| PWOnlyIAS Extra Edge:
About Heat Waves:
-
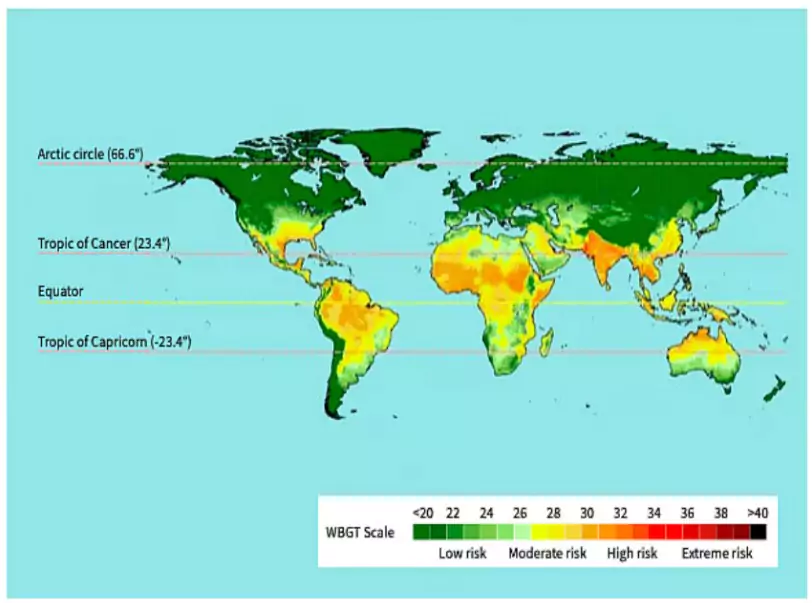
- Heatwaves: Heatwaves are extended periods of excessively high temperatures that can have severe implications on human health, environment, and the economy. India being a tropical country is particularly vulnerable to heatwave conditions.
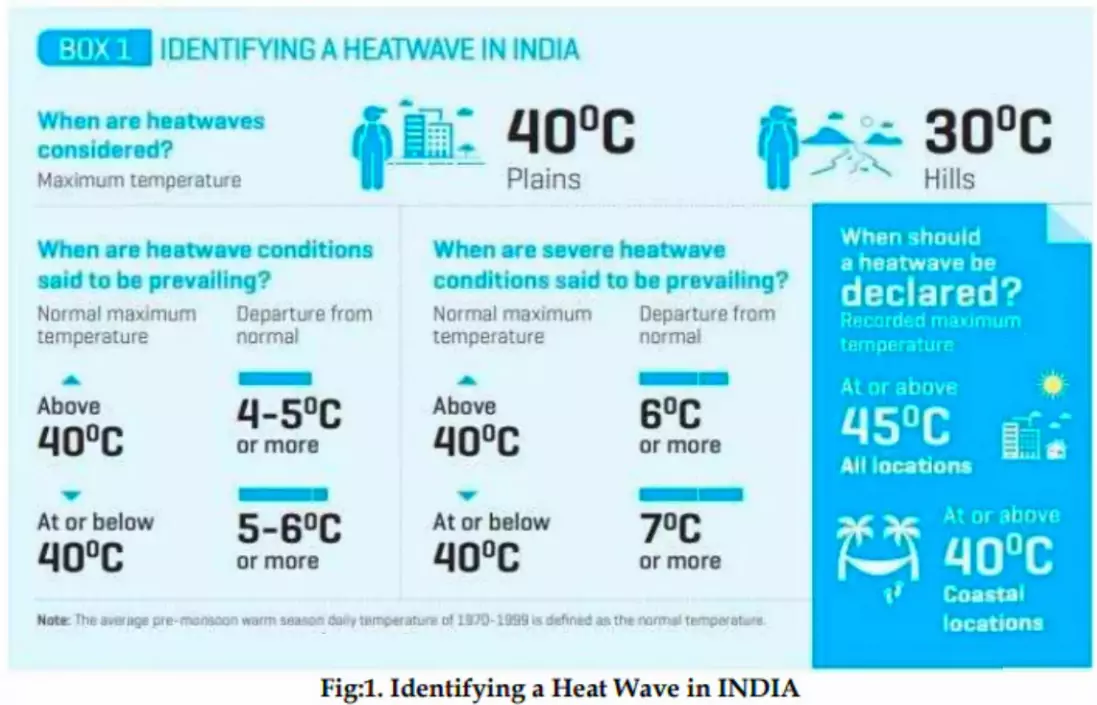
- Declaration of Heatwaves: According to IMD, the definition of a heatwave depends on the physiography of regions.
