Explore the innovative world of GM Crops! Learn how GM Crops revolutionize agriculture with improved yields, pest resistance, and sustainability.

GM Crops: Genetically modified (GM) crops have transformed agriculture by introducing innovative and modernistic solutions to age-old challenges. With over 10% of the world’s croplands now dedicated to GM crops have revolutionised the way to grow food. Their DNA, modified through advanced genetic engineering techniques, enables the introduction of traits like pest resistance, tolerance to harsh environmental conditions, and improved nutritional profile qualities.
Genetically Modified or GM crops, also referred to as genetically engineered (GE) plants, transgenic crops, or living modified organisms (LMOs), these crops are agricultural plants whose DNA is altered through genetic engineering techniques. This technology is implemented especially to induce new traits that are not naturally present in the species, such as resistance to pests, diseases, herbicides, or environmental conditions. GM crops are also engineered to enhance nutritional content or facilitate the production of pharmaceuticals and biofuels.
Here are the objectives of GM crops:
The first GM crops were introduced in the USA during the mid-1990s and have since witnessed widespread global adoption. By 2017, GM crops covered approximately 189.8 million hectares across 24 countries, with an additional 43 countries importing GM products for food, feed, or other uses. Commonly cultivated GM crops include corn, soybean, cotton, and canola, such food crops are especially modified for insect resistance and herbicide tolerance.
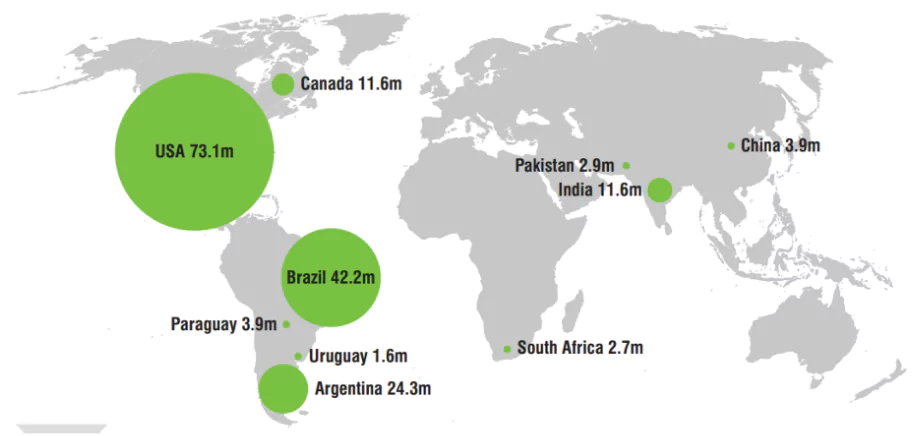
The top GM Crops growing nations include the USA, Brazil, Argentina, India, and Canada, which together make up 90% of the global GM crop cultivation area.
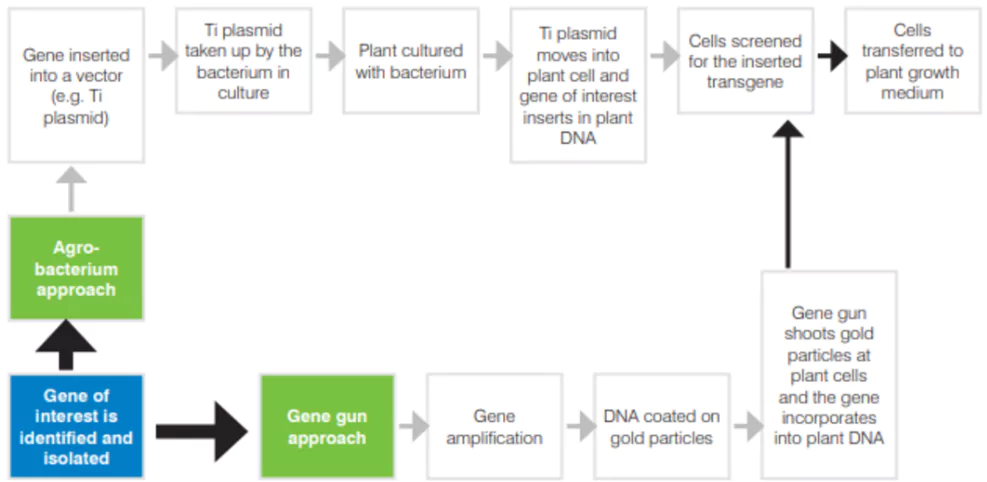
The development of GM crops begins with identifying a gene of interest and then isolating it from the donor organism. This method is implemented while utilizing laboratory techniques like gene gun or Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, the gene is incorporated into the plant’s DNA. The resulting GM crop is tested intensively under controlled laboratory and field conditions before approval.
