The government in the Budget speech of 2025-26 has announced the setting up of the Nuclear Energy Mission for Viksit Bharat for research and development of small modular reactors (SMRs).
About the Nuclear Energy Mission for Viksit Bharat
- Aim: To enhance domestic nuclear capabilities, promote private sector participation, and deploy advanced nuclear technologies.
- Funding: The Union Budget 2025-26 has allocated ₹20,000 crore for R&D in Small Modular Reactors, targeting at least five indigenously designed operational SMRs by 2033.
- Target: India has targeted 100 GW nuclear power capacity by 2047
- Private Sector Entry: The government plans to amend the Atomic Energy Act of 1962 and the The Civil Liability for Nuclear Damages Act to facilitate the entry of the private sector in nuclear energy with the motive of,
- Setting up Bharat Small Reactors,
- Research & development of Bharat Small Modular Reactor, and
- Research & development of newer technologies for nuclear energy.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
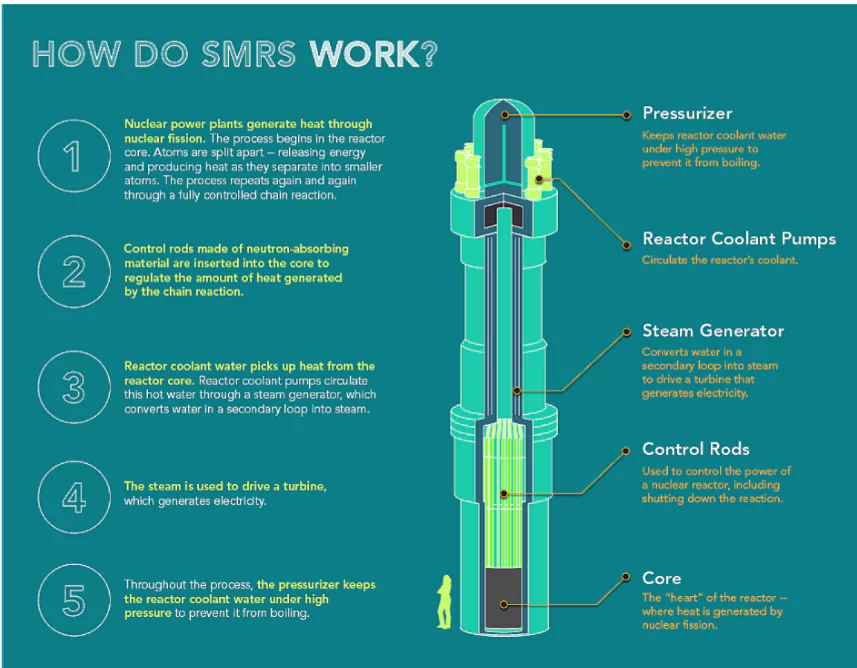
About Small Modular Reactors
- SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with the maximum power producing capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit.
- It is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors (capacities of 500 MW of electricity or more)
- Modular Design: The modular design of the reactors means the systems and components are factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation instead of being constructed on-site
- Application Areas: SMRs targets varied outputs and different applications, such as electricity, hybrid energy systems, heating, water desalinisation and steam for industrial applications.
 Operational Status: SMRs are mostly still under the development stage with just a couple of experimental SMRs being operational right now.
Operational Status: SMRs are mostly still under the development stage with just a couple of experimental SMRs being operational right now.-
- Example: Russia’s Akademik Lomonosov (world’s first floating nuclear power plant) is producing energy from two 35 MW(e) SMRs.
- Development Status: More than 80 different designs for SMRs are under development, across the world with countries like the United States, China, Russia and South Korea constructing such reactors.
- India is developing Bharat Small Modular Reactors (BSMRs) as part of its energy transition strategy
- Advantages:
- Design: SMRs are small and modular in design making them more affordable to build and install at any given location. SMRs offer savings in cost and construction time, and they can be deployed incrementally to match increasing energy demand.
- Inbuilt Safety Provisions: SMRs are passive systems that rely on physical phenomena (like, natural circulation, convection, gravity and self-pressurization) significantly lowering the chance of unsafe release of radioactive waste in the environment in case of an accident.
- Fuel Requirements: SMRs may require less frequent refuelling (every 3 to 7 years) as compared to 1 to 2 years for conventional plants. Some SMRs are designed to operate for up to 30 years without refuelling.
- Energy Inclusivity: SMRs are better suited for regions inaccessible to clean, reliable and affordable energy providing low-carbon power for industry and the population.
- It can be installed into an existing grid or remotely off-grid, as a function of its smaller electrical output.
