Lachit Borphukan
Context: PM Modi and Home Minister Amit Shah honoured Lachit Borphukan on Lachit Diwas.
- Lachit Diwas is celebrated annually on 24th November to commemorate the birth anniversary of Lachit Borphukan
About Lachit Borphukan
- Lachit Borphukan was born on 24th November 1622 in Charaideo, Assam.
- Lachit Borphukan is revered in Assam as the commander who defeated the Mughal forces (led by Raja Ram Singh) in the Battle of Saraighat (1671).
- Military Leadership: Served as the commander of the Ahom armies during the Battle of Saraighat fought on the Brahmaputra River in Guwahati.
- Known for exceptional strategic skills and effective guerrilla warfare tactics, enabling smaller Ahom forces to outperform a much larger Mughal army.
- Position in the Ahom Administration: Appointed as one of the five Borphukans by King Charadhwaj Singha.
- Borphukans held combined administrative, judicial, and military authority in the Ahom kingdom.
- They effectively acted as viceroys for the Ahom King in the western part of the kingdom.
- Final Years: He passed away in 1672, a year after the victory at Saraighat, due to a prolonged illness.
About the Ahom Kingdom
- The Ahom kingdom was established by Sukaphaa, a Shan prince from the Mong Mao region (Myanmar), who entered present-day Assam in 1228 CE.
- The kingdom ruled large parts of present-day Assam for nearly 600 years (13th–19th century).
- Political and Social Structure: It was a prosperous, multi-ethnic kingdom centred on the fertile Brahmaputra valley, sustained by extensive rice cultivation.
- Known for strong administrative systems and resistance to external invasions.
- Conflicts with the Mughals: Fought multiple clashes with the Mughal Empire between 1615–1682, from Jahangir to Aurangzeb.
- The Battle of Saraighat remains the most defining victory against Mughal expansion in the Northeast.
Uranium (U-238) Contamination
Context: A new study has detected uranium (U-238) in breastmilk samples across Bihar, raising concerns about infant exposure despite levels remaining below global safety thresholds.
Key Findings on Uranium Contamination
- A study of 40 lactating mothers across Bihar detected uranium in 100% of breastmilk samples, with highest individual values in Katihar and highest district average in Khagaria.
- All breastmilk samples contained uranium; 70% of infants showed Hazard Quotient (HQ) > 1, indicating potential non-carcinogenic risk.
- Despite measurable presence, researchers note that most uranium absorbed by mothers is excreted in urine, not concentrated in breastmilk.
- Experts emphasise that breastfeeding should continue, unless clinically contraindicated, given its overriding nutritional and immunological benefits.
About Uranium contamination
- Uranium contamination refers to the presence of excess uranium in soil, groundwater, surface water, or food sources, usually due to natural geological processes or human activities.
- It becomes a public health and environmental concern when uranium levels exceed safe limits.
- WHO prescribes a provisional limit of 30 µg/L for uranium in drinking water; some countries adopt stricter norms such as 10 µg/L (Germany).
- Measured breastmilk concentrations in the study ranged 0–5.25 µg/L, below WHO’s water guideline.
- Sources Of Contamination
- Uranium occurs naturally in granite and rock formations and reaches groundwater through weathering.
- Anthropogenic sources include mining, coal combustion, nuclear industry emissions, and phosphate fertilizers.
- India reports contamination in 151 districts across 18 States, with 1.7% of Bihar’s groundwater affected.
Health Impact of Uranium Exposure
- Infants face higher vulnerability due to limited detoxification capacity.
- Potential impacts include kidney development impairment, neurodevelopmental delay, and cognitive deficits such as reduced IQ with prolonged exposure.
Vikram-I Orbital Rocket
Context: Recently PM Narendra Modi inaugurated Skyroot’s new Infinity Campus and unveiled the Vikram-I orbital rocket marking a milestone for India’s private space sector.
About Vikram-I Orbital Rocket
- Vikram-I is Skyroot Aerospace’s first orbital-class launch vehicle, designed to place small satellites into low-Earth orbit (LEO) efficiently and rapidly.
- A Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is a near-Earth orbit ranging roughly from 160 km to 1,000 km altitude, where most satellites including the International Space Station (ISS) are placed.
- LEO is preferred due to lower launch energy requirements and optimal conditions for Earth observation.
- Developed By: Skyroot Aerospace, Hyderabad
- Private body founded by IIT alumni and former ISRO scientists.
