The NITI Aayog’s Frontier Tech Hub, in partnership with International Business Machines-IBM, has released a national roadmap to transform India into one of the world’s top-three quantum economies by 2047
- Quantum technologies stand at the threshold of becoming one of the most transformative forces of our time.
- Impact: Their impact will cut across sectors, redefining healthcare, finance, logistics, materials, energy and national security.
- Significance: The nations that act decisively today will not only command the next generation of computing, communication, and sensing capabilities, but will also shape the very architecture of global innovation and trust.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Vision for India as a Leading Quantum Economy by 2035: India aims to emerge as one of the world’s foremost quantum-powered economies with strong capabilities across computing, communication, sensing, and materials.
- Development of a Globally Competitive Quantum Industry: The roadmap targets the creation of at least 10 globally competitive Indian quantum startups achieving global scale and significant commercial impact.
- Leadership in Quantum Software and Services: India seeks to dominate the global quantum software, algorithm development, and cloud-based quantum services market.
- Clear Two-Phase Milestone Plan (2025–30 and 2030–35): The roadmap provides sequential goals for capacity building, testbeds, PQC pilots, industry adoption, export readiness, and global leadership.
- Building a Self-Reliant Quantum Supply Chain: The mission outlines the creation of a robust domestic ecosystem covering quantum hardware, processors, materials, cryogenics, fabrication, and full software stacks.
- Large-Scale Deployment Across Strategic and National Sectors: Quantum technologies are envisioned to be operational across defence, intelligence, healthcare, finance, logistics, materials, climate, and energy systems by 2035.
- Rapid Workforce Expansion and Talent Development: A massive increase in quantum-skilled scientists, engineers, and professionals is targeted to support ecosystem growth.
- Focus on Standards, Regulation, Global Partnerships and PQC Deployment: India aims to lead global quantum standards, strengthen quantum diplomacy, and transition national systems to quantum-resilient cryptography.
About Quantum Technologies
- They are advanced technologies that harness quantum mechanical principles such as superposition, entanglement, tunnelling, and quantisation to achieve capabilities that classical systems cannot.
- They operate using quantum states of particles (atoms, photons, electrons), enabling exponential computational speed-ups, ultra-secure communication, and high-precision sensing.
Current State of Quantum Computing
- NISQ Era: Quantum computing is still in its early stages, often referred to as the NISQ (Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum) era.
- Advancements in Quantum Computing: Current quantum computers have limited qubits (typically 50-100) and are prone to errors.
- Quantum Supremacy: In 2019, Google claimed to achieve quantum supremacy by performing a calculation in 200 seconds that would take a classical supercomputer 10,000 years.
- While this milestone is debated, it highlights the potential of quantum computing.
- Microsoft’s Majorana 1 Quantum Chip
- Resilient Qubits: Uses a novel approach for greater stability.
- Improved Scalability: Advances over existing quantum platforms.
- Lower Error Rates: Enhances error correction and reduces faults.
- Google’s Willow Chip: Willow enables multiple physical qubits to work together to store a single unit of quantum information, creating a built-in self-checking mechanism that detects and corrects errors in real time.
|
Key Principles Of Quantum Mechanics
- Superposition: In quantum computing, a qubit can exist in a superposition of both 0 and 1 simultaneously.
- This means a qubit can represent multiple states at once, enabling quantum computers to process vast amounts of information in parallel.
- Entanglement: Entanglement is a phenomenon where two or more qubits become interconnected, such that the state of one qubit is directly related to the state of another, no matter how far apart they are.
- Quantum Interference: Quantum computers use interference to amplify correct solutions and cancel out incorrect ones. By carefully manipulating qubits, quantum algorithms can guide the system toward the most probable correct answer.

Four Vectors of Quantum Technologies
- Quantum Computing: Uses qubits to perform computations exponentially faster for certain tasks like simulation, optimisation, machine learning, and breaking traditional cryptography.
