First indigenous Automated Bio Medical Waste Treatment Plant
Context: Recently, Union Minister launched India’s first indigenous Automated Biomedical Waste Treatment Rig, named Sṛjanam, at AIIMS New Delhi.
About Sṛjanam Rig
- It is an automated bio medical waste treatment plant.
- It is the first of its kind in the country.
- Developed by: CSIR National Institute for Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (NIIST) in Thiruvananthapuram developed this innovative rig.
- It showcases India’s progress in advanced waste management technology.
- Special Features of Sṛjanam
- Sṛjanam disinfects biomedical waste such as blood, urine, sputum, and laboratory disposables.
- It does this without using expensive and energy-heavy incinerators.
- Odor Control and Capacity:
- The rig removes bad odors and adds a pleasant smell to the treated waste.
- It can process up to 400 kg of waste per day.
- In the initial phase, it can handle 10 kg of degradable medical waste per day.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Chandrayaan-3’s Shiv Shakti landing point
Context: Scientists from the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, conducted a morphological and topographic analysis of the Chandrayaan-3 landing site
About Chandrayaan-3 Landing Site
- Chandrayaan-3 Landing Site is 3.7 billion years old.
- This age coincides with the time when primitive microbial life first emerged on Earth.
- It was mapped by Indian scientists using high-resolution remote sensing data.
- Significance of the Study
- Lunar History Insights: Reveals how meteor impacts and debris shaped the Moon’s surface.
- Historic Landing
- On August 23, 2023, Chandrayaan-3, with Vikram lander and Pragyan rover, landed near the Moon’s South Pole.
- India became the fourth country to make a soft landing on the Moon, after the USSR (Russia), US, and China.
Key Findings of ISRO’s Study on Chandrayaan-3 Landing Site
- Terrain and Crater Analysis
- The landing site is located in an area with low-relief smooth plains.
- The surrounding region also includes:
- High-relief rugged terrain
- High-relief smooth plains
- Geological Influences on the Area
- The area was mainly formed by ejecta from secondary craters, including:
- Manzinus crater (96 km diameter, ~3.9 billion years old)
- Boguslawsky crater (95 km diameter, ~4 billion years old)
- Schomberger crater (86 km diameter, ~3.7 billion years old)
- Impact of Space Weathering
- The region is affected by micro-meteorite bombardments and extreme temperature changes.
- This caused the rock fragments to break down into regolith (lunar soil) over time.
- Rock and Crater Distribution
- The Pragyan rover found several rock fragments larger than 1 cm.
- The largest rock samples were found near:
- A fresh crater (14 km south of the landing site)
- Another crater (1.8 km in diameter) 8 km west of the landing site.
Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) 2024
Context: India has ranked 96th out of 180 countries in the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) 2024.
About Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI)
- CPI is an annual report published by Transparency International.
- It is the most widely used global corruption ranking in the world.
- The CPI ranks 180 countries and territories based on their perceived levels of public sector corruption.
- The scale ranges from zero (highly corrupt) to 100 (very clean).
India’s CPI Performance Over the Years
- 2024: Rank 96, Score 38
- 2023: Rank 93, Score 39
- India’s declining score and rank reflect ongoing challenges in tackling corruption, despite efforts like the Right to Information Act and anti-corruption laws.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Global Findings
- Top Performers: Denmark topped the list as the least corrupt nation, followed by Finland and Singapore.
- Global Average Stagnant: The global average score remains at 43, with over two-thirds of countries scoring below 50.
- Worst Performers: Countries like Somalia, South Sudan, and Syria rank at the bottom due to weak governance and conflict.
- Corruption and Climate: The 2024 report highlights how corruption undermines climate action, with funds often misused or stolen.
Transparency International
- Transparency International is a global non-governmental organization (NGO) founded in 1993.
- Transparency International works to combat corruption and promote transparency, accountability, and integrity in governments, businesses, and civil society.
- It is headquartered in Berlin, Germany, and operates in over 100 countries through its national chapters.
Panama withdraws from Belt and Road Initiative
Context: Panama has officially announced its withdrawal from China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), marking a significant geopolitical realignment.
US Influence and Panama’s Decision
- The recent decision by Panama to withdraw from the BRI follows a visit by US Secretary of State Marco Rubio to the country.
- This visit is widely seen as a catalyst for Panama’s decision to step back from the BRI.
- The US has been increasingly vocal about its concerns regarding China’s growing influence in Latin America.
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
- The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a global infrastructure development strategy launched by China in 2013.
