Learn the 7 continents name list ( Asia, Europe, Africa, North America, South America, Australia, Antarctica) and the 5 oceans list of the world (Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean (Antarctic Ocean), and Arctic Ocean) with maps, and facts.

The Earth is comprised of seven continents and five oceans. The continents are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. The oceans are: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (or Antarctic), and Arctic. These continents and oceans play vital roles in shaping the planet’s geography, climate, and ecosystems.
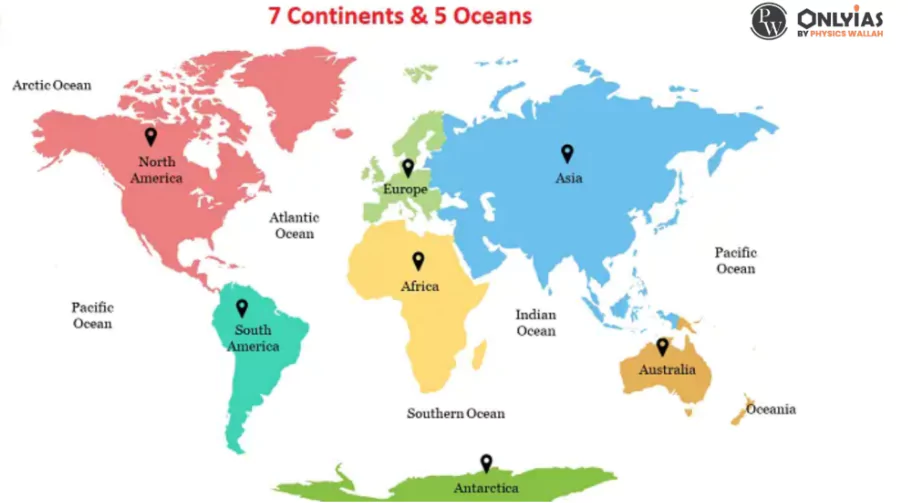
7 Continents and 5 Oceans Map
Earth’s landmass is divided into seven continents, each with its own unique characteristics and number of countries. These continents – Asia, Africa, Europe, Australia, North America, South America, and Antarctica – vary in size and geography. Interestingly, if North and South America are considered as a single continent, all seven continents share the commonality of starting and ending with the same alphabet. While approximately 71% of Earth is covered by water bodies, the remaining 29% is land.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
A considerable span of time ago, the continents were united as one colossal landmass called Pangaea, but geological movements led to their gradual separation. For instance, Europe and North America are still drifting apart at a rate of 7 cm per year, as per scientific studies.
The seven continents are collectively referred to as Asia, Africa, Europe, Australia, North America, South America, and Antarctica. Each of these continents boasts unique cultures, environments, and histories, contributing to the rich tapestry of Earth’s geography and diversity.
Among the seven continents, South America takes the lead. Let’s delve into some intriguing aspects of this continent. South America hosts the Amazon, the world’s largest river in terms of volume and the second-longest spanning 6,440 kilometers. Notably, it is also home to the Angel Falls, the planet’s highest waterfall.
