Important Maratha Rulers played a crucial role in India's history. Learn about the Important Maratha Rulers, their achievements, and impact on politics and warfare.

Important Rulers of the Maratha Empire played a crucial role in making the Marathas one of the most challenging forces in Indian history. Known for their military prowess, administrative efficiency, and strategic alliances, these rulers shaped the Maratha Empire, leading it to its peak in the 18th century. From Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj to the last Peshwa Baji Rao II, the Marathas stood as a strong opposition to the Mughal and British forces.
Read on to cover the Maratha Empire Kings List, the list of all Chhatrapati of Maratha Empire, and the list of Peshwa of Maratha, while also explaining the difference between the Maratha Chhatrapati vs Peshwa.
The Maratha Empire was established in 1674 by Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj. Originating from the Deccan region, it grew into a powerful kingdom through warfare, diplomacy, and administrative reforms. By the mid-18th century, it had expanded across India, controlling major territories including Maharashtra, Gujarat, Punjab, and Tamil Nadu.
A unique aspect of Maratha rule was the distinction between Chhatrapati (sovereign ruler) and Peshwa (prime minister). Initially, the Chhatrapati held supreme power, but over time, the Peshwas became the real rulers of the empire.
| Maratha Empire Overview | |
| Aspect | Details |
| Founded By | Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj |
| Year of Establishment | 1674 |
| Capital Cities | Raigad, later shifted to Satara and Pune |
| Major Rulers | Chhatrapati Shivaji, Chhatrapati Shahu, Peshwa Baji Rao I, Peshwa Madhav Rao I |
| Prominent Battles | Battle of Palkhed (1728), Battle of Delhi (1737), Third Battle of Panipat (1761), Anglo-Maratha Wars (1775-1818) |
| Administration System | Chhatrapati as the supreme ruler, Peshwa as the Prime Minister, Ashtapradhan (Council of Eight Ministers) |
| Military Strength | Guerrilla warfare, cavalry dominance, naval fleet established by Shivaji |
| Territorial Expansion | Covered most of present-day Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and parts of North India |
| Economic System | Revenue collection through Chauth and Sardeshmukhi, efficient trade policies |
| Decline | Began with the defeat in the Third Battle of Panipat (1761), worsened due to internal conflicts and British intervention |
| Final Collapse | 1818, after the Third Anglo-Maratha War against the British |
The Maratha Empire was a powerful Indian dynasty that ruled from the 17th to 19th century. It was founded by Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj in 1674, who laid the foundation of Swarajya (self-rule) and a strong military administration. The Marathas emerged as a dominant force in India, successfully challenging the Mughal Empire and later resisting British expansion.
During its peak in the 18th century, the Maratha Empire controlled large parts of India, stretching from Tamil Nadu in the south to Punjab in the north. The empire was known for its well-organized administrative system, guerrilla warfare tactics, and naval strength.
By the early 19th century, the British East India Company defeated the Marathas in the Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817-1818), marking the end of Maratha rule.
The Maratha Empire played a crucial role in Indian history, emerging as a dominant power after the decline of the Mughal Empire. The Marathas, known for their guerrilla warfare and administrative reforms, expanded their influence across India. Below is a detailed list of the most significant rulers of the Maratha Empire and their contributions:
The list of all Chhatrapati of Maratha Empire includes rulers who carried the legacy of Shivaji Maharaj and led the empire in various capacities.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj was the founder of the Maratha Empire. He established a strong naval force, introduced a well-organized administrative system, and implemented the concept of Swarajya (self-rule). His guerrilla warfare tactics played a vital role in resisting Mughal expansion in the Deccan.

Sambhaji, the son of Shivaji Maharaj, succeeded him and continued the fight against the Mughals, particularly Aurangzeb. He was known for his fierce resistance against the Mughal forces but was captured and executed by Aurangzeb in 1689.

After Sambhaji’s execution, Rajaram Maharaj took over the leadership and shifted the Maratha capital to Gingee Fort in Tamil Nadu. He played a crucial role in continuing the struggle against the Mughals.

Tarabai, the wife of Rajaram Maharaj, became the regent of her minor son, Shivaji II. She was an intelligent administrator and led the Maratha resistance against the Mughals after Rajaram’s death.

Shahu Maharaj was released by the Mughals in 1707 and emerged as the ruler of the Marathas. His reign marked the rise of Peshwas (prime ministers), who played a key role in expanding the Maratha Empire across India.

