The Union Cabinet recently approved the development of the National Maritime Heritage Complex Lothal in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
About the project
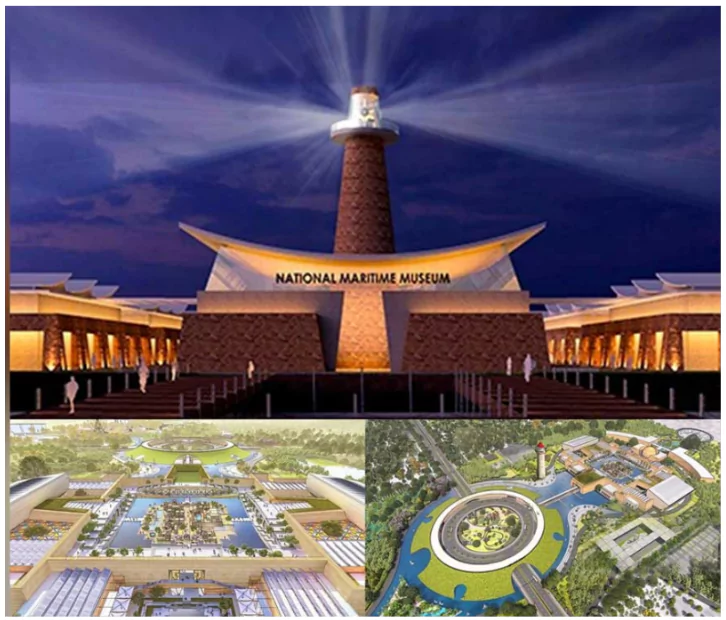

- Project: Development of the National Maritime Heritage Complex at Lothal, Gujarat.
- Aim: To showcase India’s 4,500-year-old maritime heritage, making it the world’s largest maritime complex.
- Nodal Authority: Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways.
Key Features
- Phase 1A:
- Currently under implementation with over 60% progress, expected completion by 2025.
- Phase 1B:
- Involves the construction of a Lighthouse Museum, expected to be the world’s tallest.
- Will feature eight galleries, including:
- Indian Navy & Coast Guard Gallery (with external naval artefacts like INS Nishank, Sea Harrier aircraft, and UH3 helicopter).
- A replica of Lothal township with an open aquatic gallery and a jetty walkway.
- Funding for the Lighthouse Museum will come from the Directorate General of Lighthouses and Lightships.
- Phase 2:
- Coastal States Pavilions to be developed by the respective coastal states and union territories.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Lothal
- Discovered: 1954 by S.R. Rao, Indian archaeologist.
- Location: Southernmost site of the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC), only port-town.
- Situated along the Bhogava River, a tributary of the Sabarmati, near the Gulf of Khambhat.
- Etymology: Derived from the Gujarati words “Loth” (dead) and “thal” (mound), meaning “the mound of the dead.”
- Trade: Thriving centre for trade in beads, gems, and ornaments, with exports reaching West Asia and Africa.
- This dockyard facilitated maritime trade with Mesopotamia, Egypt, and other regions.
Key Features
- Tidal Dockyard:
- Oldest known artificial dockyard in the world.
- Connected the city to an ancient course of the Sabarmati River.
- Architecture:
- Divided into two parts:
- Citadel (Upper Town)
- Lower Town
- Seals:
- Lothal has the 3rd largest number of seals among IVC sites.
- Depicted animals: short-horned bulls, mountain goats, tigers, composite animals like the elephant bull.
- Pottery: Redware pottery used for daily activities.
- Terracotta Art:
- Gamesmen resembling modern-day chess pieces.
- Animal figures with wheels and movable heads (used as toys).
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
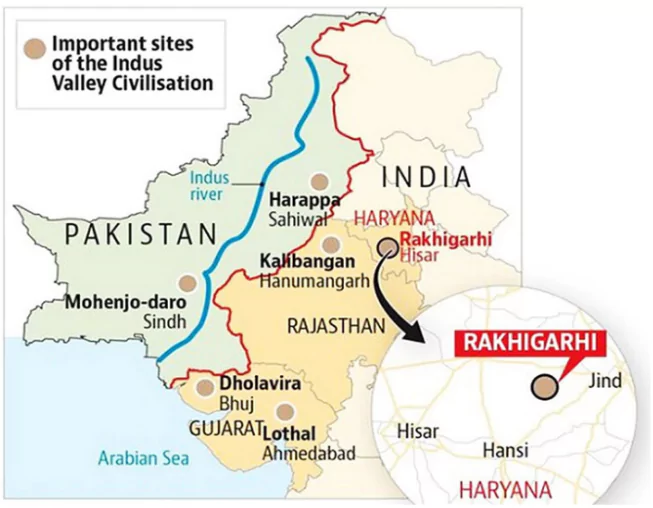
Important Sites of IVC
- Harappa in present Pakistan: Granaries with big platforms, Stone symbol of lingam and yoni, Mother goddess figure, Wheat and barley in wooden mortar, Dice, Copper scale and Mirror.
- Dholavira in Gujarat: Giant water reservoir, Unique water harnessing system, Stadium, Dams and embankments, Inscription comprising 10 large sized signs like an advertisement board.
- Ropar in Punjab: Dog buried with human oval pit burials
- Mohenjo–daro in present Pakistan: Bronze dancing girl, the sculpture of a bearded priest, the great bath, the great granary.
- Balathal and Kalibangan in Rajasthan: Bangle factory, toy carts, bones of camel, decorated bricks, citadel and lower town.
- Banawali in Haryana: Toy plough, barley grains, oval-shaped settlement, the only city with radial streets.
|
![]() 10 Oct 2024
10 Oct 2024

