A recent study estimated that Space-Based Solar Power (SBSP) could meet up to 80% of Europe’s renewable energy needs by 2050.
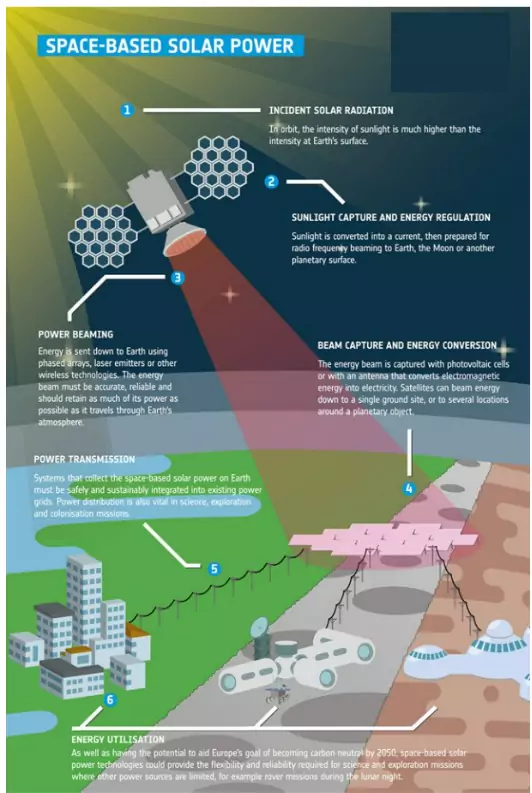
About Space-Based Solar Power (SBSP)
- Concept: SBSP proposes launching satellites in geostationary orbit equipped with solar panels that collect uninterrupted sunlight.
- Energy is transmitted to Earth as microwave beams, later converted into electricity.
Feasibility and Supporting Studies
- King’s College simulations tested NASA’s two models:
- Heliostat Swarm Design (continuous collection using reflectors).
- Planar Array Design (intermittent but scalable).
- Results showed near-continuous energy delivery, bypassing terrestrial solar limitations.
Potential Advantages
- Continuous Power Supply: Unlike ground solar, SBSP avoids intermittency caused by night or weather.
- Higher Efficiency: Solar radiation in space is stronger than on Earth’s surface.
- Zero-Carbon Dispatchable Energy: Can complement wind and terrestrial solar to stabilize renewable grids.
Challenges to SBSP
- Scale and Infrastructure: A single SBSP satellite may exceed 1 km in diameter, with ground stations ten times larger.
- Hundreds of rocket launches would be needed, compared to 40 for the International Space Station.
- Economic Viability: Despite falling launch costs, deployment and maintenance remain prohibitively expensive.
- Operational Risks: Issues include orbital congestion, transmission interruptions, and beaming variability, not yet addressed in models.
- Large-scale space infrastructure could also face security and debris risks.
Relevance for India
- India’s ambitious net-zero 2070 target makes SBSP worth exploring.
- ISRO’s low-cost launch capabilities + India’s solar leadership (International Solar Alliance) can make it a strategic future technology.
- Collaboration with global initiatives (e.g., UK, Japan, EU projects on SBSP) may fast-track feasibility.
Conclusion
Space-Based Solar Power, though technologically and economically challenging today, holds immense potential as a future clean energy source, aligning with India’s net-zero goals and global renewable energy leadership.
![]() 26 Aug 2025
26 Aug 2025


