Yala glacier, one of Nepal’s most extensively studied glaciers, is expected to vanish by the 2040s.
- According to WMO and UNESCO, there are more than 275,000 glaciers worldwide.
- It covers approximately 700,000 sq km and with ice sheets, storing about 70% of the global fresh water.
About Yala glacier
- Yala Glacier is situated in the Langtang Valley, central Nepal.
- Significance and Monitoring
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
- Global Glacier Casualty List
- Launch: The project was launched in 2024.
- Main Collaborators : Rice University, University of Iceland, Iceland Glaciological Society, and UNESCO.
- Purpose: To track the status of glaciers worldwide and raise awareness about their decline.
|
-
- It is a key representative of the Hindu Kush Himalayan region in the World Glacier Monitoring Service (WGMS) database.
- Critical Status : It’s the only glacier in the Himalayas on the Global Glacier Casualty List.
- It plays a vital role in studying the cryosphere.
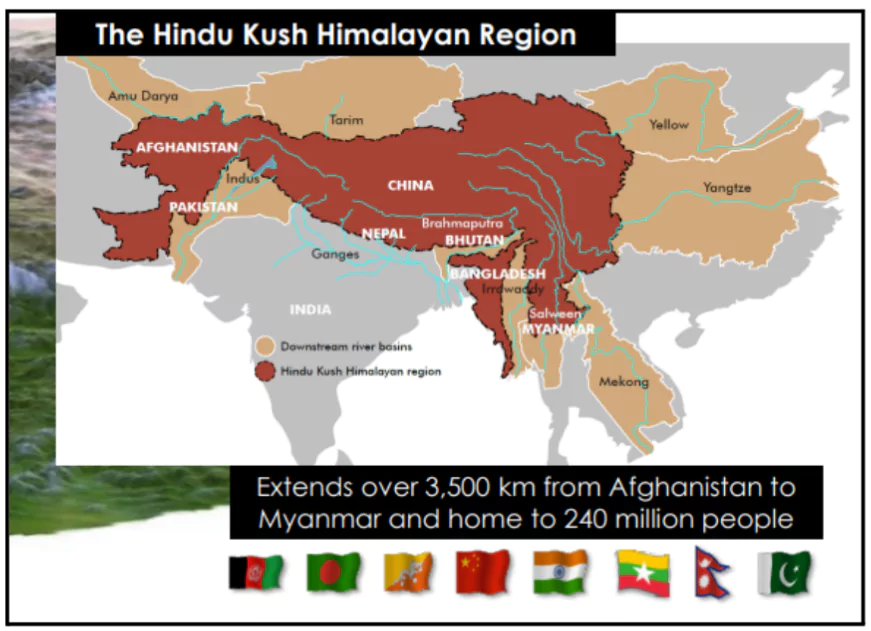
About Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH)
- It is a mountain range in central Asia.
- Known as: Third pole
- This region comprises the third-largest storage of frozen water.
|
What is Glacier Retreat?
- Glacier retreat refers to the shrinking of glaciers in size and mass due to melting, evaporation, and other environmental factors.
 Retreat of Yala Glacier
Retreat of Yala Glacier
- The glacier has lost 36% of its total area during the period between 1974 and 2021
- Impact of Warming
- The Hindu Kush Himalayan cryosphere is warming twice as fast as the global average, leading to the accelerated melting and retreat of glaciers in the region.
- Other Critically Endangered Glaciers
- Pico Humboldt Glacier: Disappeared in Venezuela in 2024.
- Sarenne Glacier: Disappeared in France in 2023.
- Dagu Glacier: In China, expected to disappear by 2030.
- Chinese Glacier Shrinkage: Chinese glaciers have shrunk by 12,442.4 sq km, losing 20.6% of their total area.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Impacts of Melting Glaciers and Cryosphere
- Disruption of Ecosystems and Livelihoods
- Glaciers and ice sheets store 70% of the world’s freshwater, essential for ecosystems and human survival.
- 240 million people in the Hindu Kush Himalayas depend on glaciers for water and livelihoods.
- Increased Risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)
- Rapid melting creates unstable glacial lakes.
- These lakes can breach, causing devastating floods in downstream areas.
- Climate Feedback Loop
- Melting glaciers reduce the Earth’s albedo (reflectivity).
- Less reflectivity increases heat absorption, accelerating global warming.
Cryosphere
- The cryosphere refers to the frozen areas of the Earth, which include:
- Snow
- Ice (glaciers, ice caps, and sea ice)
- Frozen ground (permafrost).
- It plays a critical role in maintaining the planet’s climate and water cycle.
- Importance to the Cryosphere
- The glacier is essential for studying the cryosphere, which serves as a vital water resource for approximately 240 million people living in the Himalayan region.
Initiatives to Protect the Cryosphere
- Global Efforts
- UN Initiatives
- 2025 is declared as the International Year of Glaciers’ Preservation.
- March 21 to be observed annually as World Day for Glaciers.
- Other Global Efforts
- Himalayan Adaptation Network by IUCN.
- Living Himalayas Initiative by WWF.
- India’s Efforts
- National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem: Focuses on preserving the Himalayan region.
- Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS): Monitors glacier-related events and issues GLOF alerts.
- Polar Missions:
- IndARC (2014): India’s observatory in the Arctic for glacier and climate monitoring.
|
![]() 20 Jan 2025
20 Jan 2025

 Retreat of Yala Glacier
Retreat of Yala Glacier
