The Coffee Prices are expected to remain high for the next two years due to global production decline, as highlighted by Ajoy Thipaiah, Vice President of the United Planters’ Association of Southern India.
Coffee Price Trends
- Firm Prices in the Near-Term: Tight global supplies and adverse weather in key producing countries (e.g., Brazil, Vietnam) are contributing to stable coffee prices.
- Domestic Robusta prices have increased by 36-48% during January–June 2024, while Arabica prices have seen a modest rise of 2.3-7.7%.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Coffee’s Impact on Climate Change
- Deforestation: Coffee cultivation, especially in regions like Latin America, often involves deforestation, leading to loss of biodiversity and increased carbon emissions.
- Water Usage: Coffee production is water-intensive, particularly in regions facing water scarcity. This can exacerbate water stress and contribute to environmental degradation.
- Pesticide Use: Conventional coffee farming relies heavily on chemical pesticides, which can pollute water bodies, harm ecosystems, and contribute to climate change.
- Climate Change Impact on Coffee: Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns are affecting coffee production, leading to lower yields, decreased quality, and potential loss of coffee-growing regions.
|
Coffee Grower Challenges
- Financial Recovery: Growers need stable prices for 4-5 years to repay debts and recover from 15 years of low prices and high costs.
- Multi-Faceted Issues: High input costs, increasing wages, and fluctuating yields due to climate change have compounded their financial struggles.
-
- Rising costs, labour shortages, lack of modernization, and increasing pest outbreaks.
United Planters’ Association of Southern India
- Origin: Founded on 28th August 1893, when 13 District Planters’ Associations met at Mayo Hall, Bangalore, to form a united organization.
- Headquarters: Located in Coonoor, Tamil Nadu.
- Objective:
- Promote knowledge, trade, commerce, and development of plantation industries.
- Undertake scientific research on plantation crops.
- Represent and protect the interests of the plantation industry globally.
- Functions:
- Research activities (e.g., Tea Research Institute established in 1936).
- Facilitate worker welfare schemes and industrial relations.
- Publish statistics and disseminate industry-related information.
- Act as a representative body for planters at various forums and committees.
|
-
- Excessive rains and temperature changes are reducing yields.
- Man-animal conflicts in plantation areas are another significant issue.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
India’s Global Position
- 7th largest producer globally, after Brazil, Vietnam, Colombia, Indonesia, Ethiopia, and Honduras.
- India has a share of about 3.50% in the global Coffee production.
- 5th largest exporter, exporting over two-thirds of its coffee production.
- Key export markets: Europe, with Italy, Germany, and Belgium as top buyers.
Key Regulatory Bodies in India
| Regulatory Body |
Established |
Administrative Body |
Headquarters |
Role |
| Coffee Board |
Coffee Act VII, 1942 |
Ministry of Commerce and Industry |
Bengaluru, Karnataka |
Promotes coffee production and industry development in India. |
| Rubber Board |
Rubber Act, 1947 |
Ministry of Commerce and Industry |
Kottayam, Kerala |
Supports overall development of the rubber industry. |
| Tea Board |
Tea Act, 1953 |
Ministry of Commerce and Industry |
Kolkata, West Bengal |
Promotes cultivation, processing, and trade of tea in India. |
| Tobacco Board |
Tobacco Board Act, 1975 |
Ministry of Commerce and Industry |
Guntur, Andhra Pradesh |
Oversees tobacco production and export. |
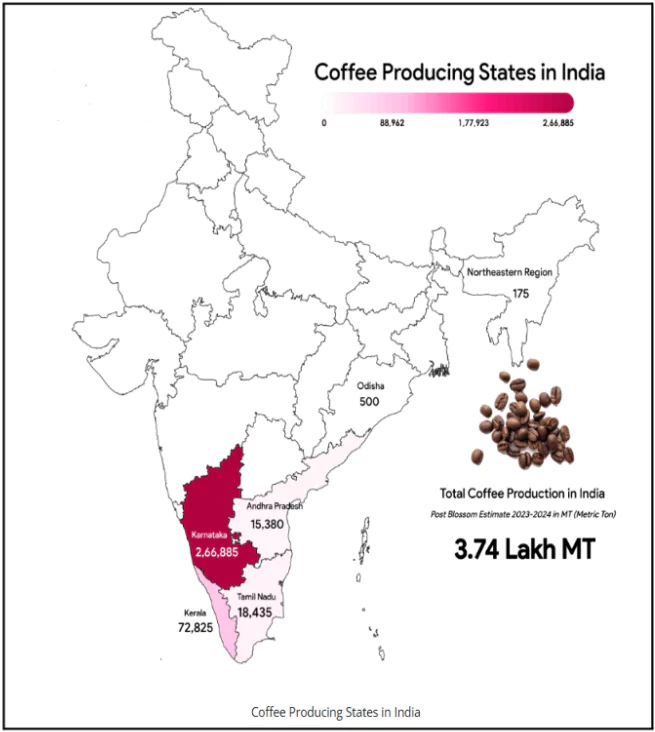
Coffee Production in India
- Varieties Produced:
- Arabica: Grown at higher altitudes, Arabica beans are prized for their superior flavor and aroma, commanding a higher market value.