- Key Features
- Multi-Stage Lightweight Design: All-carbon-fibre body enabling high strength-to-weight performance.
- Multi-stage solid-fuel configuration for simpler, robust and low-maintenance operations
- Capability: Can place ~300 kg payloads into LEO and is capable of deploying multiple satellites in a single mission
- Rapid Launch Readiness: Solid propulsion enables quick assembly and launch within 24 hours.
- Requires minimal launch infrastructure, suitable for flexible launch locations
Significance
- Boost to India’s Private Space Ecosystem: Strengthens India’s emerging small-satellite launch market.
- Demonstrates success of space sector reforms enabling private manufacturing and innovation
- Industrial Expansion: Supported by Skyroot’s new 200,000 sq ft Infinity Campus, capable of producing one orbital rocket per month
- Strategic Value: Enhances indigenous access to space, reducing dependence on foreign launchers and supporting commercial, scientific, and defence payloads
Orbital and Suborbital Rockets
- Orbital Rocket : It places a payload into Earth’s orbit, requiring very high velocity (≈7.8 km/s) so the object continuously circles the planet.
- PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle) is ISRO’s most reliable orbital rocket,
- Sub-Orbital Rocket : A sub-orbital rocket reaches space but does not achieve orbital velocity, causing it to return to Earth without completing an orbit.
- RH-200 (Rohini Sounding Rocket) of ISRO.
- Purpose: Orbital rockets are used for satellite deployment and long-duration missions, while sub-orbital rockets are mainly used for technology testing, microgravity experiments, or short spaceflights.
National Gopal Ratna Awards 2025
Context: Recently the National Gopal Ratna Awards 2025 were Conferred on National Milk Day, along with major initiatives to strengthen India’s dairy sector.
About the National Gopal Ratna Awards (NGRA)
- One of the highest national recognitions in the livestock and dairy sector, awarded annually on National Milk Day.
- Aims to promote excellence in breed improvement, milk production, and scientific dairy practices.
- Launched under the Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) in 2021 to advance indigenous cattle and buffalo development.
- Objectives
- Recognize and reward dairy farmers, cooperatives, and stakeholders for outstanding contributions.
- Promote scientific management of native breeds and sustainable dairy practices.
- Encourage innovation in breeding, feed management, and production efficiency.
- Strengthen India’s leadership as the world’s largest milk producer.
- Awards and Benefits: Certificate of Merit and Memento for all winners.
- Categories of the Award
- Best Dairy Farmer rearing Indigenous Cattle/Buffalo Breeds
- Best Artificial Insemination Technician
- Best Dairy Cooperative Society (DCS) / Milk Producer Company / Dairy Farmer Producer Organization
- Special Category Awards: Special Award in each of the above three categories for winners from the North Eastern Region (NER) / Himalayan States.
- Other Initiatives to be Launched
- Breed Multiplication Farms to enhance high-quality livestock production.
- Guidelines for Minimum Veterinary Infrastructure for uniform national standards.
- Basic Animal Husbandry Statistics 2025 for data-driven policy planning.
- Flagging off 20 NPDD-assisted milk tankers to strengthen dairy logistics and supply chains.
About National Milk Day
- Introduction: National Milk Day is observed every year on 26 November to commemorate the birth anniversary of Dr. Verghese Kurien, the “Father of the White Revolution.”
- Significance: The day honours India’s millions of dairy farmers whose efforts ensure national food security and drive the country’s leadership in global milk production.
- India’s Dairy Sector: India contributes nearly one-fourth of global milk output, with the sector growing 70% in the last 11 years (since 2014) employing over 8 crore farmers and enabling inclusive, women-led rural growth.
Exercise AJEYA WARRIOR-25
Context: India and the United Kingdom have begun the eighth edition of Exercise AJEYA WARRIOR-25 in Rajasthan to enhance joint counter-terror operational capabilities.
About AJEYA WARRIOR-2025
- AJEYA WARRIOR is a biennial India-UK joint military exercise aimed at strengthening professional cooperation and improving interoperability between the two armies.
- Venue: Foreign Training Node, Mahajan Field Firing Ranges, Rajasthan.
- Focus Area
-
- The exercise is held under a United Nations mandate and focuses on counter-terrorism operations in semi-urban environments.
- It includes joint mission planning at brigade level, integrated tactical drills, simulation-based scenarios, and company-level field exercises.
