Recently, the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) has proposed a National Global Capability Centres (GCC) Policy Framework to transform India into the global headquarters for innovation-led GCCs.
- The aim is to generate 20–25 million jobs and create an economic impact of $600 billion by 2030.
- The Union Budget 2025–26 proposed a National Framework for GCCs to guide states, especially in Tier-II cities, for establishing capability centres.
- This will complement CII’s upcoming Model State GCC Policy, ensuring centre–state alignment and doubling India’s GCC footprint by 2030.
About Global Capability Centres (GCCs)
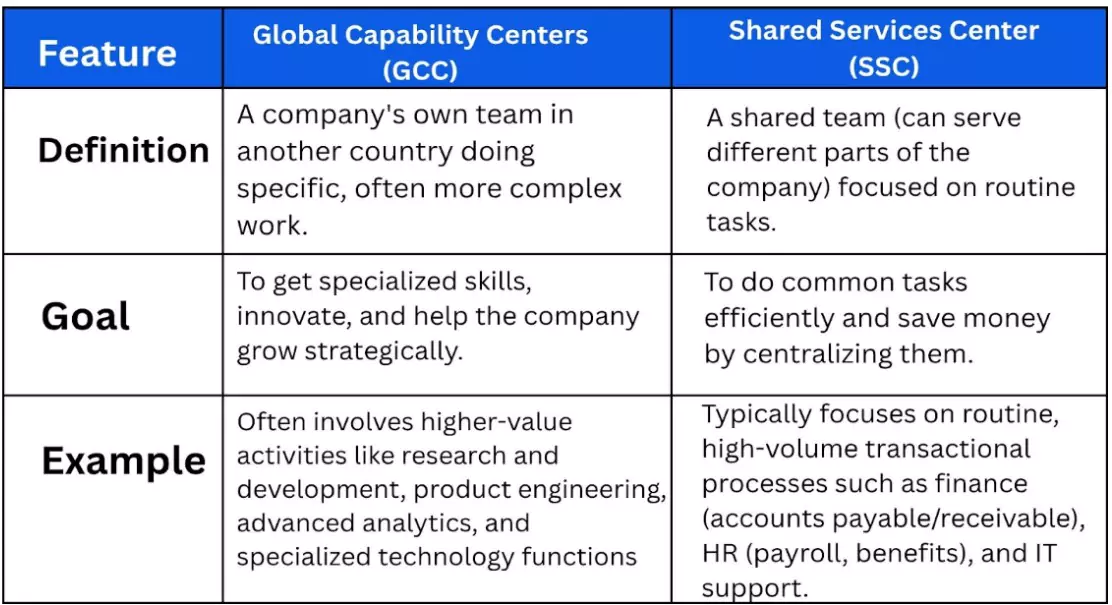
- Definition: A Global Capability Centre (GCC) is a strategic offshore or nearshore entity established by a multinational corporation (MNC) to build in-house capabilities across diverse business functions.
GCC and GIC (Global In-house Center)
- A GIC, or Global In-house Center, is essentially the same concept, with one key distinction– a GCC is the company’s global hub for multiple activities, whereas a GIC is the company’s own center located in another country.
|
- Ownership and Functions: They are wholly owned subsidiaries that manage critical operations such as IT development, finance, research & development (R&D), human resources, and analytics.
- Example: In 2024, Goldman Sachs expanded its Bengaluru GCC into a global innovation hub focusing on AI-driven financial analytics, underlining India’s transition from cost centre to value creator.
- Evolution of Role: Initially seen as cost-saving “back offices,” GCCs today are evolving into innovation and digital transformation hubs for global enterprises.
Key Elements of Proposed Framework
- The CII has suggested a comprehensive framework for GCCs to transform India from a back-office destination into a global hub for innovation, digital services, and high-value enterprise solutions.
- Aim: The proposed National GCC Policy aims to:
- Double India’s GCC footprint by 2030.
- Transform GCCs from cost-saving back offices into R&D powerhouses for global enterprises.
- Align growth with sustainability, innovation ecosystems, and balanced regional development.
- For example, Hyderabad and Bengaluru already house over 40% of India’s GCCs, but the framework wants to expand to Tier-II hubs like Vizag, Indore, and Coimbatore, ensuring inclusive urban growth.
- Pillars of the Policy: CII’s proposed framework rests on three pillars – national direction, enabling ecosystem, measurable outcomes – supported by four critical success factors – talent, infrastructure, regional inclusion, and innovation.
- Strategic Shift: The policy framework shifts the focus from cost-arbitrage to value-creation and innovation, positioning India as a premier global GCC hub competing with emerging destinations like the Philippines, Vietnam, and Poland.
Key Recommendations of CII Framework
- Digital Economic Zones: Create plug-and-play hubs with seamless digital connectivity and utilities.
- GCC Council: Set up an inter-ministerial body to ensure coordination between Centre and States.
 Industry–Academia Partnerships: Joint research centres, similar to IIT–Infosys partnerships, to skill students in AI and green tech.
Industry–Academia Partnerships: Joint research centres, similar to IIT–Infosys partnerships, to skill students in AI and green tech.- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Incentives: Tax breaks for green buildings and responsible AI adoption, aligned with India’s net-zero target (2070).
- “ESG incentives” refers to rewards, penalties, or policy mechanisms designed to encourage businesses, investors, or individuals to adopt sustainable practices aligned with ESG goals.
- Integration with National Schemes: Link GCC expansion with Smart Cities Mission (SCM) and PM Gati Shakti for holistic infrastructure growth.
