Core Demand of the Question
- Discuss the major earthquake-prone zones in India as it is located in a seismically active region due to the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates.
- Discuss the challenges associated with disaster preparedness in these regions
- Suggest the measures to mitigate these challenges
|
Answer
India lies in a seismically active region, as the Indian Plate continues to push northward into the Eurasian Plate at a rate of ~5 cm per year, creating immense geological stress. The February 2024 Delhi earthquake, with tremors felt across North India, highlights the growing seismic risk. With 59% of India prone to earthquakes, preparedness is crucial.
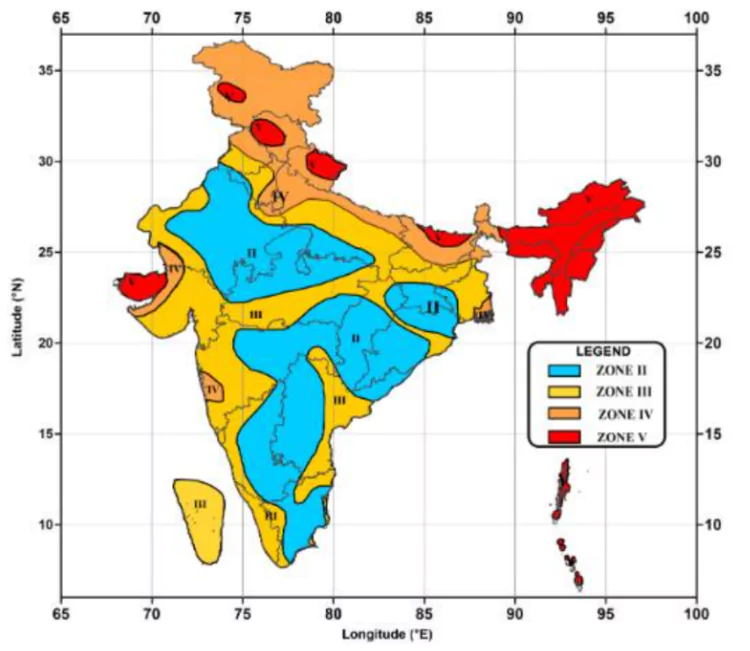
Major Earthquake-Prone Zones in India
- Himalayan Seismic Belt: The collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates creates high seismic activity, covering Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Arunachal Pradesh in Seismic Zone V.
For example: The 2015 Nepal earthquake caused widespread destruction in Bihar, Sikkim, and West Bengal, demonstrating the vulnerability of northern India to Himalayan quakes.
- Indo-Gangetic Plain: This densely populated region lies in Seismic Zones III and IV, facing risks due to alluvial soil amplifying seismic waves, affecting Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal.
For example: The 1934 Bihar-Nepal earthquake devastated Patna, Munger, and Muzaffarpur, leading to severe casualties and infrastructure collapse in soft-soil regions.
- Northeastern Seismic Zone: This zone is affected by subduction of the Indian Plate under the Burmese Plate, covering Assam, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Tripura in Seismic Zone V.
- Western and Central India: The Kutch and Saurashtra regions in Gujarat lie along the Kathiawar Fault, making them vulnerable to intraplate earthquakes, classified under Seismic Zone IV.
For example: The 2001 Bhuj earthquake caused over 20,000 deaths and massive destruction, highlighting the risks of poor building compliance in seismically active zones.
- Peninsular India’s Stable Cratonic Regions: While geologically stable, regions like Maharashtra (Latur), Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu experience intraplate seismic activity due to ancient faults reactivating.
For example: The 1993 Latur earthquake, despite occurring in a low-risk zone, resulted in over 9,000 deaths, proving that even stable regions need preparedness.
Challenges Associated with Disaster Preparedness
- Weak Building Code Enforcement: Many structures do not adhere to the National Building Code (NBC) 2016, making urban areas vulnerable to collapse during major earthquakes.
For example: The 2011 Sikkim earthquake caused significant damage to poorly built structures, despite occurring in a region with known seismic risks.
- Rapid Urbanization Without Planning: Unregulated construction in seismic zones increases disaster risks, especially in Delhi, where high-rise buildings violate safety norms.
For example: The 1991 Uttarkashi earthquake destroyed thousands of homes, many of which were built with poor structural integrity in high-risk areas.
- Limited Early Warning Systems: India lacks an efficient earthquake early warning system comparable to Japan or the U.S., reducing the time available for evacuation.
For example: The 2015 Nepal earthquake saw thousands killed in Bihar, highlighting the need for better regional seismic monitoring and warning systems.
- Vulnerability of Critical Infrastructure: Dams, bridges, nuclear plants, and power stations in seismic zones face high risks, with Narora nuclear plant (Zone IV) needing urgent retrofitting.
- Inadequate Public Awareness and Drills: Lack of community preparedness programs, mock drills, and safety training means people do not know how to react during tremors.
For example: During the 2017 Tripura earthquake, panic led to stampedes and injuries, showing the importance of public education on earthquake response.
Measures to Mitigate These Challenges
- Strict Enforcement of Building Codes: Ensure mandatory compliance with the National Building Code (NBC) 2016 and retrofitting of old structures in seismic zones to withstand earthquakes.
- Implementation of Early Warning Systems: Establish advanced seismic monitoring networks and deploy earthquake early warning systems like those in Japan and Mexico for timely evacuation.
For example: The DMRC (Delhi Metro Rail Corporation) has an earthquake warning system in place called the EqWS (Earthquake Warning System), installed since June 2015.
- Seismic-Resilient Infrastructure Planning: Design critical infrastructure like bridges, dams, and nuclear plants with base isolation technology and shock-absorbing materials to minimize damage.
For example: The Kolkata Metro East-West Corridor was built with earthquake-resistant tunneling methods, ensuring safety in seismic-prone areas.
- Public Awareness and Community Preparedness: Conduct regular earthquake drills, safety training in schools and workplaces, and introduce earthquake education in disaster-prone areas.
- Strengthening Emergency Response and Healthcare: Improve NDRF capabilities, train local disaster response teams, and equip hospitals with seismic-resistant infrastructure and trauma care units.
Strengthening early warning systems, enforcing seismic-resistant infrastructure, and fostering community awareness are crucial for mitigating earthquake risks. Integrating advanced technology, improving disaster response mechanisms, and promoting adaptive urban planning will ensure a safer, disaster-resilient India. A proactive, multi-stakeholder approach is the key to minimizing devastation and safeguarding lives.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


Latest Comments