The Satpura Range is a central Indian mountain system located between the Narmada and Tapi rivers. Spanning Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Chhattisgarh, it includes Dhupgarh Peak, rich forests, national parks, mineral resources, and unique geological features. Essential geography notes for students.

Satpura Range is one of the most important mountain systems in Central India. Located between the Narmada and Tapi rivers, the Satpura Range plays a major role in India’s physical geography, climate, biodiversity, and natural resources.
For students preparing for competitive exams or school geography, understanding the Satpura Range in detail is essential. Here explains its location, origin, geology, length, peaks, rivers, forests, and importance in simple yet formal language.
Satpura Range Key Highlights
The Satpura Range is an important mountain system of Central India with significant geographical, ecological, and economic value. Understanding its location, geology, rivers, climate, forests, and natural resources is essential for students preparing for academic and competitive examinations.
Below highlights the major features and details of the Satpura Range in a clear and exam-focused format.
|
Satpuda Range Key Highlights |
|
| Feature | Details |
| Satpura Range location | Central India, between Narmada (north) and Tapi (south) |
| Satpura Range states | Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh |
| Satpura Range length and extent | Approx. 900 km, east–west direction |
| Satpura Range highest peak | Dhupgarh (1,350 m approx.) |
| Dhupgarh Peak Satpura | Located in Pachmarhi, MP (Mahadeo Hills) |
| Satpura Range origin and geology | Formed by block faulting; Gondwana rocks, sandstone & basalt |
| Satpura Range plateau region | Includes Pachmarhi Plateau |
| Satpura Range between Narmada and Tapi | Acts as natural barrier separating North India and Deccan Plateau |
| Satpura Range rivers | Narmada, Tapi, Wardha, Wainganga, Pench |
| Satpura Range passes | Asirgarh Pass (important historical route) |
| Satpura Maikal Hills | Eastern extension of the Satpura Range |
| Satpura Range climate | Tropical monsoon; moderate to heavy rainfall |
| Satpura Range forests and biodiversity | Tropical deciduous forests, teak, sal; tiger habitat |
| Satpura Range national parks | Satpura NP, Pench NP, Melghat Tiger Reserve |
| Satpura Range natural resources | Coal (Gondwana coalfields), manganese, bauxite |
Satpura Range Physical Features and Map Overview
A Satpura Range map shows its east–west alignment across central India. The Satpura range map highlights important hills such as Rajpipla Hills, Mahadeo Hills, and Satpura Maikal hills.
The Satpura Range is not a single continuous chain but a series of hills and plateaus forming part of the Central Highlands.
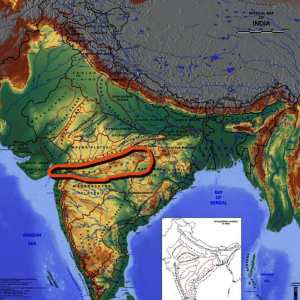
The Satpura Range begins in eastern Gujarat. It runs eastward through Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh. It finally ends in Chhattisgarh. This range lies south of the Vindhya Range. Both ranges form an east-west mountain system. They separate the Indo-Gangetic Plain from the Deccan Plateau. The name “Satpura” means “Seven Folds.”
The Satpura Range formed through folding and uplifting. Geologists classify it as a ‘horst’ or structural uplift. This means it is an elevated fault block. The mountains mainly consist of schists, granites, and quartzites. Basalt lavas cover these rocks in many areas. The range is bounded by grabens. The Narmada Graben is to the north. The Tapi Graben is to the south.
The Satpura Range extends for about 900 kilometers. Its western part is known as the Rajpipla Hills. The central part includes the Mahadeo Hills. Further east lies the Maikala Range. These components together form the complete Satpura Range.
Dhupgarh is the highest peak in the Satpura Range. It stands at 1,350 meters (4,429 feet). This peak is located in the Mahadeo Hills. It is near the popular hill station of Pachmarhi in Madhya Pradesh.
The Satpura Range acts as a watershed for major rivers. The Narmada River originates near Amarkantak. It flows westwards in the valley north of the Satpura Range. The Tapti River rises in the eastern Satpura. It flows west along the southern slopes of the range. The Godavari River and its tributaries drain the Deccan Plateau to the south. The Mahanadi River drains the easternmost section of the range.
The eastern part of the Satpura Range receives more rainfall. It supports wet deciduous forests. This forms the eastern highlands wet deciduous forests ecoregion. The western part is drier. It features dry deciduous forests, also seen in the Narmada Valley and western Vindhya Range. Teak, sal, and bamboo are common trees in the Satpura range forests.
The Satpura Range is rich in biodiversity. Its forests are home to many threatened species. These include the Bengal tiger, barasingha, gaur, and sloth bear. Several protected areas exist within the range. These include Satpura National Park, Pench National Park, Gugamal National Park, and Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve. Melghat Tiger Reserve and Bori Reserve Forest also protect its unique wildlife.
The Satpura Range offers significant natural resources. It is rich in minerals like coal, bauxite, and limestone. These resources support mining activities. The range also attracts tourists. Pachmarhi, known as the “Queen of Satpuras,” is a popular hill station. It offers trekking, fishing, and scenic beauty. The range’s ecological services include water purification and climate regulation.
The Satpura Range is important because:
For competitive exams, questions frequently appear on the Satpura Range highest peak, Satpura Range states, and Satpura Range rivers.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
The Satpura Range is located in Central India between the Narmada and Tapi rivers. It extends across Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Chhattisgarh.
The highest peak of the Satpura Range is Dhupgarh Peak Satpura, located in Pachmarhi, Madhya Pradesh, with a height of about 1,350 meters.
The Satpura Range origin and geology are related to block faulting and tectonic uplift during ancient geological periods, including the Gondwana era.
Major Satpura Range rivers include the Narmada, Tapi, Wardha, and Wainganga rivers, which form important drainage systems in Central India.
The Satpura Range is important for its location between Narmada and Tapi, rich forests and biodiversity, mineral resources, and national parks, making it significant for exams and environmental studies.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>