New Statue of Lady Justice
Context: The new Lady Justice statue in the Supreme Court has shed its blindfold, with the Constitution now replacing the sword in one hand, symbolizing that the law in India is neither blind nor punitive.
Significance of the Changes
- Shedding Colonial Tradition: Redesign of ‘Lady Justice’ coincides with broader efforts to move away from British-era traditions as the country steps into a new era with the Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita.
- Constitution in Hand: She represents a justice system that is no longer focused on punishment but rather on ensuring fairness and equality based on constitutional principles.
- Retaining the Scales of Justice: Scales in ‘Lady Justice’s’ right hand have been retained which continue to symbolize Balance of justice, ensuring that courts weigh the facts and arguments from both sides before reaching a fair and impartial decision.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Origin of Lady of Justice
- The figure of Lady Justice originates from ancient Greek and Roman iconography.
- She is believed to be the allegorical personification of the law and moral force that drives society.
- In ancient Greece, Themis was a Titaness, often depicted with scales and a sword, who was associated with divine law and moral justice.
- It is widely believed that the origin of modern-day Lady Justice is Justitia, the goddess of Justice in Roman mythology, who was also known as Iustitia.
Symbolism in old Statue
Lady Justice therefore embodies the symbolic attributes of impartiality (the blindfold), fairness (the scales), and enforcement (the sword).
Abhidhamma Divas and Recognition of Pali as a Classical Language
Context: The Ministry of Culture, in collaboration with the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), celebrated International Abhidhamma Divas, marking the recent recognition of Pali as a classical language.
About International Buddhist Confederation (IBC)
- It is a Buddhist umbrella body with its base in New Delhi that serves as a common platform for Buddhists worldwide.
Abhidhamma Divas
- Significance of the Day: Abhidhamma Divas marks Lord Buddha’s descent from the celestial realm of the thirty-three divine beings (Tāvatiṃsa devaloka) to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur) in Farrukhabad district, Uttar Pradesh.
- Historical Marker: The Asokan Elephant Pillar at Sankisa serves as an enduring symbol of this significant event.
- Cultural Significance: The celebration of Abhidhamma Divas coincides with the end of the first Rainy Retreat (Vassa) and the Pavāraņā festival, a time when monks and nuns conclude their retreat period with a ceremony.
Pali Language
- Pali is a blend of various dialects, adopted by Buddhist and Jain sects in ancient India.
- Pali is the foundational language of Buddhist literature, including the Tripitaka (Triple Basket): the Vinaya, Sutta, and Abhidhamma Pitaka as well as the Jataka Kathas, which recount the Buddha’s previous lives.
- Continued Study of Pali: Pali is still studied in Buddhist-majority countries like Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Chittagong, Japan, Korea, Tibet, China, and Mongolia.
Karakoram Wildlife Sanctuary
Context: The National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) has approved five important road stretches, four of which pass through the Karakoram Wildlife Sanctuary along the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
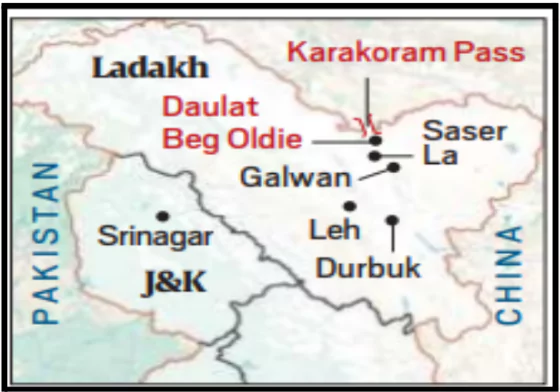
About Karakoram Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Situated in the easternmost part of the Karakoram range in Leh district, Indian Union Territory of Ladakh.
- Establishment: The sanctuary was established in 1987.
- Fauna: Home to species such as the snow leopard, Tibetan antelope (chiru), Tibetan wild ass (kiang), ibex, and blue sheep (Bharal).
- Altitude Range: Elevations range from about 4,200 m to over 7,500 m at Saltoro Kangri peak.
- Climate: Cold desert climate with harsh winters and low temperatures.
- Flora: Sparse Vegetation such as hardy grasses, shrubs.
- The harsh ecological conditions have led to the development of plants with high medicinal properties Example: Himalayan Rhubarb (Rheum emodi)
- Rivers: The Shyok and Nubra Rivers flow through the region.
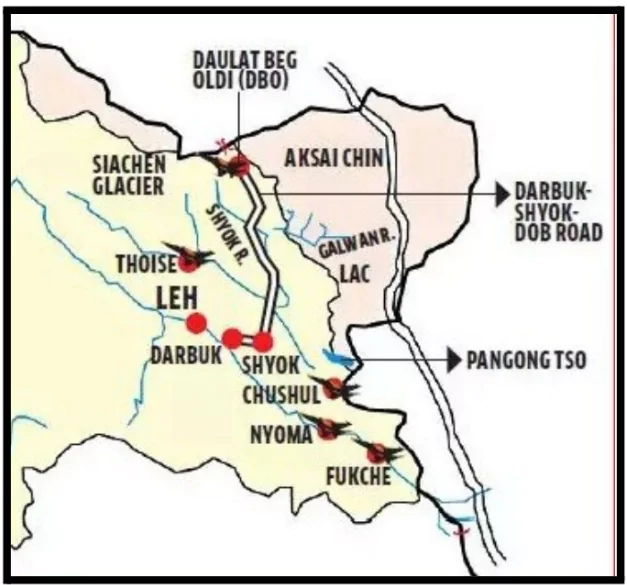
About Line of Actual Control (LAC)
- The LAC is the demarcation that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory.