- The exercise features equal participation of 240 personnel from both armies, with the Indian Army represented by the Sikh Regiment.
- Significance: The exercise strengthens operational coordination, facilitates sharing of best practices, and reinforces India-UK defence cooperation to support regional stability and global missions.
Biomass Pellet Plant
Context: A new biomass pellet plant was inaugurated in Rewari, Haryana.
About Biomass Pellets
- Biomass pellets are compressed biofuel units made from agricultural residues, designed to replace coal in thermal power plants for cleaner combustion.
- Produced Using: Torrefied or processed crop residues such as paddy straw, mustard straw, cotton stalks and organic waste.
- Feature: The compression process creates uniform, high-density fuel that is an efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels for heating, cooking, and power generation
- Significance
-
- Enables co-firing with coal, reducing carbon emissions and air pollution
- Creates additional income streams for farmers through residue procurement
- Generates rural employment and supports circular bioeconomy
- Helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels and supports India’s net-zero goals
Government Initiatives to Promote Waste-to-Energy
- Mandatory Biomass Co-Firing Policy: All coal-based thermal power plants must co-fire 5% biomass/MSW (municipal solid waste) charcoal, while NCR plants must use 7%.
- At least 50% of biomass in NCR plants must be sourced from local paddy residue, directly reducing stubble burning.
- Strengthening Waste Supply Chains: Government expanding source segregation systems, regulatory frameworks, and MSW-charcoal processing capacity.
- Policy push aims to build a robust waste-to-energy ecosystem, addressing challenges of wet and unsegregated waste.
Mahabharata Anubhav Kendra
Context: Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated ‘Panchjanya’ and visited the Mahabharata Anubhav Kendra in Kurukshetra, Haryana.
About ‘Panchjanya’
- ‘Panchjanya’ is a monument dedicated to the sacred conch of Lord Krishna, symbolising divine power and righteousness in the Mahabharata.
- Significance
-
- Represents the spiritual and cultural legacy associated with Kurukshetra, the land of the Bhagavad Gita.
- Reinforces the historical importance of Krishna’s call to duty and dharma.
- Adds a major cultural landmark to Kurukshetra, strengthening heritage tourism and pilgrim routes in Haryana.
About Mahabharata Anubhav Kendra
- The Mahabharata Anubhav Kendra is an immersive experiential centre created to bring alive key episodes of the Mahabharata for visitors through modern storytelling.
- Location: Kurukshetra, the traditional battleground of the Mahabharata and the place where the Bhagavad Gita was revealed.
- Features: Digital installations, thematic galleries, interactive displays, and artistic recreations of major events from the Mahabharata.
- Designed to highlight the timeless philosophical, cultural, and moral teachings of the Mahabharata.
- Significance: Serves as an educational and cultural hub for students, researchers, and pilgrims.
Fujiwhara Interaction
Context: Weather models indicate the possibility of two cyclonic storms forming in the Bay of Bengal, with a rare chance of a Fujiwhara-type interaction.
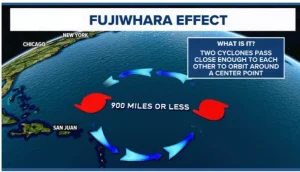
About Fujiwhara Effect
- Definition: The Fujiwhara Effect, also known as the Fujiwhara interaction or binary interaction, is a natural atmospheric phenomenon that occurs when two nearby cyclones or hurricanes begin to interact with each other in mid-to-upper atmospheric layers.
- Mutual Orbiting: During the Fujiwhara interaction, the centers of the two cyclones start rotating around a common point between them. This orbiting takes place in a counterclockwise direction.
- Determining Factor: The location of this central rotation point depends on the intensity and relative mass of the cyclonic vortices.
- Discovery: It was first identified and described in 1921 by Japanese meteorologist Dr. Sakuhei Fujiwhara, after whom the phenomenon is named.
- Occurrences: The interaction typically occurs when two cyclones come within ~1,400 km of each other (distance varies with size and intensity).
- Possible Outcomes:
-
- Intensification: The interaction may also enhance the development of a more powerful cyclone.
- Merger: A stronger cyclone may absorb the weaker one.
- Repulsion: In some cases, the systems may move apart after interaction.
- Track Alteration: Their movement may become erratic, complicating forecasts.
- The Fujiwhara Effect can alter or divert the original paths of one or both cyclones.
![]() 26 Nov 2025
26 Nov 2025