- It aims to enhance connectivity and economic cooperation across Asia, Europe, and Africa by investing in infrastructure projects like roads, railways, ports, and energy networks.
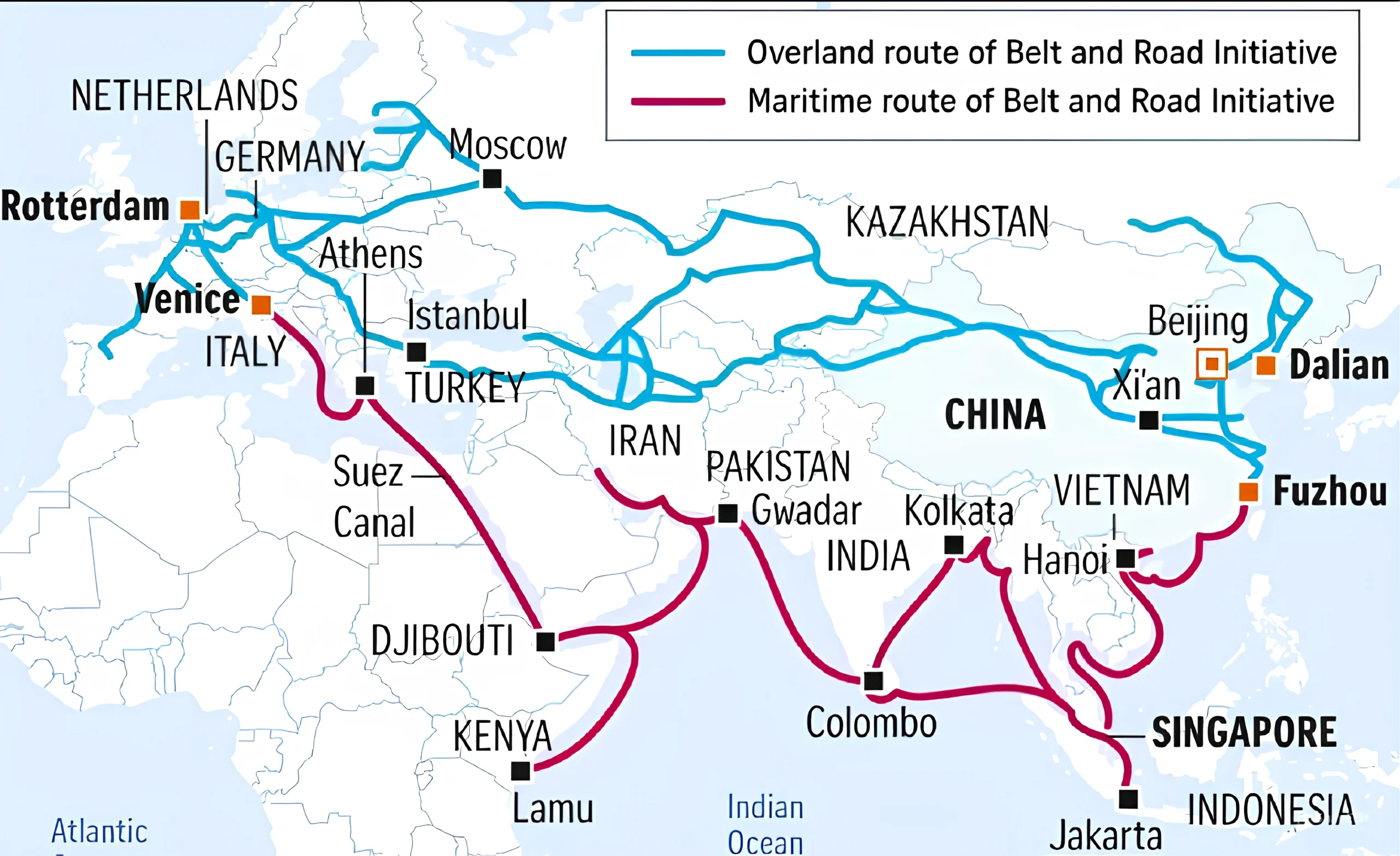
Key Components of BRI
- Silk Road Economic Belt: A land-based network linking China to Europe through Central Asia.
- 21st Century Maritime Silk Road: A sea route connecting China to Southeast Asia, Africa, and Europe.
New HS code GI-recognised rice varieties
Context: India has amended the Customs Tariff Act to introduce a new HS (Harmonised System) code for exporting Geographical Indication (GI)-recognised rice that will allow the export of these special rice varieties without requiring special notifications from the Finance Ministry.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
What is HS?
- HS (Harmonized System) is a global product classification system.
