Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative (IFFCO) is set to organize the ICA Global Cooperative Conference with support from India’s 18 International Cooperative Alliance (ICA) member organizations.
Key Highlights of the ICA Global Cooperative Conference 2024

- Objective: The ICA Global Cooperative Conference 2024 aims to showcase India’s leadership in cooperative innovation and to strengthen global cooperation among cooperative organizations.
- Expected Outcomes: The conference is expected to foster knowledge sharing, networking, and collaboration among cooperatives worldwide, leading to innovative solutions for global challenges.
About International Cooperative Alliance (ICA)
- Establishment: Founded in 1895 in London, UK.
- Objective: To promote the cooperative idea and to support the development of cooperatives worldwide.
- Membership: Comprises national cooperative organizations, international cooperative organizations, and individual cooperative societies.
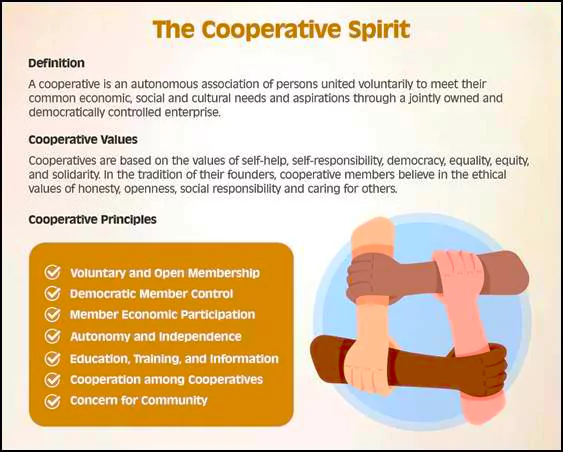 Some notable members of ICA are IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited), KRIBHCO (Krishak Bharati Cooperative Limited), Amul Dairy Cooperative, The Cooperative Group (UK), Groupe Crédit Mutuel (France), Coop Italia, WOCCU (World Council of Credit Unions), etc
Some notable members of ICA are IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited), KRIBHCO (Krishak Bharati Cooperative Limited), Amul Dairy Cooperative, The Cooperative Group (UK), Groupe Crédit Mutuel (France), Coop Italia, WOCCU (World Council of Credit Unions), etc
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium.
- Role of ICA:
- Advocates for cooperative principles and values.
- Provides technical assistance and capacity building to cooperatives.
- Conducts research and policy analysis.
- Organizes international events and conferences.
- Represents the interests of cooperatives at the global level.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Constitutional Provisions for Cooperatives in India
- 97th Constitutional Amendment : Added Part IXB (The Co-Operative Societies) to the Constitution.
- The Right to Form Cooperative Societies was included as the Right to Freedom under Article 19 (1).
- Article 43-B that deals with Promotion of Cooperative Societies was also inserted as one of the Directive Principles of State Policy.
- Multi-State Co-operative Societies (Amendment) Act, 2023: Amendment has been brought in the MSCS Act, 2002 to strengthen governance, enhance transparency, increase accountability, reform electoral process and incorporate provisions of 97th Constitutional Amendment in the Multi State Cooperative Societies.
|
About Cooperative Societies
- Cooperative societies are voluntary associations of individuals who join together to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations.
- They operate on the principle of mutual help and self-help, prioritising the well-being of their members over profit maximisation.
- Status of Cooperative Societies In India:
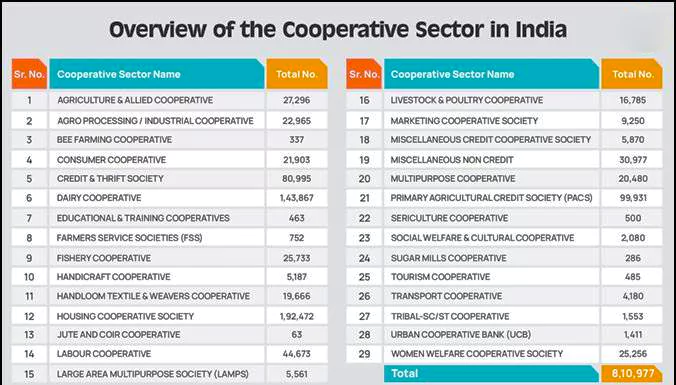
- Currently there are more than 8 lakh cooperative societies registered in various fields like Housing, Dairy, Agriculture, Finance, etc.
