The Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics (CDFD) in a DNA Analysis conducted on a family has revealed the practice of Levirate, raising questions about maintaining Genetic Privacy.
- The DNA profiles of the donor (father), the patient, and the patient’s mother were generated.
- The DNA showed that the woman’s husband was not the actual father of the patient but a close paternal relative, possibly a brother of the actual father suggesting the practice of Levirate.
About DNA Profiles
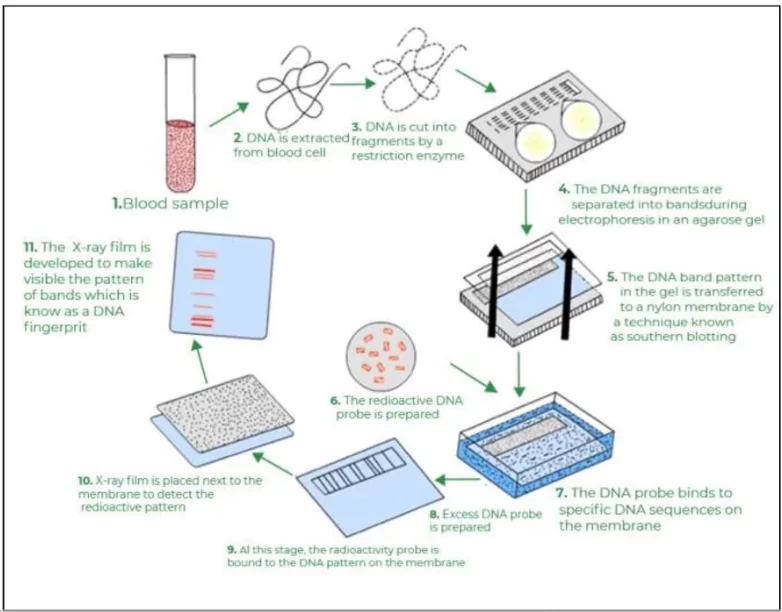
- A DNA profile is a set of genetic characteristics that are obtained from a person by analyzing their DNA markers.
- DNA Profiling: It is also known as DNA fingerprinting, is a scientific technique employed to identify individuals based on their unique genetic makeup.
- Discovery: A British geneticist Alec Jeffreys discovered that certain regions of DNA contained patterns that were unique to each individual in the 1980s
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
The Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics (CDFD)
- The CDFD is an Indian autonomous biotechnology research centre located in Hyderabad, India.
- Funded By: The Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India.
- Recognition: CDFD is a Sun Microsystems centre of excellence in medical bio-informatics, supported with a strong bioinformatics facility, and is the India node of the EMBnet.
- The centre is recognised by the University of Hyderabad and Manipal University for pursuing a doctor of philosophy in life sciences.
- Areas: Research at CDFD has focused largely on molecular epidemiology of bacterial pathogens, structural genetics, molecular genetics, bioinformatics and computational biology.
|
- Process of DNA Profiling:
- Isolation: It is to create lots of copies of DNA from a sample (using the polymerase chain reaction, PCR)
- Fragmentation: Using an enzyme to break the DNA into short lengths
- Separation: The DNA fragments are segregated by size using a technique called capillary gel electrophoresis (Passing an electric current across a layer of gel)
- Comparison: Matching the pattern of fragments on the gel with other samples of DNA
- Methods:
- Short Tandem Repeats (STR) Analysis: STRs are non-coding regions of DNA that contain repeats of the same nucleotide sequence therefore focusing on specific regions of DNA that contain short sequence repetitions.
- Example: GATAGATAGATAGATAGATAGATA is an STR where the nucleotide sequence GATA is repeated six times.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is a technique used to amplify specific regions of DNA, making it easier to analyse. It has proved indispensable in cases where only a small amount of DNA is available.
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Analysis: SNPs are variations at a single base pair in the DNA sequence. With millions of SNPs spread across the human genome, their analysis can provide a detailed DNA profile.
- Use Case:
-
- Criminal Investigation and Forensics: DNA profiling plays a critical role in the field of forensic science. It is employed to link suspects to crime scenes.
- DNA Profiling technique was first applied in a criminal case in 1986, marking the dawn of a new era in forensic science.
- Determining Genetic History: DNA profiling offers a reliable and accurate method for exploring ancestral lines in genealogical research and establishing biological relationships.
- Genetics Based Treatment Routine: The use of DNA profiling helps in understanding a patient’s predisposition to certain diseases and providing treatments according to their genetic makeup, leading to more effective and personalised healthcare.
- Wildlife and Conservation Genetics: In wildlife and conservation, DNA profiling helps track animal migration, monitor genetic diversity, and manage breeding of endangered species.
DNA Profiling and Privacy Concerns
- Reveal Sensitive Information: DNA Profiling can reveal sensitive private information relating to ancestry, medical history etc. to 3rd parties without taking prior consent leading to a breach.
- Surveillance Tool: The Technique can be used by governments in suppressing and discriminating against every dissenting voice raising against it leading to the annihilation of democratic values.
- Security: Lack of effecting laws and its enforcement regarding DNA profiles can make them prone to leakage and misuse
- Discrimination: DNA information could be used to discriminate against different sections of the society based on religion, caste, race, class and sex and health by those having a control of it.
- Data Collection: Direct-to-consumer genetic testing companies may collect and share non-DNA information about you. This information could be sold to data brokers, who may use it to set insurance rates or home loan interest rates.
- Forensic use: Law enforcement agencies may retain DNA samples and profiles for law enforcement purposes, such as identifying criminals or missing persons.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Legal Provisions Regarding DNA Profiling in India
- Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC):
- Section 53: It allows DNA profiling of suspects at the request of an investigation agency. It also allows a police officer to seek the aid of a medical professional to conduct an inquiry.
- Section 53A: It specifically allows DNA profiling for rape suspects.
- Evidence Act, 1872: Sections 45-51 of the Indian Evidence Act determines the admissibility of expert testimony, including DNA evidence, in court.
- The Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022: It is an Indian law that allows police to collect identifiable information from individuals for criminal investigations like to take measurements, collect fingerprints, footprints, biological samples, and behavioral attributes from arrested people, including convicts
- The DNA Technology (Use and Application) Regulation Bill, 2018: The Bill was withdrawn from the Lok Sabha due to opposition on grounds of the accuracy of DNA technology, potential threats to individual privacy, and the possibility of abuse.
- Objectives:
- To set up a DNA profiling board as the regulatory body, one of the functions of which would be to provide accreditation to laboratories authorised to carry out DNA sample tests.
- DNA Data Banks : To create databases ie. DNA Data Banks for storing of DNA information collected from convicts and accused. This database could be indexed and searched for matching samples from crime scenes
- To facilitate collection of DNA samples from the convicts and accused.
Levirate
- The term comes from the Latin word levir, which means “husband’s brother”
- Levirate is the custom where a woman who is widowed or one whose husband is mentally or physically incapacitated has children fathered by her husband’s brother.
- Levirate marriage was practiced in societies with a strong clan structure, where exogamous marriage (marriage outside the clan) was forbidden.
- Purpose: It is practiced to ensure that the function of male heir i.e. the making of ancestral offerings and the maintenance of a biological or genetic lineage is maintained.
- Prevalence: Levirate marriage was more common and acceptable in the south of India than in the north.
|
![]() 3 Dec 2024
3 Dec 2024

