Hornbill Restaurants
Context: The Chhattisgarh Forest Department is creating six “hornbill restaurants” to protect the rare Malabar Pied Hornbill and help forests grow naturally.
About the Hornbill Restaurants
- The “hornbill restaurants” refer to a unique wildlife conservation initiative by the Chhattisgarh Forest Department.
- These are not conventional eateries but natural clusters of fruit-bearing trees planted in designated areas to provide abundant food sources for hornbills, particularly the rare Malabar Pied Hornbill.
- Location: The initiative is located in the Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve (USTR) in Gariaband district, Chhattisgarh.
- This reserve spans three ranges: Kulhadighat, Indagaon, and South Udanti, covering a mountainous terrain with elevations up to 1,000 meters.
- The area has a climate similar to the Western Ghats, making it suitable for hornbills.
- Objective: To provide a permanent, food-rich haven for the Malabar Pied Hornbill, whose population has been growing in the reserve.
- Hornbills require large quantities of fruit (e.g., figs) for survival, and these clusters ensure availability throughout the year.
- Biodiversity Benefits: Hornbills are keystone seed dispersers in tropical forests.
- They consume fruits and disperse seeds over wide areas, aiding natural forest regeneration, maintaining plant diversity, and supporting large-seeded tree species.
- Conservation and Tourism: By planting trees in visible areas, the project encourages eco-tourism, allowing visitors and locals to spot hornbills safely.
- Inspiration from Similar Models: This builds on successful “vulture restaurants” in Chhattisgarh’s Indravati National Park, where food supply chains were created for scavengers.
About the Malabar Pied Hornbill
- The Malabar Pied Hornbill (Anthracoceros coronatus), also called lesser pied hornbill, is a large bird in the hornbill family, endemic to India and Sri Lanka.
- Appearance: It is a medium-sized bird with striking black and white plumage and a prominent casque.
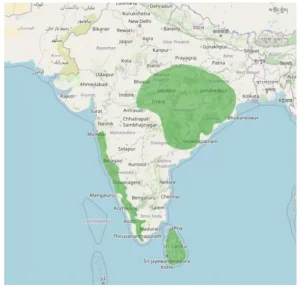 Habitat: Evergreen and moist deciduous forests, forest edges, riverine areas, plantations, and near human settlements; often below 600 m elevation.
Habitat: Evergreen and moist deciduous forests, forest edges, riverine areas, plantations, and near human settlements; often below 600 m elevation.- Distribution: Western Ghats (south India), central/eastern India (e.g., Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha), and Sri Lanka.
- Diet: Mainly frugivorous (especially figs); supplements with insects, small reptiles, mammals, and birds. Key seed disperser (“farmers of the forest”).
- Conservation Status: Near Threatened (IUCN Red List).
- As per the IUCN, there are 3,000–32,000 mature individuals of the species in existence.
- Population decreasing due to habitat loss/fragmentation.
‘Bee Corridors’ along the National Highways
Context: The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has announced a first-of-its-kind initiative to create pollinator or “Bee Corridors” along national highways as part of its sustainable infrastructure programme.
About the Bee Corridors
- ‘Bee Corridors’ are proposed continuous linear stretches of pollinator-friendly vegetation established along national highways.
- Purpose: They are designed to support honeybees and other pollinators by providing nectar and pollen resources throughout the year.
- Ecological Importance: It represents a shift from ornamental roadside plantations to ecological, biodiversity-enhancing plantations.
- Vegetation: Corridors will include a mix of trees, shrubs, herbs, and grasses that are nectar- and pollen-rich and suited to local agro-climatic conditions.
- Native species like Neem, Karanj, Mahua, Palash, Bottle Brush, Jamun, and Siris are planned for planting along these corridors.
- The selection of species is intended to ensure staggered flowering across seasons for near-continuous bloom and food supply for pollinators.
- Implementation Targets: NHAI plans to develop at least three dedicated pollinator corridors during FY 2026–27.
- Around 40 lakh (4 million) trees will be planted along national highways in 2026–27, with approximately 60 % of them under the Bee Corridor initiative.
- Broader Impact: The initiative aligns with sustainable and environmentally responsible infrastructure development, enhancing biodiversity and ecological balance while expanding highway networks.
What Are Bees?
- Bees are flying insects, primarily known for feeding on nectar and pollen and for their vital role in pollination.
- There are over 20,000 species worldwide, including social and solitary forms.
- Taxonomy: Belong to Phylum Arthropoda and Order Hymenoptera; closely related to wasps and ants.
- Body Structure: Three-part body (head, thorax, abdomen); covered with branched hairs that trap pollen efficiently.
- Diet: Herbivorous; feed on nectar (energy source) and pollen (protein source).
- Social Structure and Castes (in Social Species like Honeybees): Honeybees live in highly organized eusocial colonies (superorganisms) with division of labor.
- Queen: Single fertile female; largest in size; lays up to 2,000 eggs per day; produces pheromones to regulate the colony.