- In 2021, the Ministry of Cooperation was created by the Government of India for realising the vision of ‘Sahkar se Samriddhi’.
- Jurisdiction: Cooperatives are a state subject under the Constitution.
- The subject ‘Cooperative Societies’ is mentioned in entry 32 of the State List under the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
Types of Cooperative Societies in India
- Consumer Cooperatives: These societies aim to provide quality goods and services to their members at affordable prices. Examples include Kendriya Bhandar and Apna Bazar.
- Producer Cooperatives: These societies support small producers by providing them with resources, technology, and market access. Examples include Amul Dairy Cooperative and Karnataka Handloom Weavers’ Cooperative Society.
- Marketing Cooperatives: These societies facilitate the collective marketing of agricultural and other products, ensuring better prices for their members.
- Credit Cooperatives: These societies offer financial services like loans and savings to their members, particularly those from rural and marginalised communities. Examples include Urban Cooperative Banks and Rural Cooperative Banks.
- Housing Cooperatives: These societies provide affordable housing solutions to their members by pooling resources and collectively developing housing projects.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Evolution of the Cooperative Movement in India
The cooperative movement in India has evolved significantly over the years, influenced by various factors, including government policies, social reforms, and economic conditions.
- Pre-Independence Era:
- Informal Origins: Early forms of cooperatives, such as Chit funds, Nidhis, and village-level mutual aid societies, existed.
- Formalisation: The Cooperative Credit Societies Act of 1904 and the Cooperative Societies Act of 1912 laid the foundation for the formal cooperative movement.
- Agricultural Credit Cooperative Society, of Kanaginahal village of Gadag District , Karnataka was the first cooperative Society formed under Cooperative Credit Societies Act of 1904.
- Gandhian Influence: Mahatma Gandhi promoted cooperative principles and encouraged their adoption as a means to empower rural communities and achieve economic self-sufficiency.
- Post-Independence Era:
- Government Support: The government recognized the potential of cooperatives in promoting rural development and economic growth.
- National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC): Established in 1963, the NCDC provides financial and technical assistance to cooperative societies.
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD): Established in 1982, NABARD promotes rural development and provides credit and other financial services to cooperatives.
- Legislative Reforms: The Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002 and 2023 Amendment for better regulation of Multi State Cooperative Societies and the 97th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2011, further strengthened the cooperative movement.
Multi-State Vs Single-State Cooperative Societies in India
|
| Feature |
Multi-State Cooperative Society |
Single-State Cooperative Society |
| Jurisdiction |
Registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002 |
Registered under the respective state cooperative societies act |
| Area of Operation |
Can operate in multiple states |
Operates within a single state |
| Regulatory Authority |
Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies |
State Registrar of Cooperative Societies |
| Ease of Formation |
More complex due to central registration and compliance requirements |
Relatively easier as it involves state-level registration |
| Governance |
Governed by the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002, and its rules |
Governed by the respective state cooperative societies act and rules |
| Financial Regulations |
Subject to central financial regulations and guidelines |
Subject to state-level financial regulations and guidelines |
| Tax Implications |
May have different tax implications across states |
Tax implications are generally governed by the state’s tax laws |
| Member Base |
Can have members from multiple states |
Members are typically from a single state |
| Scale of Operations |
They offer greater flexibility and potential for larger-scale operations, they also require more stringent compliance and regulatory oversight. |
They have more localised focus and may be better suited for smaller-scale operations. |
| Examples |
IFFCO, Amul, NCDFI |
State-level cooperative banks, primary agricultural credit societies, housing societies |
The Role of Cooperatives in India
Cooperatives have played a pivotal role in India’s socio-economic development, particularly in rural areas. They have empowered millions of people, improved livelihoods, and contributed to national growth. Here’s a detailed look at their key roles:
- Rural Development
- Credit and Financial Services: Cooperative banks and credit societies provide affordable credit to farmers and rural entrepreneurs, enabling them to invest in their businesses and improve productivity.