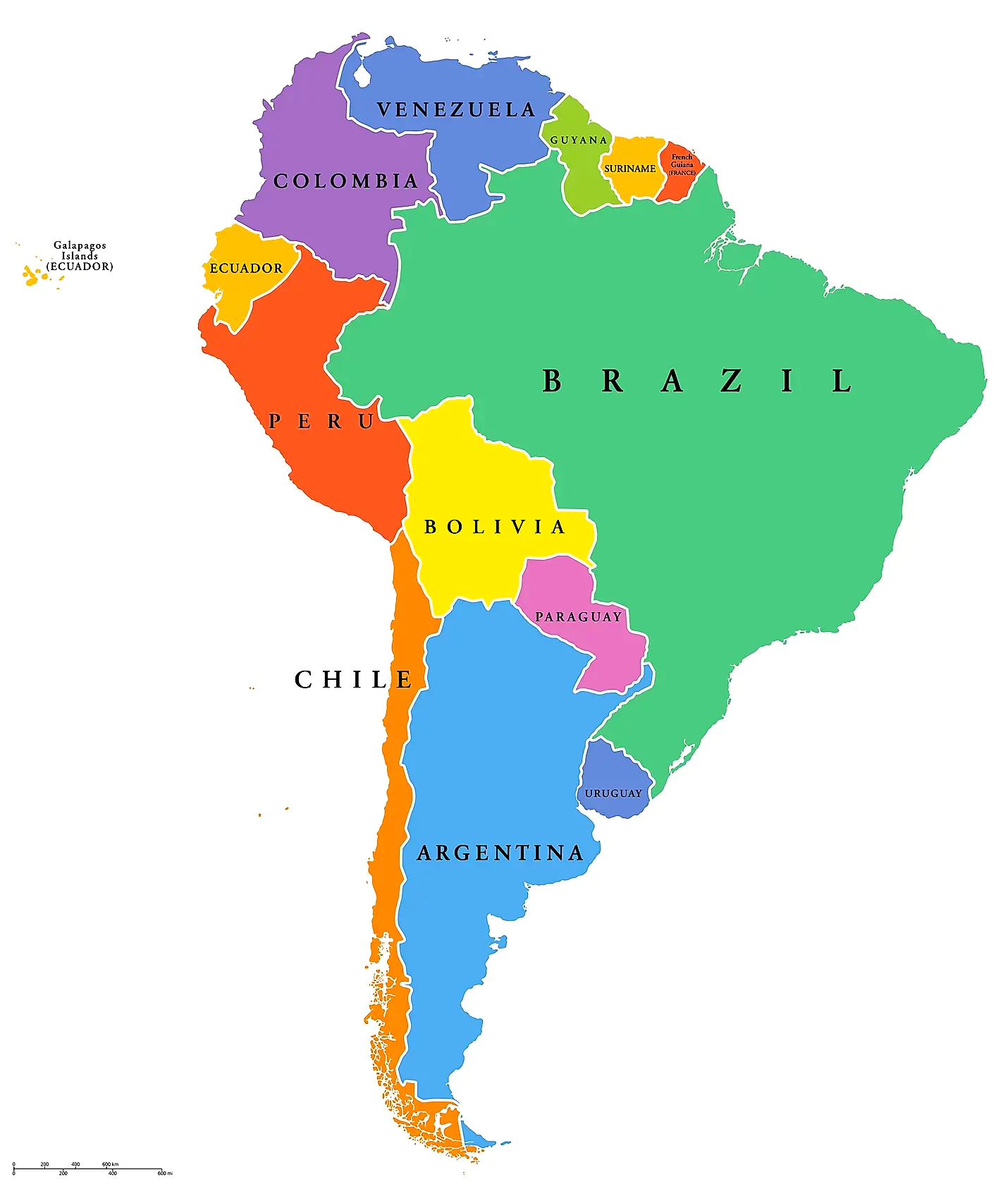
South America Continent Map
The remarkable green anaconda, the world’s largest snake by size and second-longest, can be found in this continent’s diverse ecosystem. South America boasts the presence of towering giants like Mt. Cotopaxi and Mt. Chimborazo, the world’s highest volcanoes.
| Area | Approximately 17,840,000 square kilometers |
| Population | Around 430 million (as of 2022) |
| Countries | 12 sovereign countries including Brazil, Argentina, Peru |
| Highest Point | Mount Aconcagua in Argentina (6,960 meters above sea level) |
| Longest River | Amazon River (Approximately 7,062 kilometers) |
| Largest City | São Paulo, Brazil (Population over 12 million) |
| Major Landmarks | Machu Picchu (Peru), Christ the Redeemer (Brazil) |
| Dominant Language | Spanish and Portuguese (with indigenous languages) |
| Main Biomes | Amazon Rainforest, Andes Mountains, Atacama Desert |
| Economic Activities | Agriculture, mining, tourism, oil and gas |
Furthermore, it claims the title of being the world’s top coffee producer, with Brazil situated within its borders. Portuguese and Spanish dominate as the most widely spoken languages. The continent is also the location of Lake Titicaca, the world’s highest and largest lake at an elevation of 3,800 meters. The Andes, standing as the second-highest mountain range globally after the Himalayas, form the backdrop of South America’s awe-inspiring landscapes.