The list of Peshwa of Maratha includes Prime Ministers (Peshwas) who controlled the empire’s administration and military.
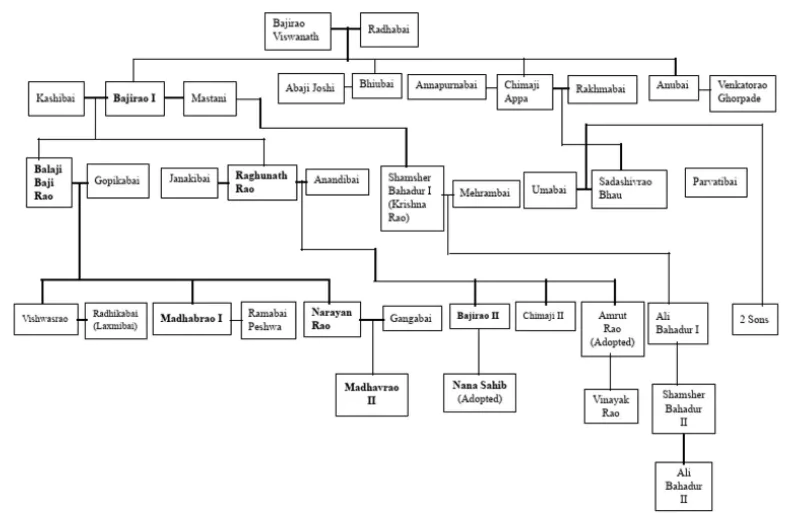
Balaji Vishwanath was the first powerful Peshwa of the Marathas. He played a crucial role in stabilizing the empire and negotiating peace with the Mughals.

Baji Rao, I was a brilliant military strategist and expanded the Maratha Empire to North India. His conquests included Malwa, Gujarat, and Bundelkhand.

Also known as Nana Saheb, he continued expanding the Maratha Empire but faced a major defeat in the Third Battle of Panipat (1761) against Ahmad Shah Abdali.

After the defeat at Panipat, Madhav Rao I worked to restore the Maratha Empire’s strength. His administration brought stability and economic prosperity.

Mahadji Shinde, a powerful Maratha leader, played a crucial role in restoring Maratha power in North India. He was instrumental in defeating the British in early conflicts.

Nana Phadnavis was a key administrator during the late 18th century, effectively handling Maratha affairs amidst British expansion in India.

Baji Rao II was the last Peshwa of the Maratha Empire. His defeat in the Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817–1818) led to the end of the Maratha rule and the establishment of British dominance in India.

The Maratha Chhatrapati vs Peshwa debate revolves around the division of power within the Maratha Empire. While the Chhatrapati was the sovereign ruler, the Peshwa held significant administrative and military control. Over time, the Peshwas became the de facto rulers, reducing the Chhatrapati’s influence.
Here is a detailed comparison table for the Difference between Maratha Chhatrapati and Peshwa:
| Maratha Chhatrapati vs Peshwa | ||
| Aspect | Chhatrapati | Peshwa |
| Meaning | The supreme ruler of the Maratha Empire | The Prime Minister of the empire, who later became the de facto ruler |
| Founder | Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj (1674) | Balaji Vishwanath (1713) |
| Position | Nominal head and sovereign of the Maratha state | Executive head of administration |
| Authority | Had supreme authority initially, but later became a symbolic figure | Started as a subordinate to Chhatrapati but eventually held real power |
| Appointment | Hereditary; passed down within the Bhosale dynasty | Initially appointed by the Chhatrapati, but later became hereditary under the Bhat family |
| Role | Guardian of Hindavi Swarajya, military leader, and supreme ruler | Responsible for military campaigns, governance, taxation, and administration |
| Political Power | Held complete control during Shivaji’s reign but later became a ceremonial ruler | Became the real decision-maker, controlling the empire’s military, economy, and expansion policies |
| Capital | Satara | Pune |
| Major Contributions |
|
|
| Famous Leaders |
|
|
| Decline | Became a ceremonial figure after the rise of the Peshwas | Lost power after defeat in the Third Anglo-Maratha War (1818) against the British |
| End of Rule | The Chhatrapati’s influence diminished under British rule | The Peshwa system was abolished in 1818 after the British victory |
| Legacy | Remembered as the founders and symbols of Maratha pride | Known for expanding and administering the Maratha Empire effectively |
The Marathas rose to power due to their military strategies, administrative reforms, and resistance against Mughal dominance. Several key factors contributed to their success:
The Maratha Empire dominated India in the 18th century. However, the empire faced challenges:
The Important Maratha Rulers shaped Indian history through their strategic military campaigns, administrative reforms, and governance. From Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj to Peshwa Baji Rao I, each leader played a crucial role in expanding and consolidating the empire. The legacy of the Maratha Empire continues to be remembered as a symbol of resilience and self-rule in Indian history.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Key rulers include Shivaji, Sambhaji, Rajaram, Shahu, and Baji Rao I, who expanded and strengthened the empire.
Shivaji founded the Maratha Empire, introduced military reforms, and established a strong administrative system.
The Maratha Confederacy dominated India in the 18th century, countering Mughal rule and influencing regional politics.
Key battles include the Battle of Pratapgad, Battle of Panipat (1761), and wars against the Mughals and British.
Baji Rao II was the last ruler before British annexation, marking the decline of Maratha power in India.
Internal conflicts, British expansion, and defeats in battles like Panipat III weakened and led to the empire’s downfall.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
