Recently, the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS), formally released the Military Quantum Mission (MQM) Policy Framework.
- The framework emphasizes Civil-Military Fusion through dedicated governing bodies with members from across government sectors.
About the Military Quantum Mission (MQM) Policy Framework
- It establishes a comprehensive strategy and a time-bound roadmap for the integration of Quantum Technologies into the Indian Armed Forces, aiming to secure a decisive edge and technological supremacy in the rapidly evolving landscape of modern warfare.
- Four Foundational Pillars:
- Quantum Communication: This involves the use of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) to create virtually unhackable communication channels.
- Unlike classical encryption, any attempt to intercept a quantum signal alters its state, immediately alerting the users, thereby ensuring Information Security.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is a secure communication technique that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to generate and share encryption keys between two parties.
- Quantum Computing: This pillar focuses on the immense processing power required for complex battlefield simulations, advanced cryptanalysis (breaking adversary codes).
- It optimizes logistics and supply chain management for large-scale troop movements.
- Quantum Sensing and Metrology: These technologies provide ultra-high precision detection.
- Quantum sensors can detect submarines by measuring minute changes in gravity (Gravimetry) or allow for Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) in environments where GPS signals are jammed or unavailable.
- Quantum Materials and Devices: This involves the indigenous development of specialized hardware, such as superconducting circuits and topological insulators.
- These form the backbone for next-generation sensors, stealth-countering systems, and high-endurance defence platforms.
PWOnlyIASExtraEdge:
About Quantum Computing
- Quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in fundamentally different ways compared to classical computers.
- Difference Between Classical and Quantum Computing: While classical computers use bits as the smallest unit of data (which can be either 0 or 1), quantum computers use quantum bits (qubits), which can exist in multiple states simultaneously.
- Core Principles of Quantum Computing:
-
- Quantum computing is based on three key principles of quantum mechanics:
- Superposition: In quantum computing, a qubit can exist in a superposition of both 0 and 1 simultaneously.
- This means a qubit can represent multiple states at once, enabling quantum computers to process vast amounts of information in parallel.
- Entanglement: Entanglement is a phenomenon where two or more qubits become interconnected, such that the state of one qubit is directly related to the state of another, no matter how far apart they are.
- Quantum Interference: Quantum computers use interference to amplify correct solutions and cancel out incorrect ones. By carefully manipulating qubits, quantum algorithms can guide the system toward the most probable correct answer.
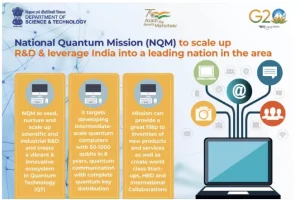
National Quantum Mission (NQM)
- Launched in 2023 under the Department of Science and Technology (DST) with an outlay of ₹6,000 crore (2023–31); aims to develop 50–1,000 qubit quantum computers, establish secure quantum communications over 2,000 km, and build national quantum networks.
- The mission strengthens India’s leadership in quantum computing, cryptography, and communication, aligning with the vision of Viksit Bharat @ 2047.
|
Why the Need for a Military Quantum Mission Policy Framework?
- The shift from classical to quantum capabilities is not merely a technical upgrade; it is a strategic necessity driven by the changing nature of 21st-century warfare:
- Countering “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” (HNDL) Threats: Adversaries are currently intercepting and storing encrypted military data with the intent to decrypt it once fault-tolerant quantum computers are available.
- A dedicated policy is needed to transition to Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) immediately to safeguard long-term state secrets.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) refers to cryptographic algorithms designed to remain secure against attacks by quantum computers.
- Negating Stealth Technologies: Traditional radar and sonar are increasingly limited against modern stealth aircraft and silent submarines.
- Quantum Radar and Quantum Gravimetry have the potential to make current stealth platforms visible, necessitating a policy that keeps India on the offensive side of this detection curve.
- Navigating GPS-Denied Environments: Modern conflict zones are often subject to heavy Electronic Warfare (EW) and GPS jamming.
- The MQM framework prioritizes Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) systems that do not rely on satellites, ensuring operational continuity in “blind” zones.
- Accelerating Decision-Making (OODA Loop): In high-intensity combat, the speed of the Observe-Orient-Decide-Act (OODA) cycle is critical. Quantum Computing can process massive datasets from drones and satellites in real-time, providing commanders with actionable intelligence far faster than classical systems.
| Global Initiatives in Military Quantum Technology |
| Nation/Bloc |
Primary Initiative |
| United States |
Pentagon’s “Quantum & Battlefield Information Dominance” (2025) |
| China |
People’s Liberation Army (PLA) Quantum Cyber Warfare Program (2026) |
| European Union |
Quantum Sensing Space & Defence Roadmap (2026) |
| NATO |
Inaugural Quantum Strategy (2024) |
| United Kingdom |
National Quantum Technologies Programme (NQTP) & Ministry of Defence (MoD) Quantum Roadmap (2023-2033) |
-
- Addressing Regional Geopolitical Shifts: With neighbors like China already operationalizing Quantum-secured satellite links, India needs a formal framework to prevent a “Quantum Gap”.
- It could lead to strategic asymmetry in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and along its borders. Significance of the Military Quantum Mission (MQM) Policy Framework:
- Technological Sovereignty: By aligning with the National Quantum Mission (NQM), the MQM ensures that the Indian Armed Forces are not dependent on foreign Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) for critical security infrastructure, fostering Atmanirbharta (Self-Reliance).
- Achieving “Jointness”: The framework emphasizes the synergy of the Army, Navy, and Air Force, ensuring that all three services use standardized quantum protocols, which is vital for the success of Integrated Theater Commands.
- Civil-Military Fusion: The policy creates a bridge between defense requirements and civilian expertise. It encourages dedicated governing bodies composed of members from the government, academia, and the private deep-tech startup ecosystem to fast-track innovation.
- Strategic Deterrence: In an era where adversaries may use “Harvest Now, Decrypt Later” tactics, this policy provides the roadmap for Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) to protect state secrets for decades to come.
Challenges in Implementation
- Extreme Operational Requirements: Most quantum systems currently require cryogenic cooling (near absolute zero temperatures).
- Making these systems “ruggedized” enough for the high-vibration and extreme-temperature environments of a battlefield is a massive engineering hurdle.
- The “Quantum Skill Gap”: There is a global shortage of quantum physicists and engineers.
- Building a specialized “Quantum Cadre” within the military will take significant time and specialized training infrastructure.
- High Gestation Periods: Quantum technology is in its nascent stages.
- The high costs of Research and Development (R&D) may not yield immediate “battlefield-ready” results, requiring sustained political and financial will.
Way Forward
- Phased Induction: The military should follow an incremental roadmap, starting with short-range QKD for localized secure links before moving to long-range satellite-based quantum networks.
- Indigenous Supply Chain: To achieve true self-reliance, India must invest in domestic manufacturing of components like dilution refrigerators and high-vacuum laser systems required for quantum hardware.
- Establishing Quantum Testbeds: The Ministry of Defence should set up dedicated testing ranges where startups and defense labs can verify quantum sensors and communication links in simulated combat conditions.
Conclusion
The Military Quantum Mission Policy Framework is a visionary step that acknowledges that the future of warfare will be decided in the “quantum realm.” By integrating these four pillars through a synergized Tri-Service approach, India is positioning itself not just as a regional power, but as a global leader in the Second Quantum Revolution, ensuring that its defense forces possess the “technological teeth” required for 21st-century deterrence.
![]() 23 Jan 2026
23 Jan 2026