GM technology directly manipulates DNA, while bypassing traditional pollination methods, to achieve specific traits in plants. Conventional breeding involves crossbreeding to combine desirable traits naturally, but genetic engineering allows the transfer of genes across unrelated species, which enables exceptional advancements.
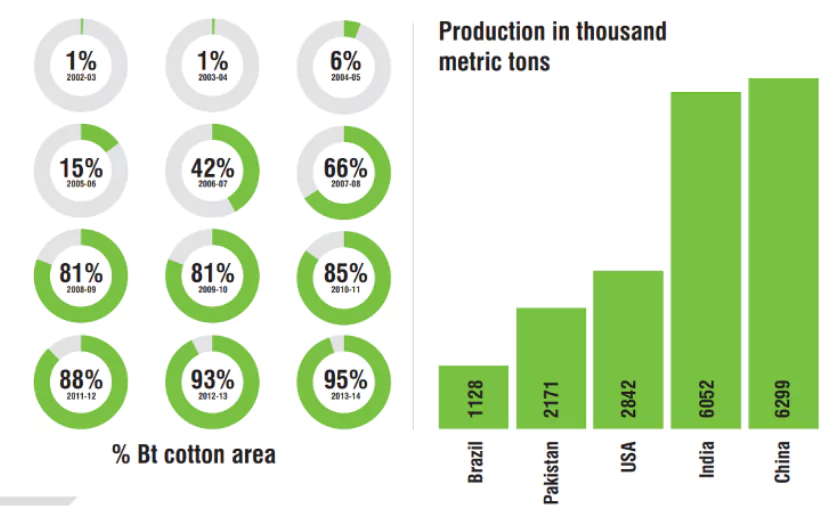
In India, Bt cotton is the only approved GM crop for cultivation. Bt cotton was introduced in 2002 and now covers over 90% of the country’s cotton-growing area, spanning around 11 million hectares. Research and field trials for other GM crops like chickpea, pigeonpea, corn, and sugarcane are ongoing. India is the fourth-largest GM crop cultivator worldwide and the second-largest cotton producer.
GM crops have been a significant topic of debate in India while balancing potential agricultural benefits with environmental and health concerns. Bt Cotton is the only GM crop approved for commercial cultivation in India, but other crops like Bt-Brinjal and GM Mustard remain under scrutiny and are limited to tests.
Bt Cotton is one of the most successful GM crops, which was developed to combat the cotton bollworm. Since no natural cotton variety resists this pest, genetic modification provided a solution by introducing the Bt gene from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis. This gene enables the cotton plant to produce a protein toxic to the bollworm, offering effective pest resistance.