In the list of seven continents, North America occupies the second spot. Let’s explore some captivating features of this continent. North America distinguishes itself as the sole continent encompassing five distinct time zones and showcasing an array of climates. Commonly referred to as the “New World,” it owes its name to the explorer Americo Vespucci.
| Continent | North America |
| Area (sq km) | 24,709,000 |
| Population (approx.) | 597 million |
| Countries | 23 |
| Highest Point | Denali/Mount McKinley (USA) |
| Longest River | Mississippi River (6,275 km) |
| Largest Lake | Lake Superior |
| Largest City | Mexico City, Mexico |
| Dominant Language(s) | English, Spanish, French |
| Main Biomes | Temperate Deciduous Forests, Prairie, Tundra |
| Economic Activities | Agriculture, manufacturing, technology |
Impressively, North America boasts the highest population density among its counterparts, with 22.9 individuals per square kilometer. The continent is graced by the presence of Lake Superior, the globe’s largest freshwater lake. The mighty Mississippi River, spanning 3,778 kilometers, ranks as the world’s third-longest river.
With a striking average per-person income, North America shines as an economic powerhouse among the continents. This region houses the United States of America, boasting the world’s largest economy.
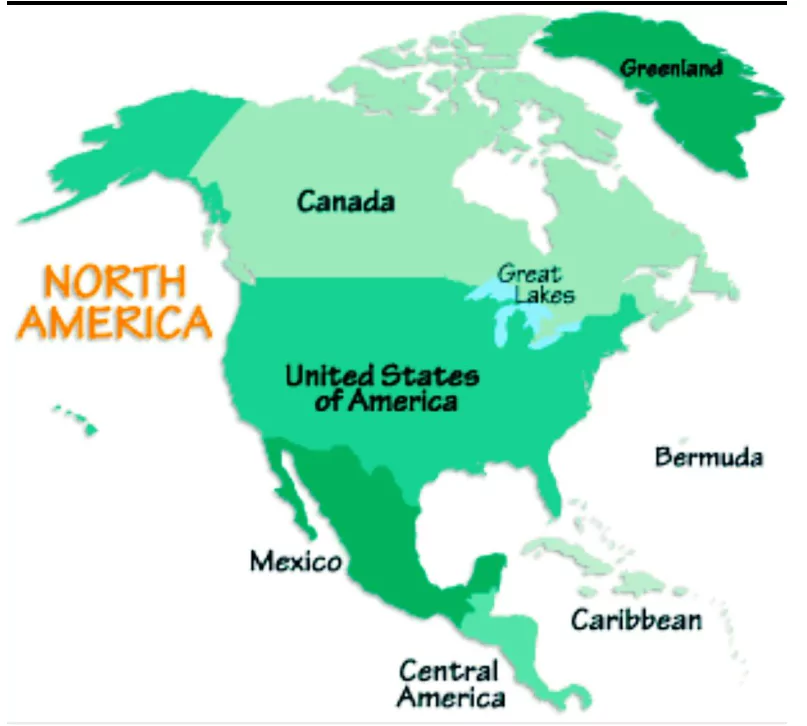
North America Continent Map
Filling plates globally, North America earns its laurels as the greatest producer of maize, wheat, and soybeans. Notably, Cuba, known as the “Sugar Bowl of the World,” thrives in North America, standing as the largest sugar exporter within the seven continents.
Taking the third position among the seven continents, we shift our focus to Antarctica. This region, not only being the Earth’s coldest expanse but also the highest, driest, windiest, and least inhabited, offers captivating insights. Embracing 75% of the world’s ice and 70% of its freshwater, Antarctica is often referred to as the “Frozen Continent” or the “White Continent.”
Historically dubbed ‘Terra Australis Incognita,’ signifying the “undiscovered southern continent,” Antarctica experiences alternating periods of extreme daylight and darkness. The summer months, spanning December to February, bask in continuous 24-hour daylight, while the winter months, from late March to late September, remain cloaked in darkness.
