![]() 7 Nov 2024
7 Nov 2024

Wave Life Sciences, a Massachusetts-based biotech company, recently became the first to treat a genetic disorder by editing RNA at the clinical level.
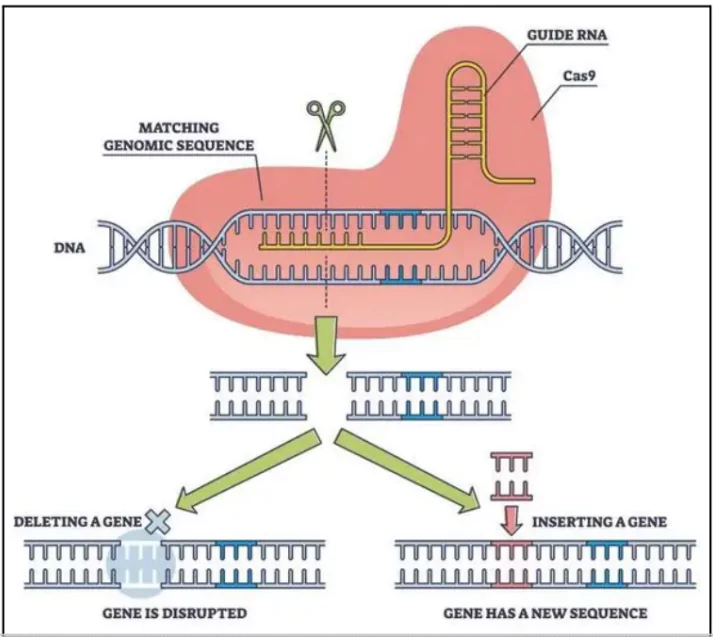
| Aspect | DNA Editing | RNA Editing |
| Target Molecule | DNA | RNA |
| Structure of Molecule | Usually double-stranded; some viruses have single-stranded DNA | Mostly single-stranded; some viruses (e.g., retroviruses) have double-stranded RNA |
| Sugar Component | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Nucleotide Bases | Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T) | Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Uracil (U) |
| Base Pairing Rules | A pairs with T, G pairs with C | A pairs with U, G pairs with C |
| Permanency of Edits | Permanent changes in the DNA sequence | Temporary changes in mRNA sequence; effects can fade over time |
| Specificity | High, but requires precise targeting to avoid permanent off-target mutations | Can be less specific; off-target edits possible if ADAR enzymes modify non-target mRNA parts |
| Risk of Immune Reaction | Potential immune reactions due to foreign proteins from bacterial sources (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9) | Lower immune risk, as ADAR enzymes used are naturally present in human cells |
| Genetic Impact | Alters the individual’s genome; changes can be passed onto future cell generations | Alters mRNA temporarily; does not change the genome, thus effects are not heritable |
| Use of Enzymes | Uses proteins from certain bacteria (e.g., Cas9 in CRISPR) for DNA cutting | Uses ADAR enzymes which convert adenosine (A) to inosine (I), mimicking guanosine (G) function |
| Safety | It has the risk of permanent damage. | RNA editing’s changes are temporary, allowing effects to fade over time, reducing the risk of permanent errors |
| Delivery Mechanisms | Often uses viral vectors (e.g., adeno-associated virus) | Typically uses lipid nanoparticles or viral vectors; however, limited capacity for larger molecules |
| Applications | Used in treating inherited diseases, gene therapy, and modifying agricultural species | Potential treatment for diseases caused by single-point mutations (e.g., Huntington’s, liver cancer) |

<div class="new-fform">
</div>