- It is called the “universal economic language” for goods.
- Developed by: World Customs Organization (WCO).
- This is the first time in the world that an HS code is introduced for GI rice.
- The HS codes are 1006-30-11 for parboiled rice and 1006-30-91 for white rice.
- Classification Structure
- Uses six-digit codes to classify different products and commodities.
- Countries can add extra digits to the six-digit code for more specific classifications.
- Governed by: The “International Convention on the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System.”
- Managed by: The HS Committee, which includes member countries.
- HS is updated every 5–6 years.
- Widespread Adoption
- Used for about 98% of international trade.
- Covers over 5,000 commodity groups.
- Implemented by more than 200 countries worldwide.
- Benefits of HS
-
- Provides a common coding system for organizing and tracking products in global trade.
- Used by governments, international organizations, and private companies for taxes, trade policies, and more.
- Lowers international trade costs and supports economic research.
Impact on Rice Exports
- Facilitating Exports During Ban
- The new HS code will help export GI-tagged rice even if the government imposes a ban on general rice exports.
- Ease of Export Process
- The amendment allows the export of GI-tagged rice without needing special permission from the Finance Ministry.
World Customs Organization (WCO)
- It is an independent governmental body.
- Established in : 1952
- Objective: aims to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of customs administration.
- Headquarter: Brussels, Belgium.
|
Exercise Cyclone 2025
Context: The 3rd edition of the Joint Special Forces Exercise CYCLONE has commenced at Mahajan Field Firing Ranges in Rajasthan, India.
About Exercise Cyclone 2025
- Exercise CYCLONE is an annual military exercise conducted alternatively in India and Egypt.
- History of Exercise Cyclone: The first edition was conducted in India in 2023.
- The previous edition (2024) was held in Egypt in January 2024.
- Objective of Exercise Cyclone 2025:
- The goal of the exercise is to enhance coordination and interoperability between the Indian and Egyptian armies.
- The training will include real-world scenarios and tactical drills to improve combat readiness.
- Both armies will train together in desert conditions to develop joint operational capabilities.
- Motto of Exercise Cyclone 2025: The motto for Exercise Cyclone 2025 is “Together we train, together we excel.”
- Key Focus Areas:
- The exercise will involve special forces from both countries.
- Training will focus on:
- Counter-terrorism operations
- High-intensity combat tactics
- Survival techniques in extreme conditions
Republic of Estonia
Context: The Indian Prime Minister met with the President of the Republic of Estonia on the sidelines of the AI Action Summit in Paris.
- This was the first meeting between the two leaders.
- India-Estonia Partnership: The two leaders noted the importance of the India-Estonia partnership in the context of the India-EU strategic partnership.
- They welcomed the initiation of ministerial exchanges in the India-Nordic-Baltic format.
About The Republic of Estonia
- Location: Estonia is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe.
- Capital City: Tallinn
- Neighbours: It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Russia
- Language: Eesti Vabariik or the Estonian language
- Political nature: It is a democratic unitary parliamentary republic, administratively subdivided into 15 maakond (counties)
- Legislature: Riigikogu
- Membership: Estonia is a member of the Eurozone and NATO
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
‘IRIS’ (Indigenous RISCV Controller for Space Applications) Chip
Context: The ‘IRIS’ (Indigenous RISCV Controller for Space Applications) chip has been developed from the ‘SHAKTI’ processor baseline.
- IRIS is the third SHAKTI chip to have been developed after RIMO in 2018 and MOUSHIK in 2020.
About the IRIS’ Chip
- It is an Atmanirbhar aerospace quality SHAKTI-based semiconductor chip.
- Developed By:The chip is developed by Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT Madras) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- Idea: The ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU) in Thiruvananthapuram proposed the idea of a 64bit RISC-V-based Controller
- Designed: IIT Madras defined the specifications and design of the semiconductor chip
- Application: It can be used in diverse domains from Internet of Things and compute systems for strategic needs.
- Need: It was part of the effort of ISRO to indigenise semiconductors used for its applications, Command and Control Systems and other critical functions
- Importance: The Chip is end to end developed in India marking a milestone in “Make in India” efforts in semiconductor design and fabrication.
About The SHAKTI Microprocessor Project
- The project aims to promote indigenous development of microprocessor-based products adopting RISC-V technology, an open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), for designing custom processors.
- Led By: The Centre for Digital Intelligence and Secure Hardware Architecture in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT Madras.
- Supported By: It is backed by the Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology under its ‘Digital India RISC-V’ initiative.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 12 Feb 2025
12 Feb 2025


