Scientists in India have reported success with using gene therapy to treat severe haemophilia A, a rare hereditary condition resulting from a faulty gene which triggers severe, spontaneous, and potentially fatal bleeding Episodes.
About Hemophilia A
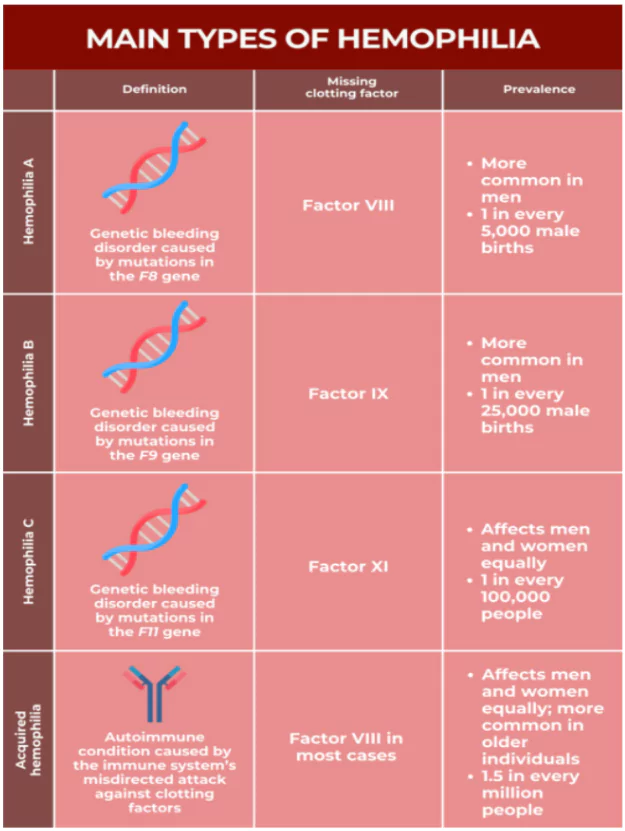
- Hemophilia A, also known as classical haemophilia, is a rare and genetic bleeding disorder caused by insufficient levels of a blood protein called factor VIII.
- Factor VIII is a clotting factor (an essential protein required for blood to clot and stop bleeding).
- Caused by: Hemophilia A is caused by disruptions or changes (variants or mutations) to the F8 gene located on the X chromosome.
- Susceptibles: Hemophilia A is mostly expressed in males but some females who carry the gene variant may have mild or, rarely, severe symptoms of bleeding.
About Hemophilia A
- Hemophilia: Group of rare bleeding disorders caused by a congenital deficiency in specific clotting factors
- Most prevalent form is Hemophilia A
- Males are much more likely to have hemophilia than are females.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Why is it more prevalent in males?
- Males have one X and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes. If a male inherits an X chromosome with the defective gene from his mother, He will have hemophilia A.
- Females with one defective copy typically do not experience symptoms because the other X chromosome usually provides enough factor VIII.
- Females can have hemophilia A if they inherit two defective copies, one from each parent (much less common).
About Gene Therapy For Haemophilia
- Gene therapy, Roctavian, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for commercial use in 2023.
- It works by transporting the therapeutic gene into the body by using an adenovirus as a carrier or vector and involves the liver in producing Factor VIII.
Additional Reading: Gene Therapy For Haemophilia A (FVIII Deficiency
![]() 12 Dec 2024
12 Dec 2024

