‘Agni 5’ Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile
Context: India has successfully conducted the test-firing of the Agni-5 Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM) from the APJ Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha.
About ‘Agni 5’ Intermediate Range Ballistic Missile
- Range: Over 5,000 km (covers entire Asia, parts of Europe & Africa)
- Stages: Three-stage, solid-fuel missile
- Guidance: Equipped with advanced navigation and guidance systems with high accuracy using Ring Laser Gyro-based Inertial Navigation System (RINS) and Micro Inertial Navigation System (MINS).
- Launch Platform: Road- and rail-mobile launchers, enhancing survivability.
- Warhead Capacity: Can carry nuclear or conventional payloads (~1.5 tonnes).
- Technology: Incorporates composite material airframes, canister launch system for rapid deployment, and high mobility.
- A canisterised launch system is a missile launch mechanism in which the missile is stored, transported, and fired directly from a sealed canister mounted on a road-mobile or rail-mobile launcher.
- Significance:
- Strategic Deterrence: This is part of India’s effort to strengthen its strategic deterrence under the nuclear triad and reinforce its commitment to a credible minimum deterrent within the framework of the No First Use (NFU) policy.
- Second-Strike Capability: Enhances survivability and credibility of India’s nuclear doctrine.
- Indigenous Technology: Reflects DRDO’s self-reliance in missile technology under the IGMDP (Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme).
- Geopolitical Signal: Positions India among a select group of nations (US, Russia, China, UK, France) with comparable IRBM/ICBM capability.
Read More About What is MIRV Technology Tested in Latest Agni 5 Missile Test “Divyastra”
India, EAEU Sign Terms of Reference (ToR)
Context: India and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU), have signed the Terms of Reference (ToR) to start Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations.
- Trade turnover between India and EAEU stood at USD 69 billion in 2024, a 7% increase over 2023.
- India EAEU combined GDP – $6.5 trillion
About Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU)
- Nature: An international organization that promotes regional economic integration among former Soviet states.
- Establishment: Created through the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union, signed on 29 May 2014, and officially came into effect on 1 January 2015.
- Membership: Five countries are part of the Union—Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Armenia.
Institutional Structure
- Eurasian Economic Commission (EEC)
-
- Nature: Permanent regulatory body of the Union.
- Role: Oversees the functioning and development of the EAEU.
- Presidency: Rotates annually among member states, with one state serving as the Union’s chairman each year.
- Current President: Bakytzhan Sagintayev from Kazakhastan
- Court of the Eurasian Economic Union: Handles dispute resolution and interprets the legal framework of the EAEU.
- Customs Union of the EAEU: A customs union among member states.
About Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
- Definition: FTAs are arrangements between two or more countries that seek to reduce or eliminate trade barriers such as tariffs, quotas, and import/export restrictions.
- They grant preferential market access through tariff reductions and by easing non-tariff barriers.
India’s Major Trade Agreements
- India–ASEAN FTA
- India–South Korea Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- India-Japan CEPA
- India-Sri Lanka FTA
- India-UAE CEPA
Terms of Reference (ToR) refers to the formal framework or guiding document that lays down Scope of Negotiation, Objectives, TImeline etc.
“Anna-Chakra” Supply Chain
Context: Recently the Union Minister of State for Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution informed the Rajya Sabha about the implementation of the “Anna-Chakra” Supply Chain Optimisation Tool under the Public Distribution System (PDS).
About Anna Chakra
- Initiative: Launched by the Department of Food and Public Distribution with World Food Programme and Foundation for Innovation and Technology Transfer (FITT) at IIT-Delhi to optimize PDS logistics.
- Objective: Use advanced algorithms to identify optimal routes, ensuring faster, cost-effective, and eco-friendly movement of food grains.
- Scale: Covers 81 crore beneficiaries, involving 4.37 lakh Fair Price Shops and ~6,700 warehouses across the country.
- Impact: Route optimization in 30 states, saving about ₹250 crore annually.
- Integration: Linked with FOIS (Freight Operations Information System) portal of the Railways through the Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) and integrated into the PM Gati Shakti platform, mapping FPSs and warehouses.
- Benefits: Improves delivery speed, lowers fuel use, reduces logistics costs, and cuts carbon emissions.
About Public Distribution System (PDS)
- PDS is India’s food security mechanism designed to provide food grains at subsidised prices to tackle food scarcity.
- Legal Framework: Functions under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013, covering about two-thirds of the population (as per Census 2011).
- Nodal Ministry: Implemented by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
PM Gati Shakti
- A national master plan for multi-modal connectivity designed to boost infrastructure development and give India’s manufacturing sector a competitive edge.
- Objective: To ensure integrated planning and coordinated execution of infrastructure connectivity projects.
- Collaboration: Brings together 16 ministries and departments of the Government of India under a unified platform.
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
Context: Researchers have now identified that a gene in the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa shows bistable expression, offering new insights into what makes it so virulent.
About Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Nature: A gram-negative, aerobic, non-spore-forming bacterium found in soil and water; highly adaptable and resistant to antibiotics.
- Pathogenicity: Acts as an opportunistic pathogen, posing serious risks to burn victims, immunocompromised individuals, and patients with chronic lung diseases.