- Expected to achieve domain-specific quantum advantage within this decade.
About Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
- QKD is a secure communication method that implements a cryptographic protocol involving components of quantum mechanics.
- It enables two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which then can be used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
|
- Quantum Communication: Uses Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), entanglement and quantum repeaters to enable unhackable communication networks.
- Any eavesdropping attempt disturbs the quantum state, making interception detectable.
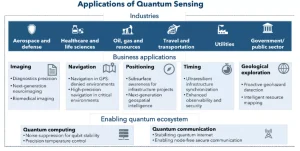
- Quantum Sensing & Metrology: Uses quantum states to make ultra-sensitive measurements, far beyond classical limits.
-
- Enables atomic clocks, magnetometers, gravimeters, inertial sensors for defence, navigation, and space.
- Quantum Materials: Materials engineered to exploit quantum mechanical properties like superconductivity, topological phases and spin systems.
- Backbone for quantum processors, photonic systems, and advanced sensors.
Strategic Significance Of Quantum Technologies
- Economic Impact: Expected to unlock USD 1–2 trillion globally by 2035 across finance, logistics, energy, healthcare, and materials.
- Creation ofOf High-Value Jobs: Quantum technologies demand highly specialized skills in both manufacturing and algorithmic domains.
- Advancements in this domain will generate roles across research, manufacturing, and software resulting in the creation of high-value, future-proof jobs that are essential for India’s economic ascent.
- Service Export Opportunities: As the global quantum economy expands rapidly in the coming decade, demand for quantum software and quantum-enabled IT services will surge.
- India, with its robust IT services and software sector, is uniquely qualified to capture a substantial share of the global quantum services market.
- New Applications Across Industries
- Healthcare and Life Sciences: Combining quantum sensing and computing can revolutionize medical diagnostics, drug discovery, genomics, and personalized medicine.
- Democratisation of Innovation: Quantum cloud and affordable systems will enable even rural regions to access precision medicine and advanced computing.
- Logistics and Supply Chains: Quantum optimization can streamline complex logistics, leading to cost savings and efficiency improvements.
- Fintech: Enhanced security and computational power can drive innovation in financial modeling, fraud detection, and data encryption.
- Chemicals, Petroleum and Mining: Quantum solutions enable better resource exploration, material discovery, and process optimization.
- National Security Imperatives: Quantum computers can break RSA encryption; Quantum communication becomes essential for secure defence networks.
- RSA: It is an asymmetric encryption algorithm that uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, making it useful for secure data transmission on the internet and digital signatures
- Scientific & Industrial Breakthroughs: Enables simulation of molecules, materials, weather and biological systems at unprecedented precision.
- Technology Sovereignty & Digital Security: Quantum-safe infrastructure becomes critical as classical cryptography becomes obsolete.
- Climate, Agriculture and Energy Innovation: Quantum models improve rainfall prediction, CO₂ capture modelling and battery material development.
- Quantum has the ability to simulate nature with unmatched precision, enabling environmental breakthroughs.
Strengths Of Indian Ecosystem In Quantum Technologies
- Strong Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI): India can rapidly deploy quantum solutions at national scale using mature DPIs.
- DPI allows quantum-enabled precision healthcare delivery even in rural settings.
- Large and Scalable STEM Talent Base: India’s engineering ecosystem offers a large foundation for quantum upskilling.
- Leadership in Software, Algorithms and Cloud Engineering: India can dominate quantum software, where the highest near-term global value lies.
- NITI Aayog’s report predicts software and services will be India’s core quantum advantage.
- Government’s Mission-Mode Commitment Through NQM: Long-term funding, institutional alignment and national targets accelerate growth.
- NQM establishes a clear vision for 2035 with coordinated national action priorities.
Key Milestones For A Quantum Economy
- Launch of National Quantum Mission (NQM) – 2023: India initiated a mission-mode national program to build indigenous quantum computing, communication, sensing and materials capabilities.
