NITI Aayog’s “Roadmap for Job Creation in the AI Economy” outlines a national action plan to transform India into the AI workforce capital of the world by 2035.
About the Report
- Developed by: NITI Aayog’s Frontier Tech Hub, in collaboration with NASSCOM and BCG, with guidance from an Expert Council of industry leaders from IBM, Infosys, Tech Mahindra, LTIMindtree, Teleperformance, and others.
- It explores how Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming India’s tech services sector and proposes strategies to convert potential job losses into job creation opportunities.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
- It is the ability of machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence.
- It enables systems to learn from experience, adapt to new situations, and solve complex problems independently.
- AI uses datasets, algorithms, and large language models to analyse information, recognise patterns, and generate responses. Over time, these systems improve their performance, allowing them to reason, make decisions, and communicate in ways similar to humans.
|
AI Ecosystem in India at Present
- Economic Contribution: India’s domestic AI market is projected to more than triple to $17 billion by 2027, making it one of the fastest-growing AI economies globally
- AI could add $1.7 trillion to India’s economy by 2035.
- Employment: Over 6 million people are employed in the tech and AI ecosystem.
- AI in Startups: India has around 1.8 lakh startups, and nearly 89% of new startups launched last year used AI in their products or services.
- NASSCOM AI Adoption Index: India scores 2.45 out of 4, showing that 87% of enterprises are actively using AI solutions.
- Leading Sectors In Ai Adoption: Industrial and automotive, consumer goods and retail, banking, financial services and insurance, and healthcare.
- Together they contribute around 60 percent of AI’s total value.
AI’s Impact On Jobs
- Disruption Across Sectors: AI is reshaping India’s $245B technology sector by automating tasks and redefining roles.
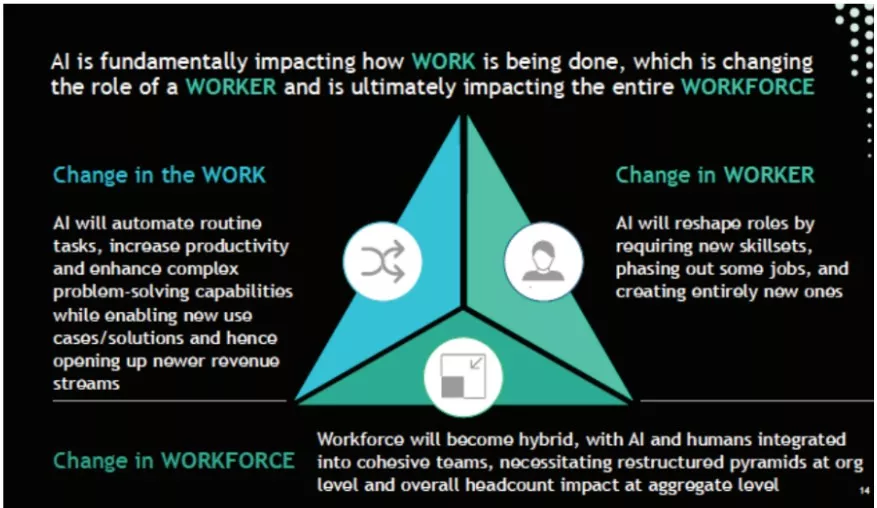 For Example: AI is already transforming the software development lifecycle, unlocking an overall productivity improvement of 10-20%. Evolution of work and workforce: AI transforms the work, worker, and workforce simultaneously by changing skills, structures, and workflows.
For Example: AI is already transforming the software development lifecycle, unlocking an overall productivity improvement of 10-20%. Evolution of work and workforce: AI transforms the work, worker, and workforce simultaneously by changing skills, structures, and workflows.-
- Organizations are becoming leaner with fewer layers and quicker releases, integrating AI-human teams for efficiency
- Crossroads of Job Security: By 2031, we could lose 1.5 million jobs or create up to 4 million new opportunities.
Ethical AI Specialists, Prompt Engineers, and Sentiment Analysts represent new employment categories.
Opportunities for India
- Productivity and Efficiency Gains: AI improves efficiency in software development, testing, and documentation by 10–20%.
- Generative AI automates routine coding and bug fixing, reducing time-to-market
- New sectors and markets: AI is expanding into healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing creating non-traditional tech jobs.
- AI-driven drug discovery and quantum computing integration are spurring job growth
- India’s demographic advantage: With 9 million tech professionals and the world’s largest youth pool, India has unmatched human capital.
-
- AI-driven skilling can convert this base into a global AI-ready workforce
- Rise of Global Capability Centres (GCCs): AI demand is attracting global R&D and innovation hubs to India.