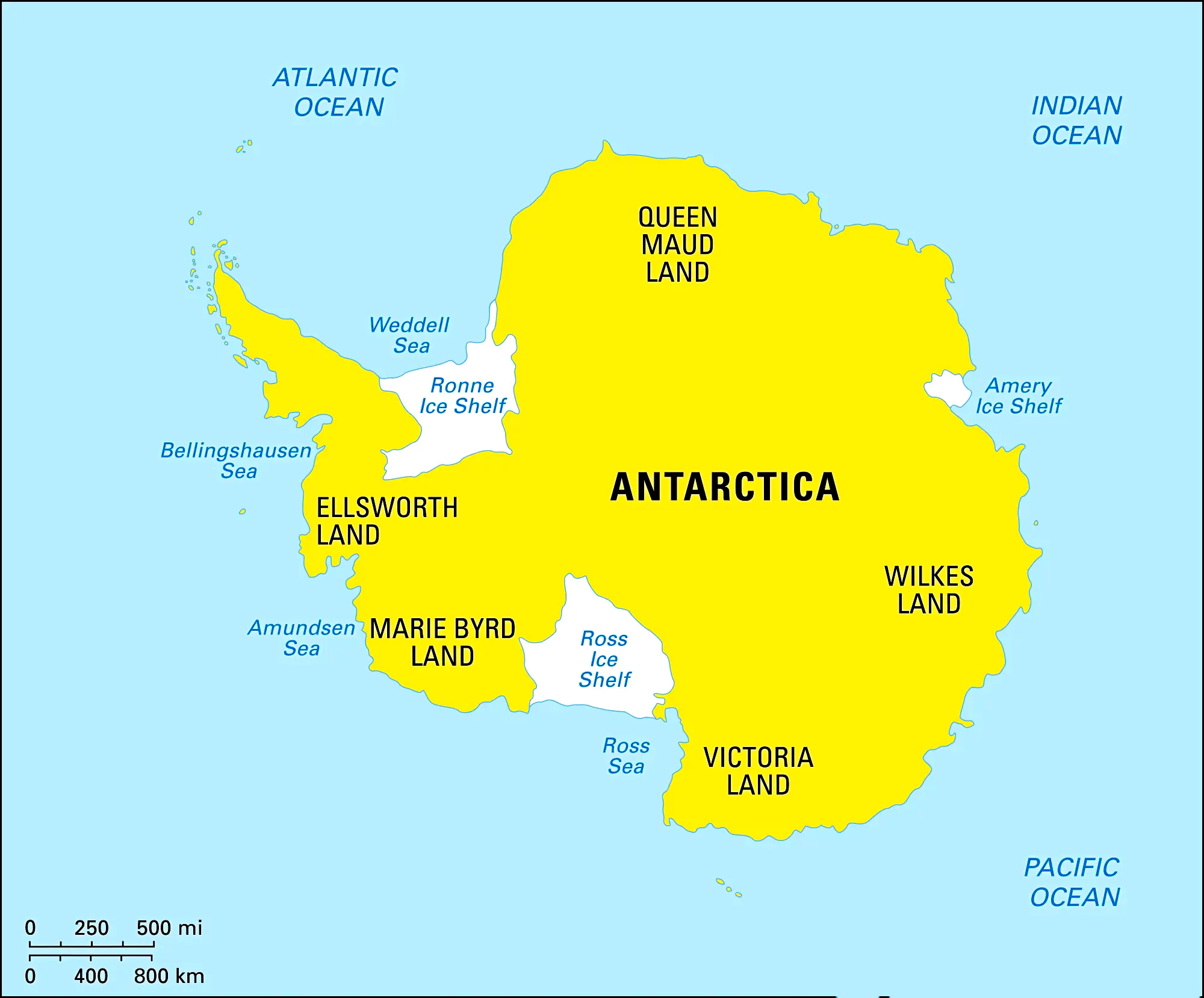
Amidst its varying temperatures, with the interior plummeting to approximately -35 degrees Celsius and coastal areas registering around 2 degrees Celsius, Antarctica holds the record for the planet’s most frigid natural temperature, a bone-chilling -89 degrees Celsius.
| Continent | Antarctica |
| Area (sq km) | 14,000,000 |
| Population (approx.) | Minimal (Research) |
| Countries | None (Treaty System) |
| Highest Point | Vinson Massif (Antarctica) |
| Longest River | None (Glacial Ice) |
| Largest Lake | Lake Vostok |
| Largest City | McMurdo Station, Antarctica |
| Dominant Language(s) | Various |
| Main Biomes | Ice Sheets, Tundra, Mountains |
| Economic Activities | Research, exploration, fishing |
Remarkably, time zones find no footing on this frozen land. The sole permanent settlements on Antarctica are the research bases, where experts from around the globe converge to conduct their vital work. Penguins, notably the Adelie penguins, call this frigid expanse home, adding life and vitality to its seemingly desolate landscapes.
