India has achieved a major milestone by successfully conducting flight trial of long range hypersonic missile from Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island, off-the-coast of Odisha.
- This hypersonic missile is designed to carry various payloads for ranges greater than 1,500 kms for the Armed Forces.
About Hypersonic Missiles
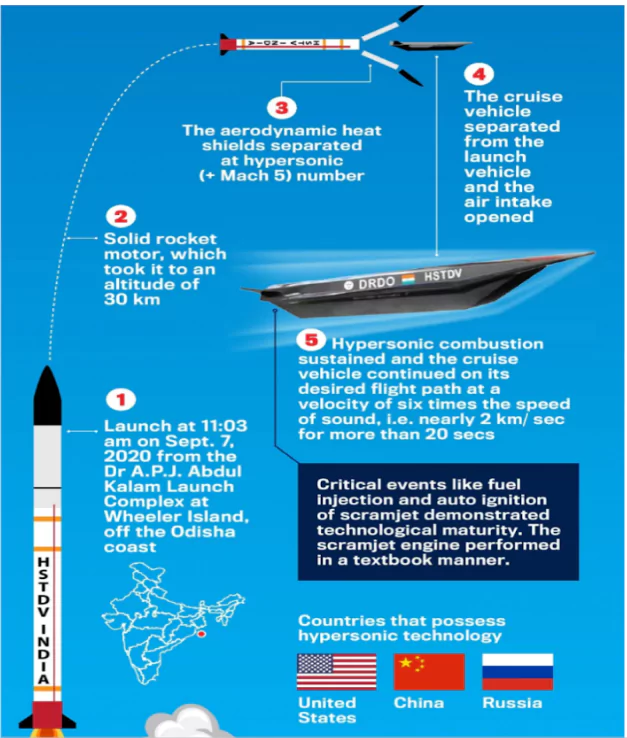
- Speed: A hypersonic missile is a weapon system which flies at least at the speed of Mach 5 i.e. five times the speed of sound and is manoeuvrable.
- Manoeuvrability: Unlike ballistic missiles, hypersonic missiles do not follow a ballistic trajectory and can be manoeuvred to the intended target.
- Types: Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGV) and Hypersonic Cruise Missiles.
- The HGV is launched from a rocket before gliding to the intended target.
- The hypersonic cruise missile is powered by air breathing high speed engines or ‘scramjets’ after acquiring their target.
- Advantage: Hypersonic weapons can enable responsive, long range strike options against distant, defended or time critical threats (such as road mobile missiles) when other forces are unavailable, denied access or not preferred.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
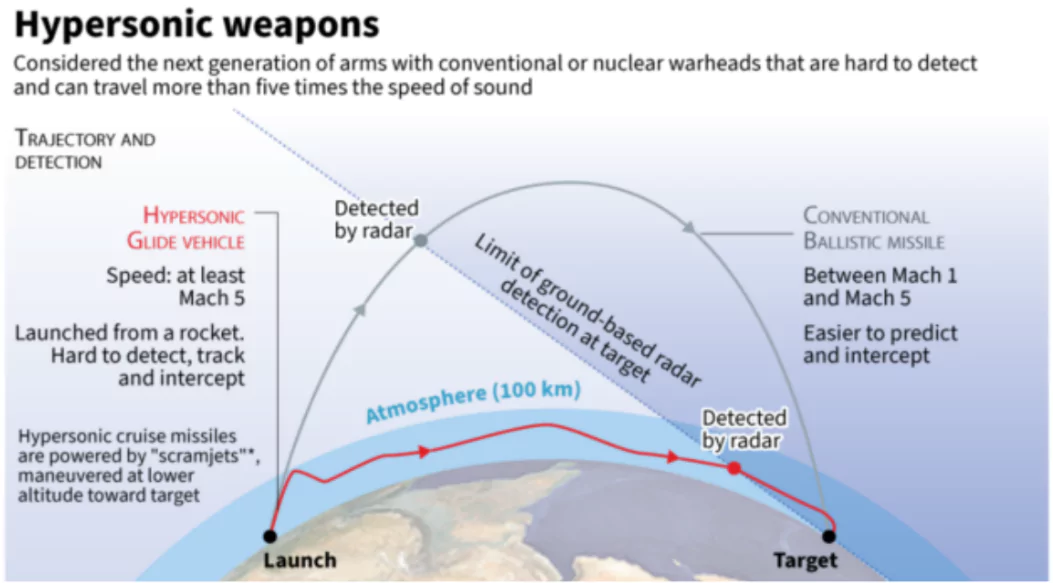
- Detectability:
- These missiles could challenge detection and defence due to their speed, manoeuvrability and low altitude of flight.
