NTPC announced successful synthesis of CO2 captured from flue gas with hydrogen produced from a Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolyzer, which was then converted into methanol.
- NTPC has also developed its first indigenous methanol synthesis catalyst.
What is Flue Gas?
- A mixture of gasses formed as a byproduct of combustion in power plants.
- Primarily composed of Carbon dioxide (CO2), Water vapor (H2O), Nitrogen (N2) and Oxygen (O2)
- May also contain pollutants such as Sulfur dioxide (SO2), Nitrogen oxides (NOx) and Particulate matter (PM).
Environmental Impact: It Contributes to greenhouse gas emissions (CO2), Acid rain (SO2, NOx) and Air pollution (PM, NOx). |
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is Methanol?
Methanol (CH₃OH), often referred to as methyl alcohol or wood alcohol, is the simplest alcohol.
- It’s a clear, colorless, and flammable liquid with a distinct odor.
- Despite its simple structure, methanol plays a crucial role in various industries.
- Key Properties:
- Miscibility with Water: Methanol is completely soluble in water, making it a versatile solvent.
- Flammability: It is highly flammable, requiring careful handling and storage.
- Toxicity: Methanol is toxic to humans and animals, particularly when ingested. Its toxicity necessitates careful handling and storage.
Applications of Methanol
- Fuel Blending: Methanol can be blended with gasoline to improve octane rating and reduce emissions.
- Direct Fuel: It can be used as a fuel in internal combustion engines, especially in racing applications.
- Fuel Cell Technology: Methanol is used as a fuel source in direct methanol fuel cells.
- Industrial Solvent: It’s widely used as a solvent in various industries, including paints, coatings, and cleaning products.
- Laboratory Reagent: Methanol is a common solvent in chemical laboratories for reactions, extractions, and chromatography.
- Automotive Antifreeze: Methanol is used as an antifreeze component in windshield washer fluids to prevent freezing in cold weather.
- Formaldehyde Production: Methanol is a primary feedstock for the production of formaldehyde, a key ingredient in many industrial products.
- Other Chemicals: It’s used to produce a variety of other chemicals, including acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), and dimethyl ether (DME).
About CO2 to Methanol Conversion
- CO₂ Capture : CO₂ is taken out from the flue gas which is the waste gasses released from power plants
- Hydrogen Production : Hydrogen gas (H₂) is created using a Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolyzer.
- PEM splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity.
- Methanol Synthesis : Captured CO₂ is combined with the hydrogen gas to create methanol which is a clean fuel and can be used in various industries.
Benefits of CO₂ to Methanol Conversion
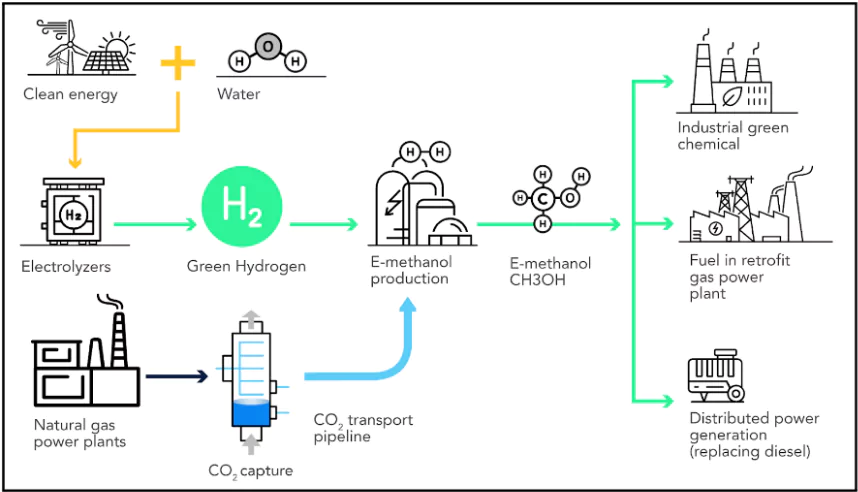
- Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU): This process provides a way to convert CO₂ into a useful product, helping to mitigate the greenhouse gas’s impact on climate change. By capturing and utilizing CO₂, we can reduce the amount of CO₂ released into the atmosphere.
- Sustainable Fuel Production: Methanol, produced from CO₂, serves as a versatile, renewable fuel.
- It can be used across sectors like transportation, power generation, and as a feedstock in various industrial processes, promoting energy independence and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Lower Energy Demand and Cost: The production of methanol from CO₂ requires less energy and is generally more cost-effective than traditional methods, enhancing its economic viability.
- Efficient Energy Storage and Transport: Methanol is easier to store and transport than hydrogen, as it is less flammable and more manageable. This makes methanol a safer alternative for large-scale storage and long-distance transport.
- Versatile Feedstock for Industry: Methanol serves as a key ingredient in manufacturing a wide range of chemicals, solvents, and plastics, supporting diverse applications in the industrial sector and contributing to economic resilience.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
NITI Aayog’s Methanol Economy Programme
- Reduction in Oil Import Bill: NITI Aayog’s program proposes blending 15% methanol into gasoline, which could reduce gasoline or crude oil imports by at least 15%, benefiting the economy and reducing energy dependence.
- Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Methanol blending results in lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fuels. It can reduce emissions of particulate matter, NOx, and SOx by around 20%, directly benefiting urban air quality.
- Improved Urban Air Quality: Urban transportation is responsible for approximately 40% of urban air pollution. By adopting methanol blending, urban air quality could significantly improve, reducing the health impacts of pollution in densely populated areas.
![]() 11 Nov 2024
11 Nov 2024