- Workers: Sterile females; majority of the colony (tens of thousands); perform foraging, nursing, cleaning, wax production, defense, and more.
- Drones: Males; larger eyes; exist mainly for mating with queens; no stinger or pollen-carrying structures.
- Colony size: Typically 20,000–80,000 bees in a hive.
- Pollination Role: Major pollinators of flowering plants; essential for biodiversity and agricultural productivity.
- Waggle Dance: The waggle dance is a communication behavior performed by worker honey bees, to inform other members of the colony about the direction and distance of a food source (nectar or pollen).
- First decoded by Austrian ethologist Karl von Frisch, who received the Nobel Prize (1973) for this discovery.
International AYUSH Conference
Context: Recently, the third International AYUSH Conference concluded in Dubai, UAE, calling for structured global integration of evidence-based traditional healthcare systems.
About International AYUSH Conference
- Intro: It is biennial conference, organised by the Science India Forum and the World Ayurveda Foundation with support from India’s Ministry of AYUSH
- Origin: The First two Edition were held in 2017 (New Delhi )and 2024 (Dubai)
- The 2026 Conference was held at the Dubai World Trade Centre.
- 2026 Theme: “Evidence-based AYUSH interventions for mind-body health.”
- Focus Areas: Discussions centred on artificial intelligence in AYUSH, research quality, medicinal botanicals, mental health, metabolic disorders, women and child health, oncology, autoimmune diseases, healthy ageing, and integration within the UAE healthcare system.
- Events and Deliberations:
- The conference featured 62 scientific sessions, 16 plenary discussions with 60 international speakers, 10 discipline-specific sessions, and conclaves on veterinary care and agroecology.
- Out of 1,200 research abstracts received, 352 oral papers and 200 posters were peer-reviewed and presented.
- An international delegate assembly of 100 experts from 20 countries released a white paper on AYUSH interventions.
- An AYUSH film festival showcased 15 entries promoting integrative wellness.
- “Wellness beyond walls” by Dr Arun won the best film and “Beyond restless” by Dr Neethu Nicholas received the second best film Awards.
AYUSH: Ayush is an acronym of medical systems that are being practiced in India – Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy.
Super-Earths
Context: Astronomers report that Super-Earths are the most common planets in the Milky Way, yet our solar system curiously lacks one.
About Super-Earths
- Super-Earths are exoplanets with masses between two and ten times that of Earth, larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune.
- The first confirmed example, Gliese 876d orbiting Gliese 876, was discovered in 2004.
- Famous Examples
- Kepler-452b (2015): Orbits a Sun-like star, in habitable zone, ~1,400 light-years away.
- Proxima Centauri b (2016): Closest known Super-Earth, just 4.24 light-years away.
- Subsequent observations by the Kepler Space Telescope revealed that such planets are extremely common across the Milky Way.
- Key Features
- Intermediate Size and Mass: They bridge the gap between rocky Earth-like planets and gas giants like Neptune.
- Diverse Composition: Some are rocky, others ocean-covered, while a few possess thick hydrogen-helium atmospheres.
- Variable Habitability: Certain Super-Earths orbit within habitable zones, such as Kepler-452b and Proxima Centauri b, where liquid water may exist.
- Stronger Gravity: Higher mass implies stronger gravity, potentially enabling better atmospheric retention.
- Significance
- Super-Earths challenge earlier assumptions that other planetary systems resemble our own.
- Their abundance reshapes theories of planet formation and expands the scope of the search for extraterrestrial life
- Advanced observatories like the James Webb Space Telescope are now analysing their atmospheres for biosignatures, making them central to future astrobiological research.
Project Vault
Context: In February 2026, the Donald Trump administration launched Project Vault.
About Project Vault
- Historical Precedent: The U.S. created the Strategic Petroleum Reserve (1975) after the 1973 Arab oil embargo to shield its economy from energy shocks.
- In the 21st century, critical minerals are as strategic as oil
- Aim: To build a strategic domestic reserve of critical minerals in the United States.
- Institutional Framework: Structured as an independently governed public-private partnership (PPP).
- Supported by:
- $10 billion financing from the Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM).
- Additional $2 billion in private sector funding.
- Scope of Mineral Coverage:
- Targets 60 critical minerals identified in the U.S. Geological Survey 2025 Critical Minerals List.
- Focuses on strengthening resilience of civilian industries against supply chain disruptions.
- Significance: Project Vault represents not another industrial policy but a new strategic doctrine, in which critical minerals and rare earth elements are not just commodities but strategic assets that underpin comprehensive national power.
![]() 18 Feb 2026
18 Feb 2026

 Habitat: Evergreen and moist deciduous forests, forest edges, riverine areas, plantations, and near human settlements; often below 600 m elevation.
Habitat: Evergreen and moist deciduous forests, forest edges, riverine areas, plantations, and near human settlements; often below 600 m elevation.