- Ground based radars or terrestrial radars cannot detect hypersonic missiles until late in the flight of the weapon.
- This delayed detection makes it difficult for the responders to the missile attack to assess their options and to attempt to intercept the missiles.
- Countries possessing: US, Russia and China are in advanced stages of hypersonic missile programmes, India, France, Germany, Japan and Australia too are developing hypersonic weapons.
About Mach number
- Mach number, in fluid mechanics, ratio of the velocity of a fluid to the velocity of sound in that fluid, named after Ernst Mach (1838–1916), an Austrian physicist and philosopher.
- In the case of an object moving through a fluid, such as an aircraft in flight, the Mach number is equal to the velocity of the object relative to the fluid divided by the velocity of sound in that fluid.
- Subsonic conditions occur for Mach numbers less than one, M < 1 .
- Sonic conditions occur for Mach numbers equal to one, M = 1 .
- Supersonic conditions occur for Mach numbers greater than one, M >1.
- For speed greater than five times the speed of sound, M > 5, the flow is said to be hypersonic.
|
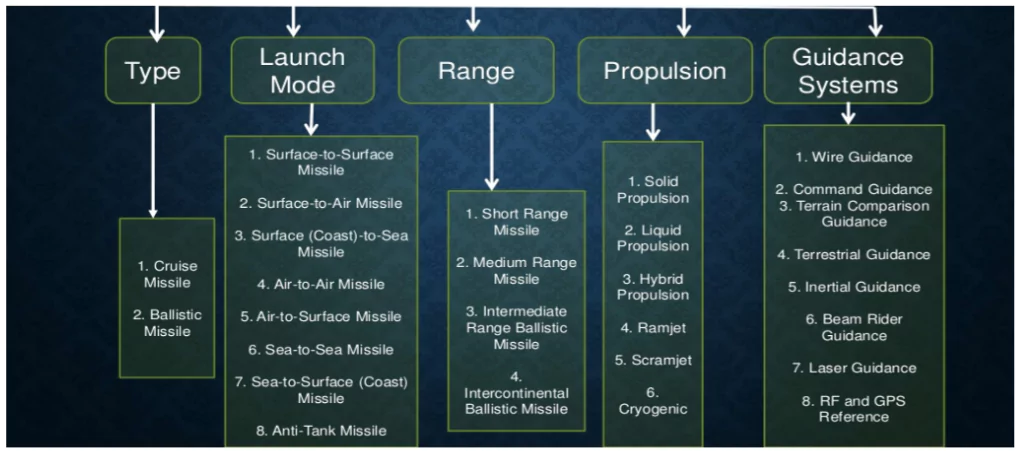
Classification of Missiles
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Types of Missiles: Based on Trajectory
| Ballistic Missile |
Cruise Missile |
- It takes a ballistic trajectory to deliver one or more warheads to a designated target.
|
- It is a guided missile that remains in the atmosphere and travels at a steady speed for most of its flight path.
|
- The target has already been decided.
- Suitable for large targets.
|
- The target may be mobile.
|
- Only guided for brief periods of flight, the rest of its trajectory is unpowered and driven by gravity
|
|
- High elevation makes it simple to follow
|
- Capable of flying at incredibly low altitudes, that makes tracking harder.
|
- Example: Agni-V is India’s first Intercontinental Ballistic Missile(ICBM), with a range of around 5000-8000 km.
|
- Example: BrahMos is the fastest supersonic missile of the world
- BrahMos II, the hypersonic cruise missile, is currently in the developing phase.
|
Also Read: List of Indian Missiles
![]() 18 Nov 2024
18 Nov 2024