- While SCM targets urban transformation, Gati Shakti ensures national connectivity, together advancing India’s vision of integrated, digital, and sustainable infrastructure
India’s GCC Journey
- 1990s – Cost-focused IT and back-office hubs
- 2000s – Multi-function delivery centres
- Post-2015 – Digital and innovation hubs
- Now (2020s) – Global enterprise hubs driving resilience and digital acceleration
|
Status of GCC in India
- Global Leadership: India now hosts 50% of the world’s GCCs, housing over 1,600 centres as of 2024 (NASSCOM 2024).
- Major firms like Microsoft, Amazon, JPMorgan, and Walmart have chosen India for their global R&D bases, cementing India’s leadership.
- Job Creation: GCCs directly employ 2.16 million professionals and support nearly 10.4 million indirect jobs (NASSCOM 2024).
- Economic Contribution: India’s GCCs contributed $68 billion in Gross Value Added (2023–24).
- Projections by experts suggest this will grow to $154–199 billion by 2030, rivaling IT exports.
Need for a National GCC Policy
- Employment Generation: A National GCC Policy could unlock 20–25 million jobs by 2030, including 4–5 million direct roles.
- NASSCOM 2024 Report: Tier-II hubs like Jaipur, Kochi, and Coimbatore will see 20% annual growth in GCC hiring, aiding urbanisation and youth employment.
- Regional Balance: Bengaluru and Hyderabad face infrastructure saturation, traffic congestion, and rising real-estate costs.
- A national policy can shift focus to Tier-II & III cities, ensuring balanced growth.
- Example: Vizag and Indore are being pitched as GCC-ready hubs under Smart Cities Mission.
- Boost to Exports and Global Competitiveness: Digital services exports already contributed USD 194 billion in FY24 (RBI).
- Strategic expansion of GCCs will help India compete with the Philippines and Poland, both emerging GCC destinations.
- Innovation & Start-up Integration: GCCs can evolve into R&D labs for global firms while linking with start-ups.
- Example: PepsiCo GCC Hyderabad’s agri-tech partnerships link farmers with AI-based crop solutions.
- Sustainability & ESG: India’s Net Zero 2070 target demands green campuses and ESG-led operations.
- GCC policy could integrate renewable energy usage, responsible AI, and circular economy practices.
Challenges & Constraints for GCC Growth in India
- Infrastructure Gaps: Tier-II cities lack world-class office spaces, metro connectivity, and reliable utilities.
- Example: Indore, despite being a Smart City, still struggles with power reliability, deterring large-scale GCC investments.
- Talent Shortage: India produces engineers in bulk, but AI, semiconductor design, and cybersecurity talent is scarce.
- NASSCOM 2023 Survey: 50% of GCCs report difficulty in hiring for emerging technologies.
- Policy Fragmentation: States like Karnataka and Telangana have robust IT/GCC policies, but others lag. This creates regional inequality in attracting GCCs.
- Global Competition: Philippines & Vietnam attract firms with lower wages.
- Poland & Ireland leverage EU benefits and fiscal incentives for R&D centres.
- ESG Compliance Pressure: With investors increasingly demanding sustainability disclosures, India risks losing green capital flows if GCCs fail to comply with ESG norms.
Global Policy & Partnership Examples Supporting GCC Growth
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Digital Economy Policy Framework: Encourages nations to harmonise digital infrastructure and governance.
- World Bank Global Skills Partnership: Trains youth for GCC roles with cross-border mobility.
- ASEAN Smart Cities Network: Demonstrates coordinated digital infrastructure planning across emerging economies.
Global GCC Best Practices & Lessons
- Singapore: “Smart Nation” initiative & corporate tax incentives created a hub for 1,600 MNC GCCs.
- Ireland (Dublin): Special International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) zones attracted major finance GCCs (Citibank, JPMorgan).
- Philippines: Leveraged English-speaking youth to dominate voice-based GCCs.
- Poland: EU-backed innovation incentives made Poland a hub for engineering GCCs.
- USA: Federal R&D tax credits drove innovation-led GCC growth.
|
Way Forward
- National GCC Council: A central coordinating body should be established under the Ministry of Commerce/IT. It will ensure policy uniformity, streamline approvals, and resolve inter-state issues, functioning on the lines of the GST Council.
- Skill Development in Tier-II Hubs: Specialised universities for AI, Data Science, and Green Technologies should be established in Tier-II cities. This will create regional talent pools, ease urban pressure, and ensure a future-ready workforce.
- Fiscal Incentives for ESG & R&D: Targeted tax breaks should be offered to GCCs investing in ESG-compliant campuses and R&D projects. A National Innovation Fund, co-financed by states, can support frontier technology initiatives.
- Global Branding of India: India should be showcased as the “World’s GCC Headquarters” at global platforms such as G20, Davos, and BRICS. This branding should highlight India’s skilled workforce, cost advantages, and innovation ecosystem.
- Model State Policies: Ready-to-use templates should be developed for states, allowing flexibility in adoption. These should cover incentives, infrastructure norms, and talent development modules, reducing uncertainty for investors.
Conclusion
The expansion of GCCs embodies constitutional values of justice, equality, and federal cooperation, while fostering innovation and sustainability. Guided by Ambedkar’s idea of constitutional morality, GCCs can anchor India’s inclusive growth and strengthen its role as the World’s GCC Headquarters.
Read More About: At FTA’s Heart, the Promise of Global Capacity Centres
![]() 16 Sep 2025
16 Sep 2025


 Industry–Academia Partnerships: Joint research centres, similar to IIT–Infosys partnerships, to skill students in AI and green tech.
Industry–Academia Partnerships: Joint research centres, similar to IIT–Infosys partnerships, to skill students in AI and green tech.