The Supreme Court of India, while hearing a bail plea in a Bitcoin-related case, remarked that trading in Bitcoin in India resembles a refined form of Hawala business, emphasizing the absence of a clear regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies.
Case Background
- Shailesh Babulal Bhatt, arrested on August 14, 2024, for alleged illegal Bitcoin trade, sought bail after the Gujarat High Court denied it on February 25, 2025.
Supreme Court (SC) Observations on Bitcoins
- 2020: In March 2020, the SC overturned the RBI’s 2018 circular banning banks from offering services for virtual currencies.
- SC ensured that cryptocurrencies could not be outrightly prohibited.
- 2025: Trading in Bitcoin, without regulation, parallels Hawala operations due to lack of transparency and oversight.
About Cryptocurrency
- A cryptocurrency is a virtual currency secured by cryptography.
- The cryptocurrency works on blockchain technology and is free from control of any central authority.
- It is designed to work as a medium of exchange wherein individual coin ownership records are stored in a computerized database.
- Bitcoin’s high value was highlighted (~₹82 lakh per Bitcoin), underscoring its economic significance.
Legality of Cryptocurrencies
- Bitcoin trading is not illegal after the Supreme Court quashed the RBI’s 2018 circular banning crypto-related transactions.
- Trading and investing in cryptocurrencies is allowed, but they are not authorised for use as currency.
- This legal ambiguity creates challenges for investors, traders, and even enforcement agencies.
- Cryptocurrency Taxation in India: The government’s taxation framework includes a 30% tax on gains and a 1% TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) on cryptocurrencies.
|
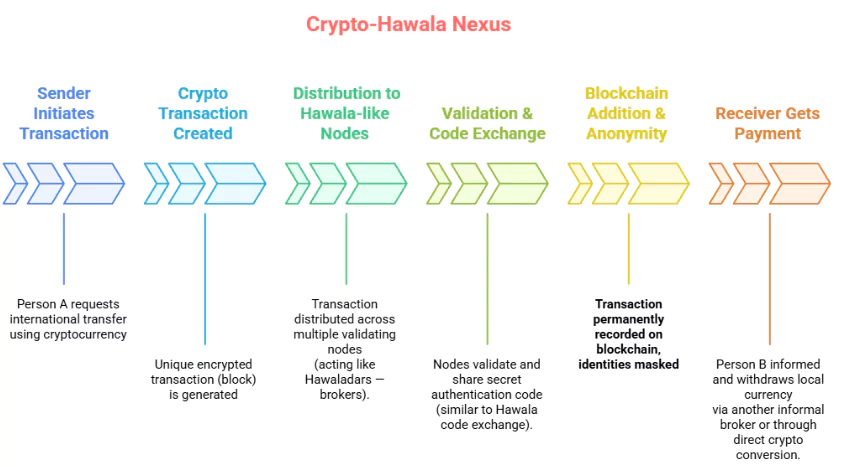
Reasons for Growing Nexus
- Anonymity and Pseudonymity: Crypto transactions often mask real identities, similar to unrecorded Hawala transactions.
- Cross-border Transferability: Cryptocurrencies can easily bypass capital controls and borders, much like Hawala networks.
- Lack of Regulatory Clarity: Absence of a clear legal framework encourages exploitation by illicit actors.
- High Liquidity and Value: High-value, portable assets make crypto an attractive medium for illegal fund transfers.
- Difficulty in Tracing: Decentralized, peer-to-peer transactions with no central authority make investigation difficult.
- Low Transaction Costs: Lower transaction fees and no requirement of formal banking infrastructure attract users seeking to avoid formal scrutiny.
Implications
- Threat to Financial Integrity: Facilitates money laundering, terror financing, and tax evasion undermining India’s financial system.
- Undermines AML (Anti-Money Laundering) Measures: Hampers enforcement of FATF (Financial Action Task Force) standards and India’s AML-CFT (Countering the Financing of Terrorism) obligations.
- Revenue Loss to the Exchequer: Evasion of taxes and duties via informal cross-border transactions.
- National Security Concerns: Potential funding channels for terror outfits and organized crime syndicates.
- Erosion of Monetary Control: Weakens RBI’s control over capital flows and monetary policy enforcement.
Way Forward
- Establish Clear Regulatory Framework: Expedite legislation or guidelines clarifying the legality, scope, and permissible use of cryptocurrencies.
- Reference global best practices (e.g., EU’s MiCA Regulation, FATF recommendations).
- Mandatory KYC and Reporting Norms: Enforce stringent Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), and Suspicious Transaction Reporting (STR) obligations on crypto exchanges and intermediaries.
- Set up Dedicated Crypto Regulatory Authority: A specialized body (or strengthening SEBI/RBI’s oversight) to regulate, supervise, and investigate cryptocurrency transactions.
- Enhance Enforcement Capability: Equip agencies like ED, FIU-India, and police with tools, training, and technology to trace crypto transactions and prosecute offenders.
- International Cooperation: Strengthen collaboration with global law enforcement and regulatory agencies to monitor cross-border crypto crimes.
- Public Awareness and Investor Education: Launch campaigns to educate citizens about risks of unregulated crypto trading and Hawala-like misuse.
- Encourage Legitimate Blockchain Innovation: Promote CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency) and regulated blockchain applications to provide safer alternatives.
Conclusion
The growing overlap between cryptocurrency and Hawala necessitates immediate, clear regulation to prevent misuse, protect financial stability, and uphold national security.
![]() 7 May 2025
7 May 2025

