The Restructured National Bamboo Mission (NBM) has played a significant role in boosting the rural economy and reducing import dependency by promoting bamboo cultivation, value addition, and market integration.
About the Restructured National Bamboo Mission (NBM)
- The mission was launched in 2018-19 as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) to enhance bamboo cultivation, processing, and market linkages.
- Aim: To support both government and private sectors in activities such as bamboo propagation, treatment, market establishment, incubation centers, value-added product development, and the development of tools and equipment.
- Funding: The funding pattern for the scheme is 60:40 between the Centre and State Governments except for Northeastern and Hilly States, where the ratio is 90:10.
- Provides 100% funding for Union Territories, Bamboo Technology Support Groups (BTSGs), and National Level Agencies.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About National Bamboo Mission (NBM)
- NBM was initially launched in 2006 to promote bamboo-based development.
- The Department of Agriculture & Cooperation (DAC) under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare is the nodal ministry responsible for its implementation.
- Between 2014 and 2016, the mission was subsumed under the Mission for Development of Horticulture.
- In 2018, the mission was restructured under the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA), focusing on market linkages, value addition, and research & development (R&D).
- A significant reform in 2018 was the amendment of the Indian Forest Act, 1927, which removed bamboo grown outside forests from the definition of trees.
- This reform eased cultivation and trade by eliminating the requirement for transit permits, boosting private bamboo farming.
About Bamboo
- Bamboo is a grass belonging to the subfamily Bambusoideae of the Poaceae family and includes over 115 genera and 1,400 species.
- It is widely distributed in tropical, subtropical, and mild temperate regions, with the highest concentration found in East and Southeast Asia and islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- Some species of the genus Arundinaria are native to the southern United States, where they form dense canebrakes along riverbanks and marshy areas.
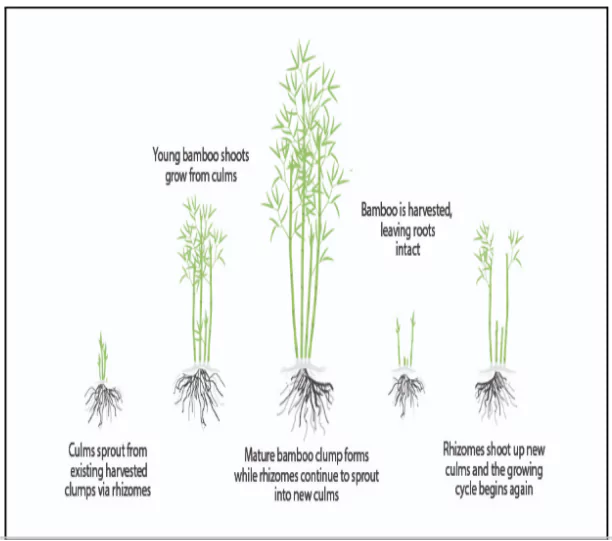
- Its woody, ringed stems (culms) are typically hollow and grow in clusters from underground rhizomes.
- Most bamboo species flower and produce seeds only once in their lifetime, with cycles ranging from 12 to 120 years, relying primarily on vegetative reproduction.
Application of Bamboo
- Carbon Sequestration: Bamboo is highly efficient in absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, contributing to carbon sequestration.
- Studies indicate that bamboo produces 35% more oxygen than most other vegetation.
- Reducing Fossil Fuel Dependence: Bamboo is among the fastest-growing plants in the world, with a growth rate of 30 cm to 90 cm (1 to 3 feet) per day.
- Its rapid growth makes it a highly efficient biomass producer, which can be utilized as an alternative to fossil fuels.
- Bamboo as Food and Medicine: In the Northeastern states of India, fresh bamboo shoots are widely consumed as vegetables and used as key ingredients in local dishes.
- Certain parts of the bamboo plant, including its roots, are believed to have therapeutic properties and are used in traditional medicine in the Northeast.
- Adaptation and Livelihood Support: Bamboo’s flexible harvesting cycle allows farmers to adapt to climate changes and provides a consistent income source throughout the year.
- Environmental Restoration: Bamboo thrives in challenging environments and plays a significant role in land restoration efforts.
- It helps prevent soil erosion and contributes to restoring degraded lands.
Culms are classified based on:
- Age: Current year, 1-2 years old, and more than 2 years old.
- Condition: Green-sound, green-damaged, dry, or decayed.
- Diameter: 1 cm to above 8 cm.
|
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Status of Bamboo Production in India
- Bamboo Distribution & Growth:
- Bamboo species were recorded in over 18,000 inventoried grids between 2016-17 and 2019-20.
- The total number of bamboo culms at the national level is estimated at 53,336 million.
- There has been a 35.19% increase in bamboo culms between ISFR 2019 and ISFR 2021, with an increase of 13,882 million culms.
- Classification of Bamboo Culms:
- Green Sound Culms: 73.40%
- Dry Sound Culms: 17.54%
- Decayed Culms: 9.06%
- The 2-5 cm diameter class has the highest contribution to the total number of culms.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 10 Feb 2025
10 Feb 2025


