Researchers at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali have developed a novel biodegradable nanocoating for fertilizers that can increase nutrient use efficiency by enabling slow release.
- This technology could reduce the amount of fertilizer required while sustaining high crop yields, offering environmental and economic benefits.
Key Features and Composition
- Nanocoating Material: The coating is made from nanoclay-reinforced binary carbohydrates, specifically chitosan and lignin, combined with an anionic clay that creates stable bonds.
- It has hydrophobic properties which allow fertilisers to be released slowly, minimising rapid dissolution and nutrient loss to soil and water.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Nanotechnology
- Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter on a near-atomic scale to produce new structures, materials and devices.
- Applications: It promises scientific advancement in many sectors such as medicine, consumer products, energy, materials, and manufacturing.
Nano fertilizers: These are nutrients that are encapsulated or coated within nanomaterial in order to enable controlled release, and its subsequent slow diffusion into a soil.
Eg. Nano Urea and Nano DAP |
Material Sustainability and Biocompatibility
- The nanomaterials used are low-cost, nature-derived materials such as nano-clay, chitosan, and starch.
- Designed to be biodegradable and mechanically stable, the coating supports sustainable agricultural practices by reducing waste and enhancing soil health.
Application Process
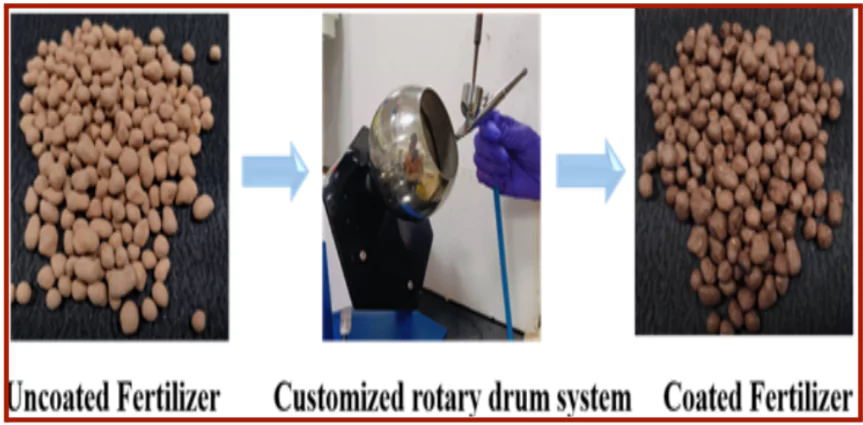
- A rotary drum system is employed to uniformly coat fertilizers like muriate of potash (KCl), which provides around 80% of potassium needed in fertilizers.
- This system, equipped with a sand air gun, achieves consistent coating that withstands transportation and handling.
Advantages and Benefits
- Improved Nutrient Use Efficiency: The slow-release mechanism aligns nutrient availability with crop needs, enhancing efficiency and reducing the total amount of fertilizer required.
- This technology reduces the recommended fertilizer dose for crops such as rice and wheat, maintaining or potentially increasing yields.
- Environmental and Economic Impact: By limiting fertilizer run-off and interaction with surrounding soil and water, this innovation mitigates environmental risks associated with conventional fertilizers.
- It also holds the potential to improve farmers’ socio-economic conditions by decreasing fertilizer costs and increasing agricultural output, which could contribute positively to the national economy.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Potential for Broader Applications
- The 3D nanostructure of these polymers has applications beyond agriculture due to its biodegradability, biocompatibility, and thermos-responsive properties.
- Future applications might involve other fields where controlled release and environmental sustainability are desired.
Further Reading: Nano Fertilizers, Nano Liquid Urea, Nano DAP.
![]() 14 Nov 2024
14 Nov 2024