Genetically Modified (GM) crops have become a pivotal area in agricultural research, addressing various challenges such as pest resistance, nutritional enhancement, and climate resilience. Below are the key R&D advancements in GM crops in India:
| Crop | Key R&D Focus |
| Rice |
|
| Wheat |
|
| Cotton |
|
| Mustard |
|
| Maize |
|
| Soybean | Resistance to Yellow Mosaic Virus |
| Eggplant | Resistance against fruit and shoot borer |
| Sorghum | Resistance to shoot fly |
| Groundnut | Resistance against Tobacco Streak Virus (TSV) |
| Chickpea | Resistance against pod borers |
GM crops offer many benefits that make them a significant innovation in modern agriculture:
Despite their benefits, GM crops face significant criticism and concerns:
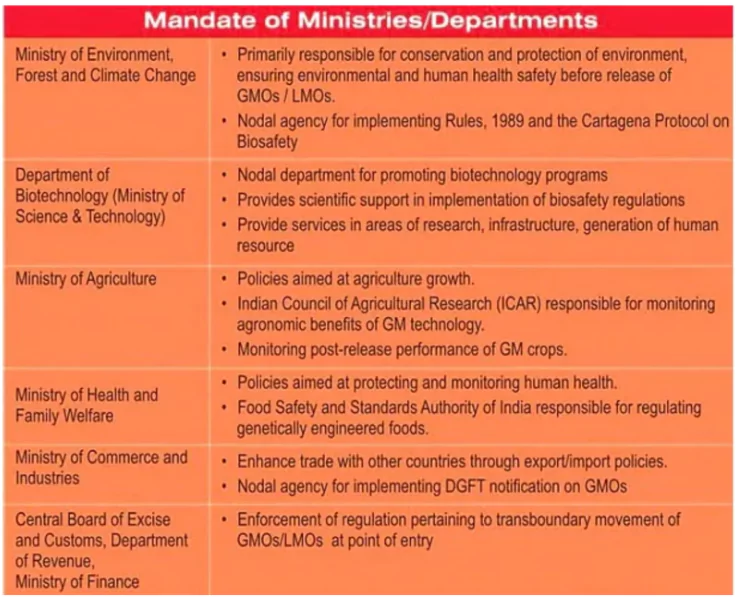
In India GMOs including GM crops, are regulated under the 1989 Rules for the Manufacture, Use, Import, Export, and Storage of Hazardous Microorganisms, Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells, established under the Environment Protection Act (1986).
The beginning of GM crops has revolutionized modern agriculture while offering a plethora of applications. Here are some key areas where GM technology in plants is making a significant impact:
The journey of genetically modified (GM) crops in India has been characterised by significant controversies and regulatory challenges. Below is a concise timeline highlighting key events related to the adoption, opposition, and regulation of GM crops in the country.
| Year | Event |
| 2002 | Bt cotton was introduced in India. |
| 2006 | Activists filed a PIL against GM crops in the Supreme Court. |
| 2010 | Environment Minister Jairam Ramesh blocked Bt Brinjal release due to scientific and state opposition; No Objection Certificates (NOCs) made mandatory for field trials. |
| 2012 | Parliamentary Standing Committee on Agriculture called for an end to all GM field trials. |
| 2013 | The SC-appointed expert panel recommended a 10-year suspension of crop trials; Environment Minister Jayanthi Natarajan halted all trials. |
| 2014 | Environment Minister Veerappa Moily approved one-acre field trials; GEAC approved trials for 11 crops under the UPA, and later NDA approved trials for 21 GM crops. |
| 2016 | GEAC approved GM Mustard for field trials, but SC stayed the order and sought public opinion. |
To harness the full potential of GM technology while addressing its challenges, the following steps are essential:
GM crops offer revolutionary agricultural benefits while raising significant concerns. As India navigates the complexities of GM crop regulation, a pragmatic approach rooted in science, sustainability, and social equity will determine the role of genetically modified crops in our future. For competitive exams like UPSC, understanding the intricacies of this topic is vital to address related questions comprehensively.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
UPSC Exam 2025 Related Articles
UPSC Prelims 2025 Exam
UPSC Notification 2025
UPSC Preparation 2025
UPSC Eligibility 2025
UPSC Exam Pattern
UPSC Syllabus
GM Crops are genetically modified plants altered in labs to improve traits like pest resistance, higher yield, and stress tolerance.
Key GM Crops include soybeans, corn, cotton, canola, and alfalfa, modified for better traits like pest resistance and herbicide tolerance.
In India, Bt cotton is the only commercially approved GM Crop, known for its pest-resistant properties.
GM Crops are made by inserting specific genes into plants' DNA using biotechnological methods for desired traits.
Yes, numerous studies and regulatory bodies ensure the safety of GM Crops for consumption and environmental impact.
GM Crops enhance food security by boosting yields, reducing chemical use, and making farming more resilient to climate changes.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