- Cooperatives provide 20% of the total agricultural credit in the country, ensuring access to finance for farmers.
- Input Supply: Cooperatives procure and distribute quality agricultural inputs like seeds, fertilisers, and pesticides at reasonable prices, ensuring timely access for farmers.
- Cooperatives distribute 35% of the total fertilisers and produce 25% of the fertilisers in India.
- Market Access: Cooperatives facilitate market access for farmers by aggregating their produce, negotiating better prices, and connecting them to domestic and international markets.
- Infrastructure Development: Cooperatives often invest in rural infrastructure, such as irrigation systems, roads, and storage facilities, which benefits the entire community.
- Poverty Reduction
- Income Generation: Cooperatives provide employment opportunities, both directly and indirectly, to a large number of people, especially in rural areas. For instance, the Amul Dairy Cooperative has provided livelihoods to millions of dairy farmers in Gujarat.
- Skill Development: Cooperatives often organise training programs to enhance the skills of their members, enabling them to improve their productivity and income.
- Social Safety Nets: Cooperatives can act as social safety nets, providing support to their members during times of economic hardship or natural disasters.
- Social and Economic Empowerment
- Women’s Empowerment: Women’s self-help groups, which are often cooperative-based, empower women by providing them with financial resources, training, and a platform to voice their concerns.
- Marginalised Groups: Cooperatives can empower marginalised groups like tribal communities and small farmers by providing them with access to resources and markets.
- Community Development: Cooperatives contribute to community development by investing in education, healthcare, and other social welfare activities.
- Food Security
- Increased Agricultural Productivity: Cooperatives promote the adoption of modern agricultural practices, leading to higher yields and improved quality.
- Cooperatives contribute to 31% of the total sugar production in the country and more than 10% of the total milk produced in India.
- They contribute to more than 21% of the fishermen’s business, supporting the fishing industry and coastal communities.
- Efficient Food Distribution: Cooperatives ensure the efficient distribution of food grains and other agricultural products, reducing wastage and ensuring food security.
- Price Stabilisation: Cooperatives can help stabilise prices by acting as both buyers and sellers of agricultural products.
- Cooperatives procure more than 13% of wheat and 20% of paddy produced in the country, ensuring fair prices for farmers.
- Consumer cooperatives provide essential goods and services to consumers at reasonable prices.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Government Initiatives to Strengthen Cooperatives
- Ministry of Cooperation: The establishment of the Ministry of Cooperation in 2021 has provided a dedicated platform for addressing the needs and challenges of the cooperative sector.
- Financial Support: The government provides financial assistance to cooperatives through various schemes and programs.
| Initiatives |
Objective |
| Model Bye-Laws for PACS |
Improve governance, transparency, and inclusivity in PACS |
| Computerization of PACS |
Modernise PACS and improve their efficiency |
| New Multipurpose PACS/Dairy/Fishery Cooperatives |
Expand the cooperative network to uncovered areas |
| Decentralised Grain Storage Plan |
Reduce post-harvest losses and improve farmers’ income |
| PACS as Common Service Centers (CSCs) |
Provide various e-services to rural citizens |
| Formation of Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) |
Empower farmers and improve their market access |
| Retail Petrol/Diesel Outlets |
Diversify PACS’ income sources |
| LPG Distributorship for PACS |
Diversify PACS’ income sources |
| PM Bhartiya Jan Aushadhi Kendra |
Improve access to affordable medicines in rural areas |
| Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samriddhi Kendras (PMKSK) |
Provide easy access to fertilisers and related services to farmers |
| PM-KUSUM Convergence |
Promote solar energy adoption among farmers |
| Operations & Maintenance of Rural Water Supply |
Utilise PACS’ reach in rural areas |
| Micro-ATMs for Cooperative Societies |
Provide doorstep financial services to rural citizens |
| RuPay Kisan Credit Cards for Dairy Cooperatives |
Provide credit and other financial services to dairy farmers |
| Formation of Fish Farmer Producer Organizations (FFPOs) |
Empower fish farmers and improve their market access |
Key Challenges for Cooperative Societies in India
- Governance Issues
- Lack of Transparency and Accountability: Many cooperatives suffer from a lack of transparency in financial dealings and decision-making processes. This can lead to corruption and misuse of funds.
