![]() 27 Dec 2025
27 Dec 2025

The Malaria Elimination Technical Report 2025 highlights a rising threat from the invasive Anopheles stephensi, which thrives in urban environments and may derail India’s 2030 malaria elimination target.
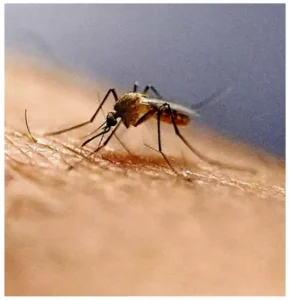 Highly efficient in densely populated human settlements.
Highly efficient in densely populated human settlements.
About Malaria
|
|---|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