- It is divided into three sectors: the eastern sector, encompassing Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim; the middle sector, covering Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh; and the western sector, located in Ladakh.
About National Board for Wildlife (NBWL)
- NBWL is a statutory Board constituted officially in 2003 under the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972.
- It is chaired by the Prime Minister.
- It is an apex body for the review of all wildlife-related matters and for the approval of projects in and around national parks and sanctuaries.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Cabinet approves 3% DA hike for Union govt. Employees
Context: The Union Cabinet recently approved an additional instalment of dearness allowance (DA) to Central government employees, and dearness relief (DR) to pensioners to compensate for price rise.
About Dearness Allowance (DA)
- Dearness Allowance (DA) is a monetary benefit given to employees in India to help them cope with the rising cost of living due to inflation.
- Purpose: DA is intended to ensure that employees’ real income remains constant or at least does not decline, despite inflation.
- Calculation:
- DA is calculated as a percentage of the basic salary.
- It is based on the All India Consumer Price Index (AICPI), which tracks retail prices across India.
- DA varies depending on the employee’s location, i.e., whether posted in an urban, semi-urban, or rural area.
- Taxability: DA is fully taxable for salaried employees.
- Impact on Pensioners: Pensioners also receive DA, referred to as Dearness Relief (DR), to help manage inflation’s impact on their pensions.
Types of Dearness Allowance
- Variable Dearness Allowance (VDA):
- Applicable to Central Government employees.
- Revised every six months based on changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- DA% = [(Average of AICPI (Base Year 2001 = 100) for the last 12 months – 115.76)/115.76] x 100
- Industrial Dearness Allowance (IDA):
- Applicable to Public Sector employees of the Central Government.
- Revised quarterly, based on the changes in CPI.
- DA% = [(Average of AICPI (Base Year 2001 = 100) for the last 3 months – 126.33)/126.33] x 100
Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra
Context: Recently, Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD) inaugurated a new ‘Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra (PMDK)’ of the Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO), at the National Institute for the Empowerment of Persons with Visual Disabilities (NIEPVD), Dehradun.
About Pradhan Mantri Divyasha Kendra (PMDK)
- PMDK is part of ALIMCO’s initiative under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It is an initiative specifically designed to support and empower senior citizens and persons with disabilities, focusing particularly on those with visual impairments.
- The first PM Divyasha Kendra (PMDK) was set up at Goa Medical College, Bambolim, Goa.
- As of now 46 PMDKs have already been opened and 34 of them made operational covering each States/UTs of the Country.
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has decided to open centres in every 100 KM radius of the Country.
- So that the benefit of Assistive Devices can be made available to the eligible beneficiary nearer to his or her doorstep with minimum waiting time.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO)
- ALIMCO is a Schedule ‘C’ Miniratna Category II Central Public Sector Enterprise, functioning under the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- Registered as a non-profit under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- 100% owned by the Government of India.
- Objective:
- Manufacture and distribute rehabilitation aids, including artificial limbs and other assistive devices, for persons with disabilities (PwDs).
- Focus on maximising benefits to PwDs rather than profitability.
- Unique Manufacturer: ALIMCO is the only manufacturer in India producing various types of assistive devices under one roof, catering to all forms of disabilities.
- Primary Focus: Provide quality aids and appliances at reasonable prices, ensuring widespread accessibility for PwDs across the country.
- Administration: Functions under the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, Government of India.
India launches first indigenous multi-purpose vessel ‘Samarthak’
Context: Recently, the Indian Navy marked a significant milestone with the launch of Samarthak, the first vessel under the two Multi-Purpose Vessel (MPV) projects being constructed by L&T Shipyard at Kattupalli.
About Multi-purpose vessel ‘Samarthak’
- The Indian Navy launched Samarthak, the first vessel under the Multi-Purpose Vessel (MPV) project on October 15, 2024.
- Constructed by L&T Shipyard, Kattupalli.
- Alignment with National Initiatives:
- Part of Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India initiatives.
- Boosts India’s indigenous shipbuilding capabilities.
- Vessel Details:
- Length: 106 metres, Width: 16.8 metres.
- Maximum speed: 15 knots.
- Named Samarthak, meaning “Supporter”, indicating its versatile role.
- Functions and Capabilities:
- Towing ships, launching/recovering targets.
- Operating unmanned autonomous vehicles.
- Testing indigenous weapons and sensors under development.
- undertake maritime surveillance and patrolling,
- Search & Rescue operations,
- Humanitarian Assistance & Disaster Relief (HADR) and
- Work as support platforms.
![]() 17 Oct 2024
17 Oct 2024


