India launched its first-ever R&D Roadmap for Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS).
About Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
- Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) refers to a set of technologies that capture carbon dioxide emissions from industrial sources or the atmosphere, transport the captured CO₂, and either utilize it for productive purposes or store it permanently underground to prevent its release into the atmosphere.
- These technologies aim to prevent CO₂ from entering and accumulating in the atmosphere, thereby reducing its impact on global warming.
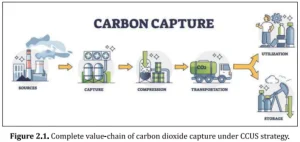
Three Stages of CCUS Technology
- Carbon Capture: The first stage focuses on capturing CO₂ from industrial gas streams. The choice of capture technology depends on the concentration of CO₂ in the stream and the intended use.
- Carbon Utilization: The second stage involves converting captured CO₂ into useful products like green urea, dry ice, carbonated beverages, building materials, and various chemicals.
- Carbon Storage: The third stage deals with the long-term storage of CO₂. The captured CO₂ is injected into geological formations such as saline aquifers, depleted oil and gas reservoirs, or other stable underground structures for permanent storage.
|
Why India needs CCUS?
- India is the world’s third-largest carbon dioxide emitter after China and the United States, releasing approximately 2.6 gigatonnes of CO₂ annually.
- Despite major progress in renewable energy, the country continues to depend significantly on coal, oil, and natural gas for industrial growth and baseload power, making immediate phase-out unrealistic.
- India’s Climate Commitments and Challenges
-
- Climate Commitments: The Indian government has pledged to cut CO₂ emissions by 50% by 2050 and achieve net-zero emissions by 2070.
- Renewable energy alone cannot decarbonise hard-to-abate industries such as steel, cement, fertilizers, and thermal energy.
- Therefore, CCUS becomes essential both to reduce ongoing emissions and to create pathways for long-term, low-carbon industrial growth.
About the Roadmap
- Prepared by DST: The roadmap has been developed by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) to guide national efforts in advancing CCUS technologies.
- It highlights the requirement for enabling frameworks including skilled manpower, robust regulatory standards, safety protocols, and early investments in shared CCUS infrastructure.
Core Components of the Roadmap
- Advancing Current Technologies: It seeks to push existing CCUS technologies to higher levels of commercial readiness through focused research and pilot deployment.
- Breakthrough Technologies: Next-generation CCUS innovations, including frontier materials and advanced chemical processes, will receive dedicated support to accelerate transformative solutions.
- Thematic Priorities: These include improving CO₂ capture efficiency, diversifying utilisation pathways, developing long-term storage capabilities, and designing integrated carbon management systems.
- Enabling Ecosystem: A strong ecosystem involving policy support, regulatory standards, safety norms, early-stage infrastructure, and capacity-building initiatives is viewed as essential for large-scale CCUS deployment.
Core R&D Framework Proposed in the Roadmap
The roadmap proposes a structured three-phase R&D programme extending from 2025 to 2045 to develop India’s CCUS capabilities.
- Phase 1 (2025–2030): Foundational Research and Pilot Demonstrations:
- This phase focuses on strengthening basic and applied research, improving the efficiency of existing capture technologies, and developing novel materials and processes that can reduce the cost of CO₂ capture.
- It also aims to raise the technology readiness levels (TRLs) of promising solutions and begin pilot-scale demonstrations in key industries.
- Phase 2 (2030–2035): Industrial Integration and Regulatory Development:
- In this phase, the report envisions the establishment of CCUS hubs and clusters in regions such as the Krishna–Godavari Basin, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and the Northeast.
- It also proposes drafting national regulatory frameworks to govern CO₂ capture, transportation, and storage, including guidelines for liability, monitoring, carbon pricing, and safety protocols.
- Phase 3 (2035–2045): Commercial Deployment and Scale-Up:
- The final phase aims to achieve widespread, commercial-scale adoption of CCUS across major industrial sectors.
- It includes building CO₂ transportation networks, enabling multi-million-tonne storage operations, and integrating CCUS with emerging hydrogen-based technologies to create a decarbonised industrial economy.
Technology Pathways for R&D
The report identifies three major R&D pathways essential for developing CCUS technologies tailored to India’s industrial landscape
- End-of-Pipe (EOP) Technologies: The roadmap states that EOP technologies will help retrofit existing industries by enabling the capture of CO₂ directly from flue gas streams.
- CCUS-Compliant Design (CCD) for New Industrial Plants: The report recommends that all future industrial plants should be designed to integrate CCUS technologies effectively.
- One-Pot (COP) Technologies for Direct Conversion:
-
- The roadmap promotes long-term investment in technologies that can convert CO₂ directly into useful products, such as low-carbon fuels, construction materials, fertilizers, and chemicals.
- It notes that although many of these technologies are still at an early research stage, they hold transformative potential for India’s manufacturing sector.
Role of CCUS in Mitigating Climate Change
- Industrial Emission Reduction: CCUS significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions by capturing CO₂ from hard-to-abate industries such as steel, cement, fertilizers, and thermal power plants, preventing it from entering the atmosphere.
- Transitional Fossil Fuel Use: CCUS allows continued use of existing fossil-fuel infrastructure during the energy transition by lowering the carbon intensity of coal, oil, and gas operations.
- Negative Emissions Potential: CCUS enables negative emissions when combined with technologies like Direct Air Capture and Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS), helping remove already-emitted CO₂ from the atmosphere.
Current Status of CCUS Development in India
- CCUS Test Beds in India: In May 2025, The Department of Science and Technology (DST) approved the establishment of five CCUS test beds for translational research and development.
- These test beds will be set up in collaboration with academia and industry under a public-private partnership (PPP) model, involving top research laboratories and leading cement companies as industry partners.
- NITI Aayog’s Policy Framework: NITI Aayog has developed a “Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Policy Framework and its Deployment Mechanism” (2022) to establish a clear regulatory environment for CCUS projects in India.
- Ongoing CCUS Projects in India:
- ONGC Hazira CCUS Project: This project involves capturing CO₂ from the Hazira gas processing plant and injecting it into a deep saline aquifer beneath the seabed for long-term storage.
- NTPC Sipat CCUS Project: The NTPC Sipat project will capture CO₂ from the flue gas of the Sipat power plant and convert it into urea, a key fertiliser.
- Reliance Industries Jamnagar CCUS Project: Reliance’s Jamnagar project will capture CO₂ from the refinery and use it to produce ethylene, a crucial petrochemical feedstock.
|
![]() 6 Dec 2025
6 Dec 2025