- The following criteria for Heat Wave declarations have been provided:
-
- Heat wave declaration is considered if the maximum temperature of a station reaches
- at least 40°C or more for Plains,
- 37°C or more for coastal stations and
- at least 30°C or more for Hilly regions.
- A heatwave’s severity is determined by its departure from normal temperature
- Normal Heatwave: When the departure from Normal is by 4.5-6.4 degrees Celsius and
- Severe Heatwave: When the departure from Normal is greater than 6.4 degrees Celsius
- Based on Actual Maximum Temperature (for plains only):
- Heat Wave: When actual maximum temperature 45°C
- Severe Heat Wave: When actual maximum temperature 47°C
- The IMD considers the criteria of “departure from normal temperature” and “actual maximum temperature”, only when at least two stations in a meteorological subdivision report such a high maximum or when at least one station has recorded a corresponding departure from the normal for at least two consecutive days.
Government Initiative Regarding Heat Waves:
- Climate Hazards and Vulnerability Atlas of India: The atlas provides a range of vulnerability with risks ranging from nil, low, moderate, high and very high categories for every Indian district with regards to major weather events.
- India’s Cooling Action Plan: It provides a long-term vision to address the cooling requirement of various sectors.
- Model Heat Action Plan: It has been released by the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) to provide hyperlocal warning systems, vulnerability mapping of cities, and climate-resilient housing policies.
About World Health Organization (WHO):
-
- It is a United Nations agency that works to promote health and safety globally.
- Establishment: The WHO was established on April 7, 1948. (World Health Day)
- The WHO began functioning in 1951 after merging with the Health Organisation of the League of Nations.
- What the WHO does:
-
- Sets standards: Sets standards for public health.
- Provides technical assistance: Provides technical assistance and support to countries.
- Helps prevent and respond to disease outbreaks: Helps to detect, prevent, and respond to health emergencies.
- Collaborates with partners: Works with governments, civil society organizations, and the private sector.
- Strengthens health systems: Works with countries to strengthen their primary health care.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Funding Structure of WHO:
-
- Assessed Contributions: Mandatory contributions from member states, calculated based on a country’s wealth and population.
- Covers less than 20% of WHO’s total budget.
- Voluntary Contributions: Contributions from member states, private organizations, philanthropic foundations, and other donors.
- Account for ~80% of WHO’s total budget.
About the World Meteorological Organization (WMO):
-
- A specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation in atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology, and geophysics.
- Establishment: Established in 1950, succeeding the International Meteorological Organization (founded in 1873).
- Became a UN specialized agency in 1951.
- Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Membership: WMO has 193 Member States and Territories, working collectively on global meteorological initiatives.
- India is a member of the WMO since 1950
- Key Publications: Releases the State of the Global Climate Report, Greenhouse Gas Bulletin, and Global Annual to Decadal Climate Update.
-
- Provides scientific input to the IPCC and global climate frameworks.
- Significance: WMO ensures the reliable exchange of weather, climate, and water information, aiding global sustainable development and safety.
|
![]() 23 Aug 2025
23 Aug 2025

 2024: Warmest year on record, global temperature +1.45 °C above pre-industrial levels.
2024: Warmest year on record, global temperature +1.45 °C above pre-industrial levels.