- Robusta: Known for its strength and higher caffeine content, Robusta beans are widely used in coffee blends.
- Despite its lower quality perception, it dominates global production, accounting for a significant 72% share.
- State-wise Production:
- Karnataka: 70% of total production.
- Kerala: 23%.
- Tamil Nadu: 5%.
- Other contributors: Odisha and northeastern states.
 Climatic and Soil Requirements for Coffee Production
Climatic and Soil Requirements for Coffee Production-
- Climate: Hot and humid, with temperatures between 15°C to 28°C.
- Rainfall: 150 to 250 cm annually.
- Soil: Well-drained loamy soil, rich in humus, with iron and calcium.
- Altitude: Grown on hill slopes between 600 to 1,600 metres.
- Shade and Dry Weather: Requires shady trees for growth and dry conditions during berry ripening.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Significance of Coffee in India’s Economy
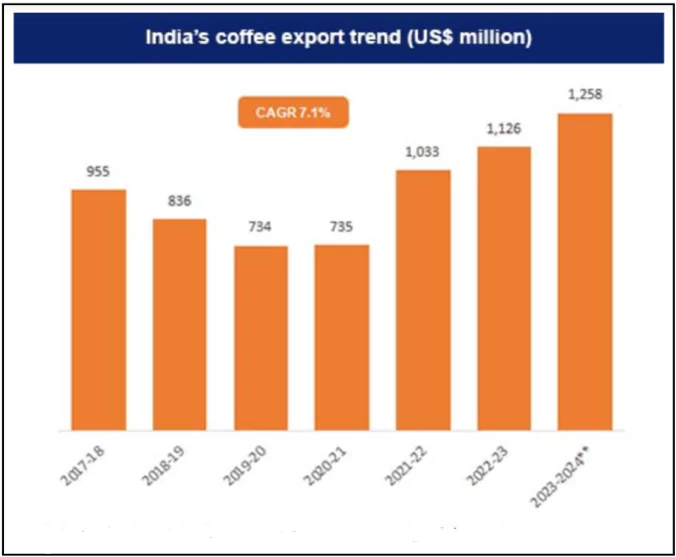
- Coffee is a vital export commodity, contributing significantly to foreign exchange earnings.
- The export of Indian coffee was valued at US$ 1.19 billion (January-August), with growth of 45% y/y over the corresponding period in 2023.
- The dominance of Robusta caters to a broad spectrum of domestic and international markets.
- Europe’s demand highlights India’s critical role in the global coffee supply chain.
- Indian coffee, being predominantly shade-grown, has natural compliance with European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) Norms.
- Current Challenges: Decline in global production, rising costs, and environmental dependencies.
- Future Opportunities: Leveraging high prices, improving sustainable practices, and expanding export destinations beyond Europe.
- India’s coffee industry remains a key driver of agricultural exports and rural livelihoods, with continued policy and market support needed to sustain growth amidst evolving global trends.
![]() 25 Nov 2024
25 Nov 2024


 Climatic and Soil Requirements for Coffee Production
Climatic and Soil Requirements for Coffee Production