A new analysis reveals that 2024 experienced the highest ocean temperatures on record, significantly impacting global climate patterns.
Key Findings of the analysis
- Highest Surface and Ocean Heat Content (OHC):
- Ocean Heat Content (OHC): it refers to the total heat stored in the ocean.
- Surface Temperature (SST): It is the temperature of the ocean surface (top few metres).
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
-
- The average global surface temperature and the heat content of the upper 2,000 metres of oceans reached record highs in 2024.
- Ocean heat content increased by 16 (± 8) Zetta Joules (ZJ) compared to 2023.
- Global Sea Surface Temperature (SST):
- The annual mean SST in 2024 was 0.61°C above the 1981-2010 baseline, slightly surpassing the previous record set in 2023.
- Climate Impacts of Ocean Warming
- Increased Atmospheric Moisture:
- Warmer oceans led to higher levels of water vapour, which traps heat and accelerates global warming.
- Evaporation rates rose, transferring more heat and moisture to the atmosphere.
- Extreme Weather Events:
- Increased atmospheric moisture contributed to severe weather events, such as:
- Heavy rainstorms in South China during the summer of 2024.
- Hurricane Helene in the United States, causing devastating floods.
- Sea Level Rise:
- Ocean warming caused thermal expansion, significantly contributing to rising sea levels.
- Regional Ocean Warming Trends
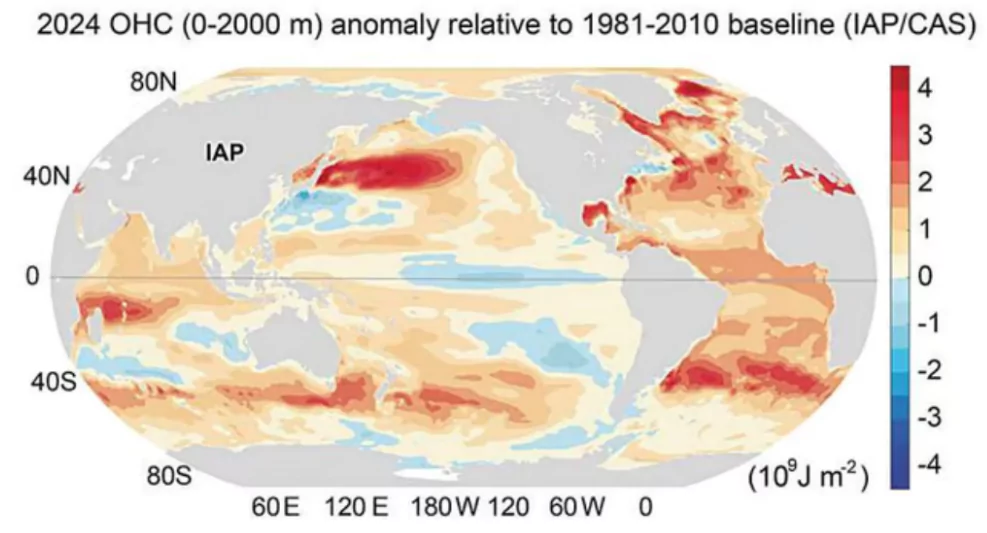 Indian Ocean:
Indian Ocean:
- Ocean heat content rose by 10.3 ZJ compared to 2023, mainly due to one of the five strongest El Niño events in history.
- Impacts included intensified monsoons and shifts in precipitation patterns in India.
- Mediterranean Sea:
- Experienced the most intensive warming rate, with a 1.1 ZJ increase compared to 2023.
- Warming rates were five times higher than the past two decades, affecting marine biodiversity and regional climates.
- North Pacific:
- OHC rose by 3.8 ZJ, continuing its long-term warming trend since the 1990s.
- Contributed to marine heatwaves and impacted intermediate water masses.
- Other Regions:
- Record-high OHC values were also observed in the tropical Atlantic, Southern Ocean, and North Atlantic.
What is Ocean Warming?
Ocean Warming is the increase in ocean temperatures over time, mainly caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels.
Consequences of Ocean Warming
- Rising Sea Levels: Expansion of seawater and melting ice sheets contribute to higher sea levels.
- Melting Ice Sheets: Polar ice caps and glaciers are melting at alarming rates.
- Marine Heatwaves: Unusual and prolonged warming events in ocean regions.