About India’s Nuclear Power Generation Capacity
- Nuclear energy is the fifth-largest source of electricity in India.
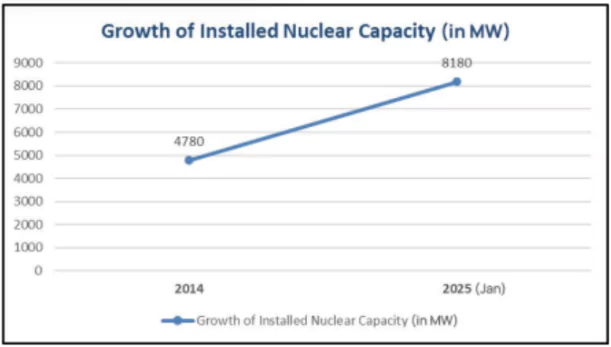
- Present Status: India’s Nuclear power generation capacity nearly doubled from 4,780 MW in 2014 to 8180 MW as of 2025, contributing about 3.11% (as of 2020-21) of the country’s total electricity generation.
 Projected: Nuclear capacity is projected to triple to 22,800 MW by 2031-32 with Nuclear Energy accounting for nearly 9% of India’s electricity by 2047.
Projected: Nuclear capacity is projected to triple to 22,800 MW by 2031-32 with Nuclear Energy accounting for nearly 9% of India’s electricity by 2047.- Operating Reactors: India has 23 operating reactors across 7 nuclear power plants, primarily composed of pressurized heavy-water reactors (PHWRs), with some light-water reactors (LWRs)
- Evolution: Electricity production using nuclear energy commenced in October 1969 with the commencement of the two reactors at Tarapur, Maharashtra.
- Ownership: Nuclear power plants in India are owned and operated by the Nuclear Energy Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL), and it’s fully-owned subsidiary Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam (BHAVINI).
- Public sector units like the NTPC or NHPC are recently allowed to enter into joint ventures with NPCIL to own and operate nuclear plants.
- Government Initiatives for Enhancing India’s Nuclear Capacity:
- Expansion: India targets nuclear energy expansion to 22,480 MW by 2031-32 which includes,
- The construction and commissioning of ten reactors, totalling 8,000 MW, across Gujarat, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Karnataka, and Madhya Pradesh.
- In- principle approval was accorded to set up 6 x 1208 MW nuclear power plant in cooperation with the USA at Kovvada in Srikakulam district in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- Achieving Controlled Fission Chain Reaction: The Rajasthan Atomic Power Project’s Unit-7 ( India’s third indigenous nuclear reactors) reached criticality recently, marking the beginning of controlled fission chain reaction.
- Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor: Progress in the country’s first Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR 500 Mwe) achieving many of the milestones in 2024 like loading of first reactor control rod in 2024.
- Bharat Small Reactors: The government is actively expanding its nuclear energy sector by developing Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs) in partnerships with the private sector
- New Generation Reactors: The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) to introduce new nuclear reactors, including high-temperature gas-cooled reactors for hydrogen co-generation and molten salt reactors aimed at utilizing India’s abundant thorium resources.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Bharat Small Reactors
- BSRs are 220 MW Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) with a proven safety and performance record.
- Objective: These reactors are being upgraded to reduce land requirements, making them suitable for deployment near industries such as steel, aluminium, and metals, serving as captive power plants to aid in decarbonization efforts.
- Partnership: The private entities will provide land, cooling water, and capital, while the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) handles design, quality assurance, and operation and maintenance, all within the existing legal framework.
Bharat Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
- The Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) is developing SMRs for repurposing retiring coal-based power plants and meeting power needs in remote locations.
- Tata Consulting Engineers is working with the Department of Atomic Energy to build 40-50 BSMRs within seven or eight years.
- Capacity: SMRs, are advanced nuclear reactors with a power generation capacity ranging from less than 30 MWe to 300+ MWe.
- Aim: It is being developed as a crucial part of its energy transition strategy, aiming to achieve net-zero emissions while ensuring energy security.
|
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 6 Feb 2025
6 Feb 2025

 Operational Status: SMRs are mostly still under the development stage with just a couple of experimental SMRs being operational right now.
Operational Status: SMRs are mostly still under the development stage with just a couple of experimental SMRs being operational right now. Projected: Nuclear capacity is projected to triple to 22,800 MW by 2031-32 with Nuclear Energy accounting for nearly 9% of India’s electricity by 2047.
Projected: Nuclear capacity is projected to triple to 22,800 MW by 2031-32 with Nuclear Energy accounting for nearly 9% of India’s electricity by 2047.