- Infections: Responsible for pneumonia, urinary tract infections, bloodstream infections, keratitis (eye infection), and post-surgical or burn wound infections.
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Many strains are multidrug-resistant (MDR), making treatment difficult; recognized by WHO as a priority pathogen for new antibiotic development.
- High-Risk Groups: Hospitalized patients, especially those on ventilators, catheters, or with open wounds.
- Transmission: Spread occurs via contaminated surfaces, water, soil, or direct contact—often through hands.
What is Bistable Expression ?
- Bistable expression refers to a biological or genetic system in which a cell can stably exist in two distinct states of gene expression (ON or OFF), rather than showing a gradual or intermediate response.
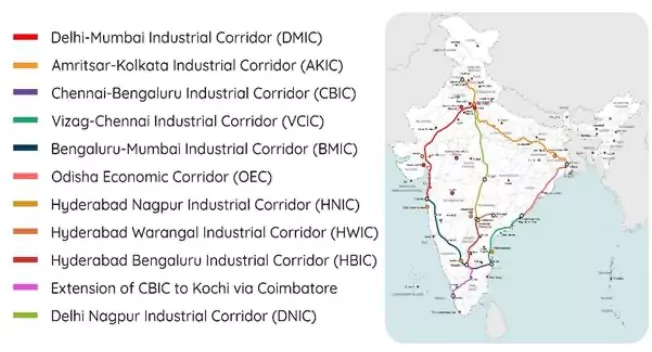
National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation (NICDC)
Context: National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation (NICDC) will support the Government of Haryana in developing an Integrated Manufacturing Cluster (IMC) at Hisar.’
- IMC Hisar, is being developed under the Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor
About National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation (NICDC)
- Origin: Began with the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC); DMICDC Ltd. was set up in 2008 under DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce & Industry as a Special Purpose Vehicle.
- Reconstitution: In 2016, DMIC Trust was expanded into NICDIT; later in 2020, DMICDC was renamed NICDC Ltd.under the National Industrial Corridor Programme.
- Mandate: Develop industrial corridors, including investment regions, industrial areas, nodes, clusters, economic zones, and townships, while supporting State Governments.
- Functions: Prepare master plans, feasibility studies, DPRs; To facilitate infrastructure projects through financial instruments, loans, resource mobilisation, and credit schemes.
About Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor (AKIC)
- Coverage: Spans across Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- Extent: Extends from Amritsar (Punjab) to Dankuni (West Bengal).
- Backbone: Anchored by the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC), which serves as the primary logistics and connectivity support for the corridor.
- Connectivity Advantage: Will leverage the Inland Water Transport (IWT) system along National Waterway-1, stretching from Allahabad to Haldia, to improve logistics and reduce transportation costs.
Launch Of New Disaster Management Tech Platforms
Context: Recently the Government of India launched three new key initiatives to strengthen disaster preparedness and response mechanisms.
Integrated Control Room for Emergency Response (ICR-ER)
- Functions: Provides near real-time information, strategic monitoring, situational awareness, and decision-making.
- Support System: Powered by National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM) 5.0, developed by ISRO-NRSC.
- Integration: Uses APIs for real-time forecasting data transmission.
- Utility: Aids in relief operations, damage assessment, and disaster risk analysis.
- Operation: Functions 24×7, coordinating responses with State and Central agencies.
NDEM Lite 2.0 App
- Nature: A lightweight version of the national emergency database app by ISRO-NRSC.
- Purpose: Assists ground-level disaster management officials in real-time operations.
- Features: Provides disaster-specific alerts to authorities for quicker responses.
Assam Flood Hazard Zonation Atlas
- Development: Jointly created by Assam State Disaster Management Authority (ASDMA) and ISRO-NRSC.
- Purpose: Serves as a planning tool for flood mitigation.
- Applications: Supports regulation of floodplain development, crop insurance, flood control planning, and relief center establishment.
About National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC)
- Institution: A key centre of ISRO, under the Department of Space (DoS).
- Mandate:
- Establish ground stations for satellite data reception and processing.
- Generate and disseminate satellite data products to users.
- Develop remote sensing applications for diverse fields, including disaster management support.
Nigeria
Context: The death toll from an attack by gunmen on a mosque and nearby homes in Katsina state, northwest Nigeria, has risen to at least 50.
About Nigeria
- Location: Situated on the western coast of Africa, often referred to as the “Giant of Africa.”
- located in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres of the Earth.
- Borders: Niger (North), Chad and Cameroon (East), Benin (West), and Gulf of Guinea (South).
- Population: Most populous country in Africa.
- Resources: Rich in Petroleum and natural gas.
- Nigeria is the Largest oil and gas producer in the continent.
- Geographical Features:
- Mountains: Mount Dimlang, Cameroonian Highlands.
- Highest Point: Chappal Waddi (also known as the “Mountain of Death).
- Major Rivers: Niger and Benue, with the Niger forming a delta draining into the Gulf of Guinea.
- Major Lakes: Lake Chad, a freshwater lake shared with Chad, Niger, and Cameroon.
- Climate: Varies from arid in the north to humid equatorial in the south.
- Vegetation: Includes rainforests, swamps, and savannah grasslands.
![]() 21 Aug 2025
21 Aug 2025

