With severe anaemia in pregnancy rising across India, several States are adopting single-dose intravenous (IV) iron therapy, as anaemia is strongly linked to pre-term births and low birth-weight babies
About Anaemia
Anaemia is a medical condition where the number of red blood cells (RBCs) or the haemoglobin levels in the blood are below normal, leading to reduced oxygen supply to the body’s tissues.
Types of Anaemia
- Iron-Deficiency Anaemia: Caused by insufficient iron levels needed to produce haemoglobin.
- Vitamin-Deficiency Anaemia: Caused by a lack of Vitamin B12 or folate, essential for RBC production.
- Sickle Cell Anaemia: A genetic condition where RBCs are abnormally shaped, leading to blockages and reduced oxygen flow.
- Thalassemia: A genetic disorder causing abnormal haemoglobin production.
|
Burden of Anaemia in Pregnancy
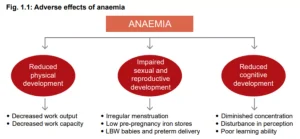
- Nature: If untreated during pregnancy, Anaemia can lead to pre-term deliveries, low birth-weight babies, and increased maternal risk.
- Rising Prevalence: Data from National Family Health Survey-5 (2019–21) shows worsening trends despite policy efforts
- Anaemia prevalence increased to 67.1% among children (6–59 months),
- 57% among women (15–49 years), and
- 52.2% among pregnant women, compared to NFHS-4 (2015–16)
- Why Pregnancy Aggravates Anaemia ?
- Increased iron requirement due to Foetal growth and Expansion of maternal blood volume
- Poor dietary intake and infections further worsen iron deficiency.
About Iron infusion
- Iron infusion is a medical procedure in which iron is delivered directly into a vein (intravenously) through a small catheter.
- Why iron infusion is needed
- Iron is essential for making hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in the blood.
- When iron levels are too low, the body cannot produce enough hemoglobin, leading to iron-deficiency anemia, the most common form of anemia.
- Types:
-
- Oral iron: First-line therapy; inexpensive and effective when taken for at least three months.
- Intravenous iron: Used when oral iron is not tolerated or absorption is poor.
Limitations of Oral Iron Supplementation
- Poor Compliance: Daily oral iron and folic acid tablets often see low adherence due to gastro-intestinal side effects such as nausea, stomach discomfort, and diarrhoea.
| Intravenous Infusions ( IV Infusions) is a medical process that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person’s vein. |
- Clinical Challenge: Oral supplementation is often ineffective for women with moderate to severe anaemia, especially in late pregnancy.
- Behavioural Factors: Many women, particularly during pregnancy, do not prioritise their own health, leading to irregular intake of tablets.
Ferric Carboxymaltose (FCM)
- Single-Dose Advantage: The newer Ferric Carboxymaltose (FCM) formulation requires only a single IV infusion, significantly improving compliance and outcomes.
- Clinical Benefits: According to obstetricians, the single-dose IV FCM leads to faster correction of haemoglobin levels, benefiting both mother and child.
- Late-Pregnancy Utility: It is particularly effective for women in advanced stages of pregnancy, where waiting for oral tablets to act is not feasible
State-Level Adoption
- Rajasthan: A pilot was launched in December 2024 under the National Health Mission-Rajasthan.
- Rajasthan introduced IV FCM following a district-level study that showed it was highly effective in correcting anaemia in pregnant women.
- Karnataka: Karnataka has begun implementing IV FCM across 31 districts for pregnant women with moderate to severe anaemia.
- Karnataka launched a digital Garbha Sutra app to calculate correct IV FCM dosage based on haemoglobin levels and body weight.
Government Initiatives to Tackle Anaemia
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat (AMB) Strategy (2018): Reduce anaemia prevalence across six age groups through the 6x6x6 strategy, which includes six interventions, six beneficiary groups, and six institutional mechanisms.
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission (2023): To eliminate sickle cell disease as a public health problem by 2047, focusing on screening, diagnosis, and management in tribal areas.
- National Iron Plus Initiative (NIPI): Provides age-specific iron and folic acid supplementation to children, adolescents, and women of reproductive age.
|
![]() 19 Jan 2026
19 Jan 2026