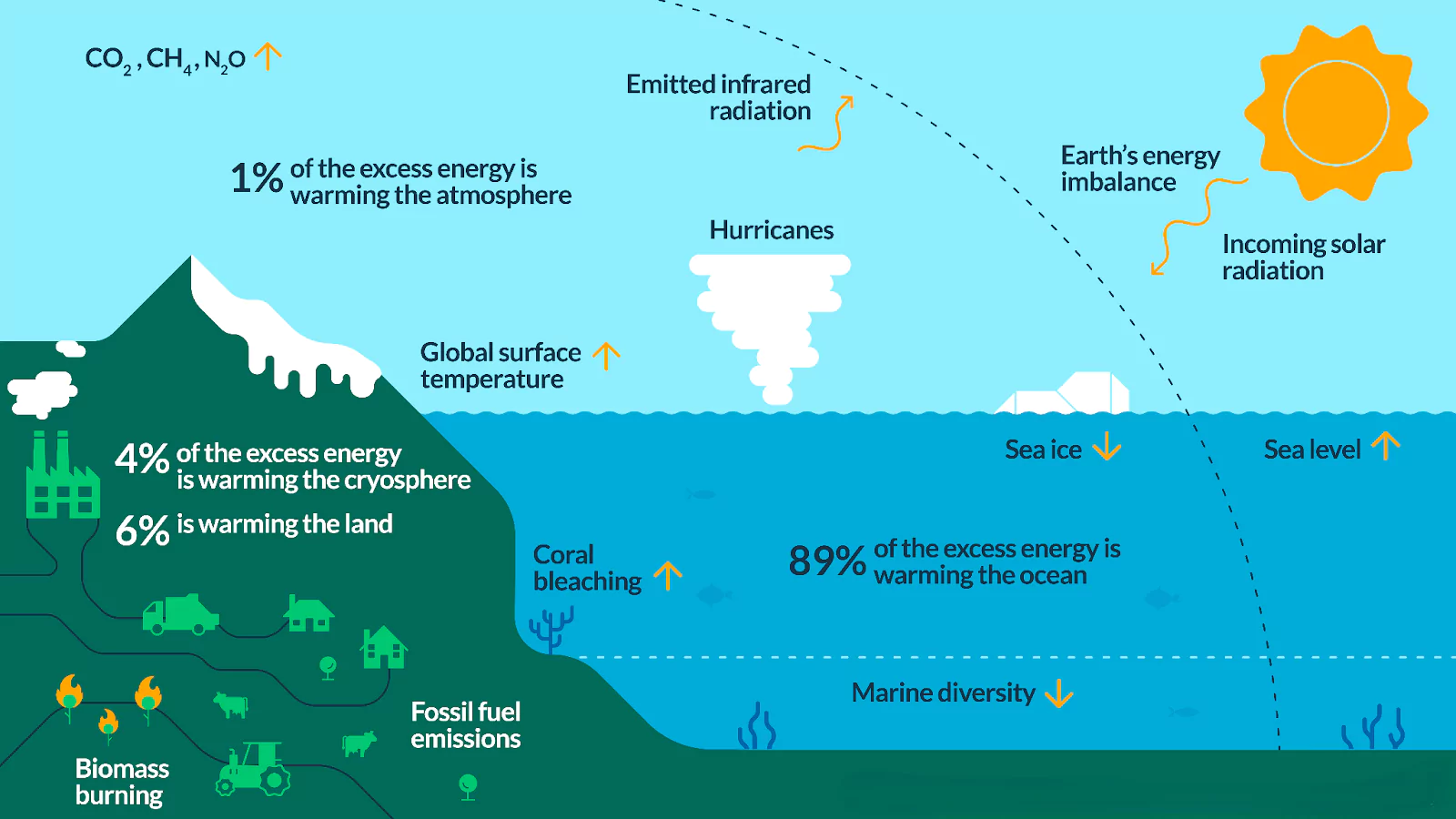 Ocean Acidification: Increased CO₂ absorption alters the pH of seawater.
Ocean Acidification: Increased CO₂ absorption alters the pH of seawater.- Coral Bleaching: Coral reefs are losing their vibrant colors and ecosystems are being damaged.
- Loss of Breeding Grounds: Marine species are losing vital habitats for reproduction.
- Extreme Weather Events: Warmer oceans intensify storms, hurricanes, and rainfall.
- Coastal Protection Loss: Degradation of coral reefs and mangroves increases coastal vulnerability.
- Reduced Carbon Absorption: Warmer oceans are less able to absorb carbon dioxide, worsening climate change.
Reasons for Ocean Warming
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Burning fossil fuels, cutting trees, and industrial activities release gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) that trap heat, making the atmosphere and oceans warmer.
- CO2 Absorption: The ocean absorbs excess CO2 from human activities. While this helps reduce climate change, it also causes ocean warming.
- Solar Radiation: Changes in solar energy can also increase ocean temperatures over long periods, but it’s a small factor compared to human activities.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Solutions to Address Ocean Warming
- Limit Global Temperature Rise: Keep the global average temperature increase well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels.
- Establish Marine Protected Areas: Safeguard critical marine habitats and ecosystems.
- Implement Adaptive Measures: Enforce precautionary catch limits to prevent overfishing and promote sustainable practices.
![]() 14 Jan 2025
14 Jan 2025

 Indian Ocean:
Indian Ocean:
 Ocean Acidification: Increased CO₂ absorption alters the pH of seawater.
Ocean Acidification: Increased CO₂ absorption alters the pH of seawater.