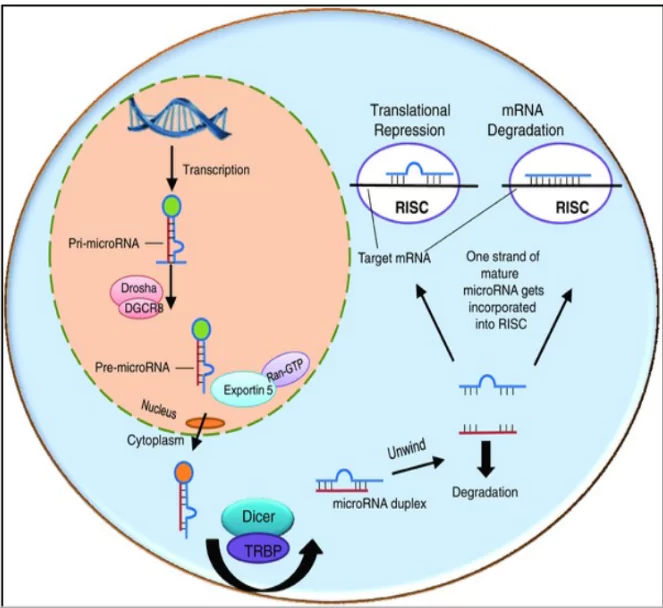
- Cells make microRNA through a process similar to the early steps of protein synthesis.
- When a microRNA gene is activated, the DNA strand opens up and is transcribed into RNA.
- The initial gene transcript is called primary miRNA (pri-miRNA).
- In the cell nucleus, these hairpin-loop molecules are cut to form double-stranded precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA).
- Pre-miRNA is transported to the cytoplasm, where it is further cut to form mature miRNA (about 22 nucleotides long).
- Mature miRNA binds with the RNA interference silencing complex (RISC).
- miRNA then binds to target mRNA, blocking its translation or triggering its degradation.
![]() 8 Oct 2024
8 Oct 2024
