With rising heat and growing AC demand, district cooling offers a way to keep Indian cities comfortable while reducing electricity use and carbon emissions.
- GIFT City Pilot Results: District cooling at GIFT City in Gujarat shows potential to cut 6,100 MW of power demand, save 7,850 GWh annually, and avoid 6.6 million tonnes of CO2 emissions each year.
Initiatives taken by India in Cooling Strategy
- India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP, 2019): First national-level cooling strategy in the world; aims to cut cooling demand by 20–25% and refrigerant use by 25–30% by 2037–38.
- National Mission on Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE): Promotes efficient industrial cooling and energy-saving technologies.
- Eco-Niwas Samhita (Building Code), 2018: Mandates thermal comfort standards and passive design for residential buildings.
- Cool Roof Programme (Telangana, 2023): To reduce urban heat and cooling energy demand by promoting widespread adoption of high-reflectance cool roofs.
|
About District Cooling
- District cooling is a centralised system that supplies air-conditioning to a cluster of buildings, like a shared air-conditioner for an entire neighbourhood or campus.
- District cooling operates like a utility with revenue from a one-time connection fee, a fixed demand charge, and a variable consumption charge.
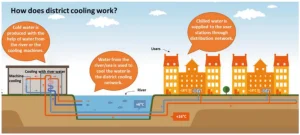
How does it work?
- Centralized Chilled Water Production: In it, a single large plant produces chilled water and distributes it via insulated underground pipes to multiple buildings, like a public utility such as piped natural gas or electricity.
- Indoor Cooling Process: Inside each building, this water passes through heat exchangers, cools the indoor air by absorbing heat, then returns slightly warmer to the central plant, where it’s cooled again and sent back into the network.
- They simply draw ‘cooling as a service’ from the network.
- District Cooling Tariff Structure: District cooling typically charges a one-time connection fee, a fixed demand charge for maximum cooling capacity, and a usage-based fee for actual energy consumed.
Challenges
- High Capital Costs: Large upfront investment for plants, distribution networks, and thermal storage.
- Fixed Demand Charges: Customers pay for reserved capacity even if building occupancy is low, making bills unpredictable.
- Right-Sizing & Design Issues: Overestimating cooling needs or inefficient internal systems can increase costs.
- Water Use Concerns: Cooling towers require make-up water, which may stress local water resources if not managed efficiently.
Benefits
- High-Efficiency Cooling: District cooling plants use large, high-efficiency chillers and cooling towers to deliver more cooling per unit of electricity than individual building systems.
- For Example: Many systems include thermal storage, producing 20–40% of cooling at night when demand and tariffs are lower.
- Efficiency & Energy Savings: Well-run district cooling systems can operate twice as efficiently as standalone building chillers.
- For Example: They reduce electricity use for cooling by 30–50% and peak grid demand by 20–30%
- Environmental Benefits: Lower electricity use can cut greenhouse gas emissions by 15–40%, centralized equipment reduces building refrigerants by up to 80%, and fewer outdoor AC units help lower urban heat, with some areas abroad seeing 1–2°C local temperature drops.
- Water Efficiency in District Cooling: District cooling uses a closed-loop system that consumes very little water about 1 kilolitre of make-up water for a 10,000-tonne plant and can use treated sewage or wastewater due to centralized large-scale design
- Alignment with India’s National Cooling Action Plan: District cooling reduces electricity use and shifts some demand to nighttime, easing grid pressure, improving energy security, and lowering outage risks during heatwaves.
- Climate & Urban Benefits: Centralized district cooling lowers emissions, allows use of low-GWP refrigerants supporting India’s Kigali commitments, and provides reliable cooling for services, IT, hospitals, and data centers in cities.
- Best Suited Areas for District Cooling: District cooling is most effective in areas with high, dense, and predictable cooling demand, such as commercial districts, transit corridors, airports, hospitals, universities, and IT parks.
Way Forward
- Demarcation of Cooling Zones: Urban authorities should demarcate district cooling zones in master plans, set aside land for plants and pipe corridors, and coordinate underground utilities.
- Role of Municipal Bodies: Municipal bodies need to be empowered and strengthened to introduce clear concession rules, service standards, and long-term frameworks so private players know how they will recover investments.
- Regulatory & Technical Support: State regulators and DISCOMs can shift cooling loads to night, link it to tariffs, and value avoided peak capacity, while central agencies provide guidelines and developers design buildings with ready connection points.
About India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP)
- Launched in 2019, India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) is about improving the quality of life and productivity of the people of India, and achieving many of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The India Cooling Action seeks to;
- Reduce cooling demand across sectors by 20 percent to 25 percent by 2037-38,
Reduce refrigerant demand by 25 percent to 30 percent by 2037-38,
Reduce cooling energy requirements by 25 percent to 40 percent by 2037-38,
- Recognize “cooling and related areas” as a thrust area of research under the national S&T Programme.
- Training and certification of 100,000 servicing sector technicians by 2022-23, synergizing with Skill India Mission.
|
![]() 17 Feb 2026
17 Feb 2026


