The Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB), in collaboration with IIT Bombay, has launched a pilot project to assess the feasibility of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology in Kerala.
- The project aims to explore how Electric Vehicles (EVs) can be integrated into the power grid to enhance grid stability and energy efficiency.
What is V2G technology?
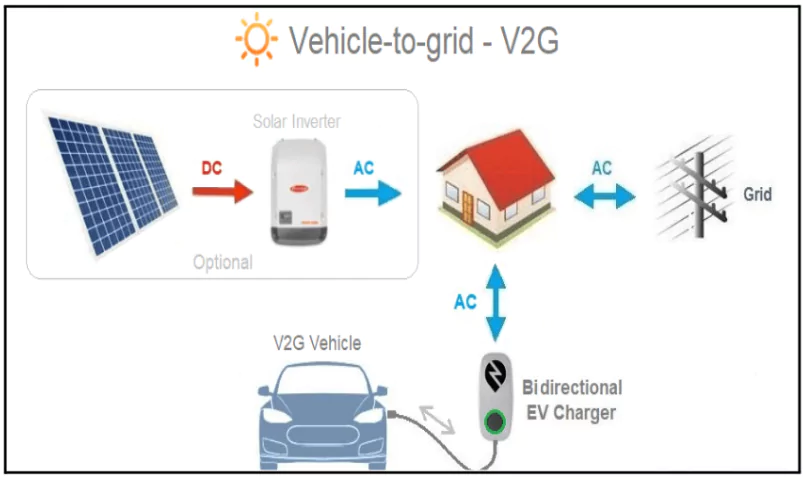
- It is an integrated system linking vehicles to grid and renewable energy sources enabling Bidirectional Power flow.
Features of V2G Technology
- Bidirectional Power Flow: V2G enables EV batteries to discharge electricity back to the grid when not in use, effectively acting as decentralized storage units.
- Smart Charging and Demand Response: Technologies such as Time-of-Use (ToU) electricity rates and smart charging can help optimize EV charging during off-peak hours and high renewable energy (RE) availability.
- Multiple Use Cases: Beyond V2G, other models include Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) and Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V), though V2G remains the most popular application globally.
Advantages of V2G technology
- Managing Load Impact: V2G and smart charging can help balance electricity demand, avoiding strain during peak hours and promoting grid reliability.
- Encouraging Solar-based Charging: Charging EVs during daytime solar peaks aligns with decarbonisation goals, reducing fossil fuel dependence and utilizing renewable energy efficiently.
- Energy Storage for the Future: EVs can serve as mobile energy storage units, storing excess solar power and discharging it when needed, enhancing the use of RE.
- Incentivizing Participation: With strategic compensation models, EV owners can be motivated to participate in grid services, improving economic viability and grid performance
Global Adoption of V2G
- Mature EV Markets: In countries like the U.S. and Europe, V2G pilot programs are well-established, often involving electric cars and buses.
- EV owners are financially incentivized to return electricity to the grid, especially during peak demand periods.
- Grid Stability and Emergency Support: In California and the Netherlands, EVs contribute to ancillary grid services and emergency power during crises, strengthening grid resilience and reliability.
- Standardization and Regulations: Efforts are underway worldwide to develop standards for bidirectional charging and supportive regulatory frameworks for V2G integration.
India’s Current Scenario
- Early-Stage Development: V2G technology in India is in its nascent phase, with pilot programs and studies underway.
- Current focus remains on EV charging infrastructure and managing its impact on the grid.
- Regulatory Challenges: India’s electricity market structure is not yet optimized for decentralised energy storage, making V2G implementation complex.
- A Central Electricity Authority (CEA) committee is drafting guidelines for reverse power flow from EVs to the grid.
![]() 18 Apr 2025
18 Apr 2025