- Over 70% of new Global Capability Centres (GCCs) list AI/ML as top hiring priorities.
- The country hosts 1,800+ Global Capability Centres, including more than 500 focused on AI.
- Boost to India’s services exports: AI-enabled voice and translation tools enhance India’s ability to serve global clients remotely.
-
- Use of tools like Meta’s SeamlessM4T and OpenAI Whisper is reducing language barriers.
Risks and Challenges
- Job Displacement Risk: Over 60% of formal jobs in India could be automated by 2030 if no interventions occur.
- Education Gaps: At the grassroots level, India’s computer science education is uneven. Computer science remains optional in Indian schools, limiting AI literacy.
- Unlike India, China and Russia made CS education mandatory from primary level
- Skilling: US graduates are skilled in specialised research-intensive courses, while the exposure of students to core AI courses in India is limited
- Weak Research Output: India’s contribution to AI innovation is low.
- For Example: AI patents dropped from 10% (2010) to <5% (2023). AI publications and citations trail behind the U.S. and China
- Critical Supply-Demand Gap For AI Talent: Supply for AI talent is now 50% of the current demand in India, and is expected to further lag in the next few years.
- Brain Drain of AI talent: India has negative net migration (-1.55/10,000) of AI professionals to countries offering better R&D incentives.
- For Example: Singapore and UAE now attract more Indian AI researchers than India retains
- Fragmented Policy Response: Multiple ministries run isolated AI skilling programs without coordination.
- For Example: Current initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), IndiaAI Mission, and academic reforms operate in silos.
Launch India AI Talent Mission
The NITI Aayog report calls for a nationally coordinated “India AI Talent Mission”
- Objective: To build a future-ready AI workforce that can both “Build AI” (create AI systems and tools) and “Use AI” (integrate AI into every sector of the economy).
- Aims to transform India’s 9 million-strong tech workforce into globally competitive, AI-augmented professional
- Vision and Scope: To position India as the global epicentre of AI talent by 2035 by empowering every Indian to Build AI and Use AI, while ensuring that AI-led growth is inclusive, innovative, and sustainable.
- Expected Impact:
- Job creation: Up to 4 million new AI-driven roles by 2031 across IT, CX, and allied sectors.
- Talent leadership: India emerges as the trusted global AI workforce and innovation partner by 2035.
- Global competitiveness: Prevents job displacement by embedding AI capabilities in education, research, and enterprise.
- Three core pillars: The mission’s scope includes three core pillars led by the India AI Talent Mission and two enabling pillars in collaboration with the IndiaAI Mission, creating a holistic national AI strategy
|
Way Forward
- Embed AI Across Education: Integrate AI literacy across school, university, and vocational systems.
- Expand AI+X programs, establish AI Centres of Excellence (CoEs), and increase AI PhD fellowships from 100 to 1,000 annually to build an academic AI pipeline
- AI+X program: It is an interdisciplinary educational approach that combines a core curriculum in artificial intelligence with a secondary, complementary field of study (the “X”)
- Build a National AI Skilling Engine: Create a reskilling and upskilling network for existing workforce through PMKVY and NAPS
- Introduce modular AI master’s and doctoral programs for mid-career professionals to transition into AI-centric roles
- Become a Global AI Talent Magnet: Retain domestic experts and attract global AI researchers and entrepreneurs.
- Launch an AI Talent Visa, provide startup relocation incentives, and offer research grants inspired by the UK’s Global Talent Visa and China’s Thousand Talents Plan
- Establish the India Open-Source AI Commons: Democratize access to high-quality datasets, models, and benchmarks for innovation.
- Create a national AI Commons Portal powered by partnerships with universities and ministries, with incentives for contributors
- Build a Federated National Compute & Innovation Grid: Provide affordable, high-performance computing (HPC) access to startups, students, and researchers.
- Implement a tiered access system under the IndiaAI Mission to consolidate fragmented compute resources and boost domestic R&D
Conclusion
The Roadmap for Job Creation in the AI Economy envisions transforming India’s demographic dividend into a global AI advantage through coordinated action in skilling, research, and innovation.
By turning disruption into opportunity, India can secure its position as the world’s AI workforce capital by 2035, driving inclusive and technology-led economic growth.
![]() 14 Oct 2025
14 Oct 2025

 For Example: AI is already transforming the software development lifecycle, unlocking an overall productivity improvement of 10-20%. Evolution of work and workforce: AI transforms the work, worker, and workforce simultaneously by changing skills, structures, and workflows.
For Example: AI is already transforming the software development lifecycle, unlocking an overall productivity improvement of 10-20%. Evolution of work and workforce: AI transforms the work, worker, and workforce simultaneously by changing skills, structures, and workflows.