- NQM allocates ₹6,003.65 crore till 2030–31, signalling the first coordinated national strategy for quantum R&D.
- Global Quantum Investments Exceed USD 10 Billion Annually: Quantum has become a defining technology race, similar to nuclear, space, and AI revolutions.
- The roadmap notes a global surge in state-led and private quantum funding, raising strategic urgency for India.
- QKD Demonstrations in India and Major Powers: India showcases capability in long-distance Quantum Key Distribution, an early proof of technological readiness.
- Successful QKD experiments in India place it among a small group—US, China—with operational prototypes.
- Quantum Advantage Expected in this Decade: Certain optimisation, cryptography and chemistry problems will become faster on quantum machines than classical systems.
- The report confirms domain-specific quantum advantage is plausible before 2030.
- USD 1–2 Trillion Global Value Creation Potential by 2035: Quantum is projected to be a major economic growth engine across industries.
Key Initiatives By India In The Sphere of Quantum Computing
- National Quantum Mission (NQM): The Mission aims to enhance the country’s capabilities in quantum-related science and technology.
- It focuses on four key domains or verticals, i.e. Quantum Computing, Quantum Communication, Quantum Sensing & Metrology, and Quantum Materials & Devices.
- The Mission has an outlay of Rs 6,003 crore, which is used to fund scientific and industrial research projects for eight years (2023-2031).
- It includes the establishment of four thematic hubs (T-Hubs) dedicated to the four domains or verticals.
- QSim: India’s first Quantum Computer Simulator (QSim) toolkit was launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- This indigenous toolkit will serve as an important educational and research tool for students and researchers in quantum computing.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) Demonstration: Startup QNu Labs demonstrated India’s first 500 km Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) network over existing optical fiber infrastructure.
- It strengthens India’s quantum capabilities and advances quantum-secure communication and cyber defense.
- Quantum Startups in India: Indian startups such as QpiAI, BosonQ Psi, and TCS Quantum Computing Lab are at the forefront of quantum innovation, advancing research and industry applications.
|
Risks Of Quantum Technologies
- Cryptographic Collapse (“Q-Day”): Quantum computers will be able to break the mathematical foundations of current public-key encryption standards like RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), collapsing global cybersecurity.
- The roadmap warns that most digital communications become vulnerable to quantum decryption.
- Disruption of Strategic Military Balance: Quantum sensors can detect stealth aircraft, submarines and encrypted communication, altering deterrence models.
- Vulnerability of Critical Infrastructure: Quantum attacks could compromise power grids, communication networks, satellites, and national digital systems if not upgraded to quantum-safe protocols in time.
- Collapse of Banking and Financial Systems: Quantum attacks can decrypt financial records, steal encrypted transactions, manipulate blockchain systems and compromise global payment rails, potentially triggering systemic banking failures if quantum-safe protocols are not adopted.
- Acceleration of Cyber Espionage and Intelligence Threats: “Store-now, decrypt-later” attacks allow adversaries to intercept encrypted data today and decrypt it once quantum capability matures.
Challenges of Indian Ecosystem In Quantum Technologies
- Significant Gaps in Quantum Computing Capabilities: India faces major deficits across quantum hardware, system integration, control electronics, and the full software stack, limiting end-to-end technological maturity.
- Heavy Import Dependence for Critical Components: Quantum peripherals such as cryogenic systems, precision optics, superconducting materials, and fabrication-grade equipment are largely imported, creating strategic vulnerability.
- Low Investment in Basic Science and Weak Research Output: With R&D spending at only 0.65% of GDP, India’s fundamental science capacity remains limited, reflected in low-quality research output and a global IP share that does not place India among the top 10 contributors.
- Weak IP Governance and Commercialization Pathways: Fragmented IP ownership, slow technology transfer processes, and weak commercialization practices hinder innovation-to-market translation.