- Limited Member Participation: Low levels of member participation in decision-making can weaken cooperatives and make them vulnerable to external influences.
- Ineffective Governance Structures: Weak governance structures, including board of directors and management committees, can hinder the effective functioning of cooperatives.
- Weak corporate governance has led to the failure of many cooperative banks, resulting in 145 mergers of non-scheduled Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) since 2004-05, including nine in 2021-22.
- Financial Constraints
- Limited Access to Finance: Cooperatives, especially those in rural areas, often face difficulties in accessing finance from traditional sources like banks and financial institutions.
- High Interest Rates: Even when they manage to secure loans, cooperatives often have to pay higher interest rates compared to other businesses.
- Non-Performing Assets (NPAs): A significant number of cooperative banks suffer from high NPAs, which can erode their financial health.
- Due to poor financial conditions, as many as 17 Cooperative banks were shut down in 2023 with the highest number of annual licence cancellations by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Capacity Building
- Lack of Skilled Personnel: Many cooperative societies lack the necessary skills and expertise to manage their operations effectively.
- Poor Financial Management: Weak financial management practices can lead to financial losses and instability.
- Limited Technological Adoption: The slow adoption of technology can hinder the growth and efficiency of cooperatives.
- Competition
- Competition from Private Sector: Cooperatives often face stiff competition from private sector entities, which may have access to better resources and technology.
- Market Dominance: Large corporations can dominate markets, making it difficult for cooperatives to compete.
- Price Fluctuations: Fluctuations in input and output prices can impact the profitability of cooperatives.
- Lack of Public Trust
- Historical Issues: Some cooperatives have been associated with financial mismanagement and corruption, leading to a negative perception.
- Lack of Transparency: A lack of transparency in operations and financial dealings can erode public trust.
- Ineffective Governance: Poor governance practices, including nepotism and favouritism, can further undermine public confidence.
- For instance, the Punjab and Maharashtra Cooperative Bank (PMC Bank) faced a major crisis due to fraudulent practices and mismanagement, leading to a severe liquidity crunch and inconvenience to its depositors.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Way Forward
- Strengthening Governance: Promoting transparency, accountability, and member participation.
- Improving Financial Management: Implementing sound financial practices and seeking alternative sources of finance.
- Capacity Building: Investing in training and development programs for cooperative members and staff.
- Policy Support: Creating a supportive policy environment to encourage the growth and development of cooperatives.
- Collaboration and Networking: Fostering collaboration among cooperatives to share knowledge and resources.
- Addressing the Lack of Public Trust: Implement robust transparency measures, such as regular financial audits, public disclosure of financial statements, and transparent decision-making processes.
![]() 18 Nov 2024
18 Nov 2024


 Some notable members of ICA are IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited), KRIBHCO (Krishak Bharati Cooperative Limited), Amul Dairy Cooperative, The Cooperative Group (UK), Groupe Crédit Mutuel (France), Coop Italia, WOCCU (World Council of Credit Unions), etc
Some notable members of ICA are IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited), KRIBHCO (Krishak Bharati Cooperative Limited), Amul Dairy Cooperative, The Cooperative Group (UK), Groupe Crédit Mutuel (France), Coop Italia, WOCCU (World Council of Credit Unions), etc
