India and Pakistan have renewed the Kartarpur Corridor agreement for another five years, ensuring uninterrupted access for pilgrims to the Kartarpur Sahib Gurudwara in Pakistan.
Kartarpur Corridor Agreement
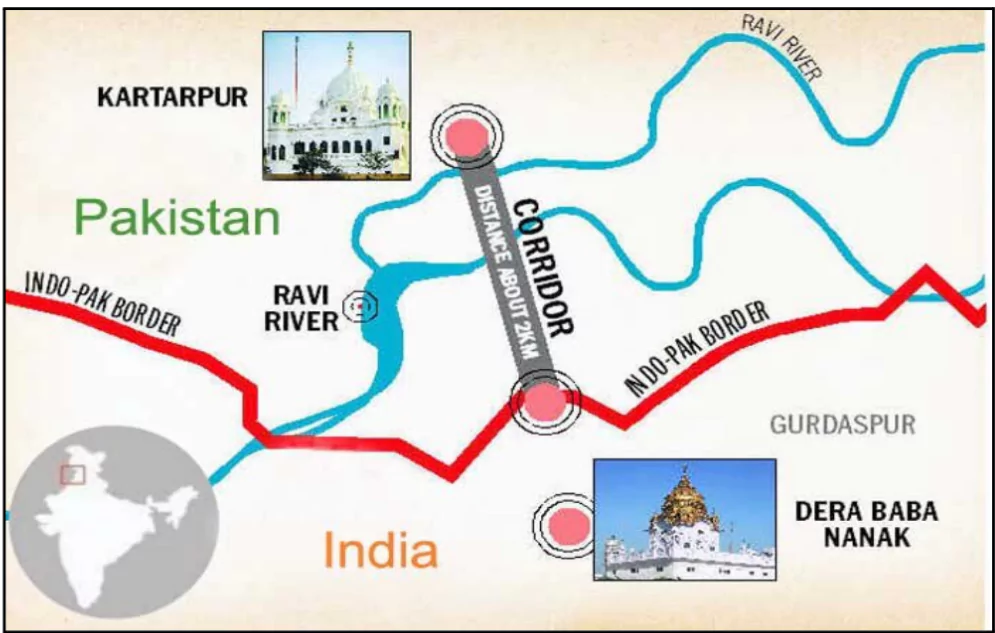
- Agreement, signed on 24 October 2019, was established to facilitate pilgrimages from India to Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur in Narowal, Pakistan, via the Kartarpur Sahib Corridor.
- The corridor will remain operational until 2029, allowing pilgrims to continue their religious visits.
- Indian External Affairs Minister, emphasised the government’s commitment to ensuring Sikh pilgrims’ access to holy sites.
About Kartarpur Corridor
- It connects Darbar Sahib Gurdwara in Pakistan with Dera Baba Nanak shrine in India’s Punjab.
- Kartarpur gurudwara is the revered shrine about 4 km across the border where Guru Nanak Dev spent the last 18 years of his life.
- The Maharaja of Patiala donated money to construct the Gurudwara in the between 1920’s.
- Protocol on Visits to Religious Shrines : Pilgrimages between India and Pakistan are governed by the 1974 Protocol on visits to Religious Shrines, which includes a list of shrines in Pakistan and India open for visitors from the other country for which visas are required.
- Kartarpur Corridor provides visa-free access from India to the shrine inside Pakistan.
- Indian pilgrims need only a permit to cross into Pakistan.
- Located on the Ravi River which is one of the rivers of the Indus System.
- Commemoration: It was built to celebrate the 550th birth anniversary of Guru Nanak Dev on November 12, 2019.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Gurunanak Dev
- Born: 1469 in Nanakana Sahib, Punjab, Pakistan.
- Died: In Kartarpur, Pakistan.
Teachings and Beliefs: Founder of Sikhism and the First of the Ten Sikh Gurus.
- Bhakti Saint: Advocated the ‘Nirguna’ form of Bhakti (devotion to a formless God).
- Message of ‘Ek Omkar’: Belief in One God, present everywhere. (“God is one”).
- Rejection of Rituals: Disapproved of sacrifices, ritual baths, image worship, and austerities. Rejected the religious scriptures of both Hindus and Muslims.
- Equality: Promoted equality for all, regardless of caste, religion, or gender.
- Caste System: Strongly opposed the caste system and social hierarchies.
Religious Practices:
- Sangat: Established the concept of Congregational Worship (Sangat) which encouraged collective prayer and recitation in a community setting.
- Langar: Introduced the tradition of Langar, a community kitchen promoting social equality where people share meals regardless of status.
Succession: Choose Guru Angad Dev as his successor, ensuring the continuity of his teachings.
- Guru Arjan Dev (the fifth Guru) compiled Guru Nanak’s hymns in the Adi Granth Sahib, which is the central holy scripture of Sikhism today.
|
![]() 23 Oct 2024
23 Oct 2024