- Supply Chain Dependence and Strategic Vulnerability: Cryogenics, qubit materials and precision fabrication currently dominated by few countries risk dependence.
- For Example: China’s investment in quantum and dominance in materials
- Acute Skills Gap Across Quantum-Enabling Disciplines: Shortages persist in cryogenics, photonics, microwave engineering, quantum control, and techno-business talent needed to scale deep-tech ventures.
- Slow Lab-to-Market Transition: Weak testbeds, procurement delays and IP bottlenecks slow commercialization
- Shortage of Quantum-Ready Workforce: While the number of graduates is high, there is insufficient inter-disciplinary breadth in the workforce and a scarcity of manpower in specialized engineering skills that can help connect lab-to-product-to-market.
Global Best Practices:
- United States: The U.S. quantum ecosystem is driven by strong government funding and a thriving private sector (Google, IBM, PsiQuantum).
- National Quantum Strategy of the US has 3 components: Getting the science right, enhancing competitiveness and enabling people.
- Quantum Economic Development Consortium (QED-C): The QED-C is an industry led consortium that was created to enable and grow-quantum industry in the United States.
- It was established with support from NIST as part of federal strategy as called out by National Quantum Initiative Act of 2018.
- China: China follows a state-driven model with massive investments in quantum research.
- Leading institutions like University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) and Zhejiang University drive major breakthroughs.
- Researchers at Peking University have achieved large-scale quantum entanglement on an optical chip, intensifying the global quantum race.
- Europe: The EU Quantum Flagship and national programs in Germany, France, Belgium, and Switzerland drive regional quantum advancements.
- Other Key Players: Targeted Investments
- Canada: Specializes in quantum software.
- Japan: Focuses on specialized quantum hardware.
- Australia: Leads in quantum sensors.
|
Strategic Recommendations
- Expand Quantum Workforce: Develop PhD tracks, quantum engineering curricula, apprenticeship programs and global faculty partnerships.
- The workforce must scale tenfold within 2–3 years to meet 2035 targets.
- Increase Industry Engagement and Investment: Provide tax credits, public procurement pipelines and co-investment funds to attract firms.
- Industry awareness and capital inflow needed within 2–5 years to avoid missing global curve.
- Accelerate Lab-to-Market Transition: Set up national quantum testbeds, sandboxes, validation hubs and expedite procurement norms.
- Improving ease of research and validation is a key near-term recommendation.
- Strengthen Fundamental Science and Boost Risk Appetite: Fund long-horizon quantum physics, materials science and experimental platforms.
- Roadmap stresses India must grow both quality and quantity of frontier scientific research.
- Improve India’s Attractiveness for Startup Domicile: Ease regulations, create domestic deep-tech funds, ensure access to hardware and infrastructure.
- Target: >90% Indian quantum startups remain domiciled in India.
- Lead Global Standards and Protocol Development: Actively shape quantum hardware, communication and cryptography standards internationally.
- Ensures Indian products face no global access barriers.
- Strengthen Quantum Trade and Supply Chains: Secure global partnerships for cryogenics, semiconductors, vacuum systems and photonics
- Roadmap highlights critical need for smooth quantum-related import/export flows.
Vision for India’s Quantum Economy in 2035
- Incubating at least 10 globally competitive quantum startups, each surpassing USD 100 million in revenue
- Capturing over 50% of the value in the global quantum software and services market by harnessing our software and engineering strength,
- Achieving meaningful, scaled deployment of quantum technologies (home-grown and global) in strategic sectors across India.
- Commanding critical positions in the global quantum supply chain for both hardware and software, creating strategic dependencies and value
- Becoming a source of foundational scientific breakthroughs, with worldclass research and intellectual property creation in quantum science and engineering
|
Conclusion
Quantum technologies offer India a once-in-history opportunity to lead a foundational technological revolution, where speed of execution will determine national strategic advantage.
![]() 5 Dec 2025
5 Dec 2025



