Researchers at CBL-I, Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST), Guwahati, have explored the therapeutic properties of Subabul seedpods for managing insulin resistance in type II diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to use insulin effectively.
- It’s often linked to lifestyle factors like poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity.
Impact of Type 2 Diabetes:
- Organ Damage: Can lead to damage to the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
- Increased Risk of Complications: Raises the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and blindness.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being.
|
Key Findings of the Study
- Active Compounds Identified: The study developed a bioactivity-guided fraction and identified four active compounds from the plant.
- Researchers isolated quercetin-3-glucoside, a compound demonstrating upregulation of mitochondrial deacetylase enzyme Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), crucial for regulating insulin sensitivity.
- Mechanism of Action: The bioactive fraction enhanced insulin sensitization in free fatty acid-induced skeletal muscle cells (C2C12).
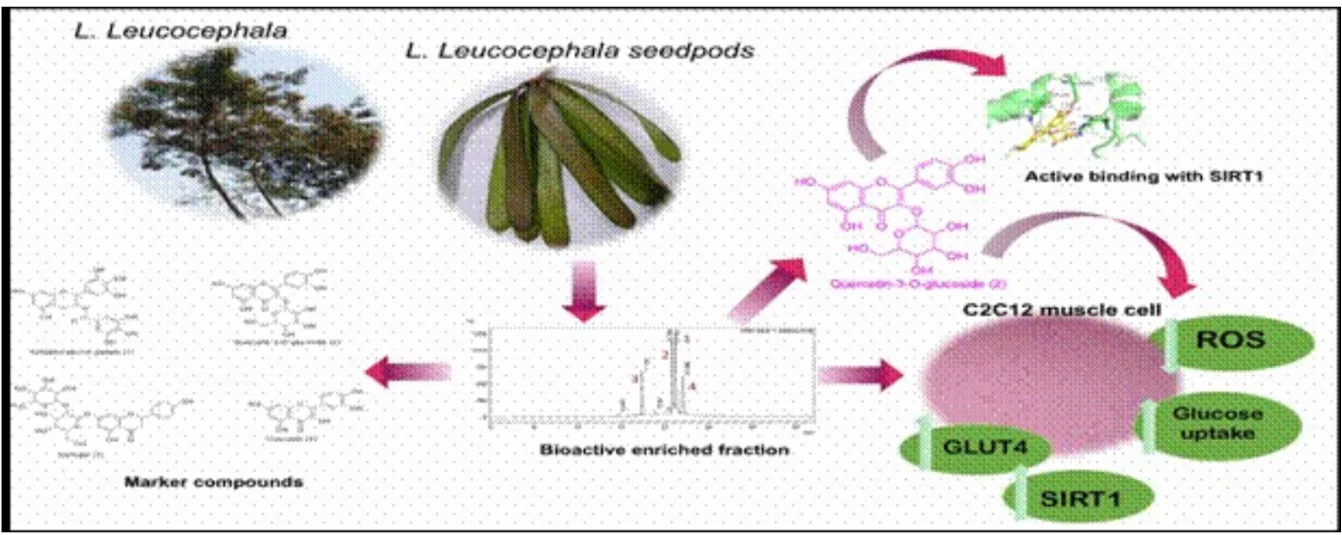 GLUT2 protein translocation which facilitates glucose and fructose transport across cell membranes was also upregulated.
GLUT2 protein translocation which facilitates glucose and fructose transport across cell membranes was also upregulated.- Molecular docking studies showed stable hydrogen bond interactions between quercetin-3-glucoside and SIRT1 residues.
- Therapeutic Implications: The study highlights the therapeutic potential of Subabul in improving glucose uptake, substantiating its ethnobotanical claims as a treatment for diabetes and related conditions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Subabul (Leucaena leucocephala)

- Plant Origin: Subabul is a fast-growing leguminous tree, native to Mexico, and thrives in tropical and subtropical regions.
- Traditional Uses: Widely used by ethnic communities for its nutritional value, with leaves and immature seeds consumed raw or cooked in soups or salads.
- Known as a rich source of protein and fiber, it has been utilized in human and animal food.
- Physical Characteristics: A small, perennial, highly-branched tree, typically with a short, clear bole.
- Economic Importance: Introduced as a cover crop in plantations and for fodder and fuel purposes.
- Valued for its wood, used in making charcoal, small furniture, and paper pulp.
- Its dual utility as a nutritional resource and a medicinal plant underscores its importance in public health and economic sustainability.
Additional Reading: Diabetes
![]() 5 Dec 2024
5 Dec 2024

 GLUT2 protein translocation which facilitates glucose and fructose transport across cell membranes was also upregulated.
GLUT2 protein translocation which facilitates glucose and fructose transport across cell membranes was also upregulated.