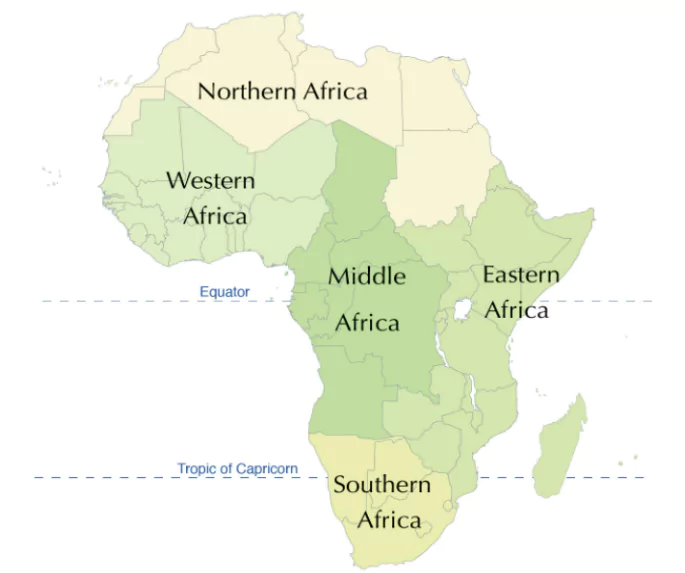 Africa Continent Map
Africa Continent Map
Seizing the fourth spot among the seven continents, our attention turns to Africa, a captivating landmass brimming with diverse attributes. As the second-largest continent after Asia, Africa’s topography was once uncharted and considered inhospitable, earning it the moniker “Dark Continent.” Boasting the world’s longest river, the Nile, and the largest desert, the Sahara, Africa holds a unique distinction.
Ethiopia, renowned as the world’s hottest country, finds its place within Africa’s borders. Situated squarely on the equator, Africa basks in direct sunlight throughout the year. It’s noteworthy that Homo sapiens are believed to have originated on this continent before dispersing to other parts of the world. Africa’s mineral-rich terrain contributes more than half of the world’s gold and an astounding 95% of its diamonds.
| Continent | Africa |
| Area (sq km) | 30,370,000 |
| Population (approx.) | 1.34 billion |
| Countries | 54 |
| Highest Point | Mount Kilimanjaro (Tanzania) |
| Longest River | Nile River (6,650 km) |
| Largest Lake | Lake Victoria |
| Largest City | Lagos, Nigeria |
| Dominant Language(s) | Arabic, French, English |
| Main Biomes | Sahara Desert, Congo Rainforest, Savannah |
| Economic Activities | Agriculture, mining, tourism, oil and gas |
Additionally, 66% of the world’s cocoa traces its roots to this continent. The captivating wildlife of Africa encompasses creatures like cheetahs, African elephants, lions, zebras, Egyptian mongooses, giraffes, and addaxes, adding to the continent’s allure.
Claiming the fifth place among the seven continents, we cast our gaze upon Europe, a realm distinguished by a fascinating interplay of geography and culture. Europe and Asia, though divided by the Ural Mountains and the Caspian Sea, are part of the same vast landmass. Rising as the tallest summit on this continent, Mt. Elbrus adds to Europe’s breathtaking scenery.
Europe boasts several significant mountain ranges, including the Balkans, Pyrenees, Apennines, Cantabrian, and Dinaric Alps. The Vatican City, acclaimed as the world’s smallest country, rests within Europe’s boundaries. The continent is adorned with an array of notable rivers, such as the Danube, Elbe, Loire, Oder, Dnieper, and Don. Boasting the world’s longest rail route, the Trans-Siberian Rail Route traverses Europe, connecting St. Petersburg in the west to Vladivostok in the east.
| Continent | Europe |
| Area (sq km) | 10,180,000 |
| Population (approx.) | 747 million |
| Countries | 50 |
| Highest Point | Mount Elbrus (Russia) |
| Longest River | Volga River (3,690 km) |
| Largest Lake | Lake Ladoga |
| Largest City | Istanbul, Turkey |
| Dominant Language(s) | Russian, German, French |
| Main Biomes | Mediterranean Forests, Taiga, Grasslands |
| Economic Activities | Manufacturing, tourism, finance, agriculture |
The Steppe region of Ukraine holds the moniker “World’s Granary” or “World’s Bread Basket.” Moscow, often referred to as the “Port of Five Seas,” intricately links five seas through its rivers and canals. Europe’s contribution to the world’s potato cultivation is a remarkable three-quarters, while the Volga River stretches as the continent’s longest.
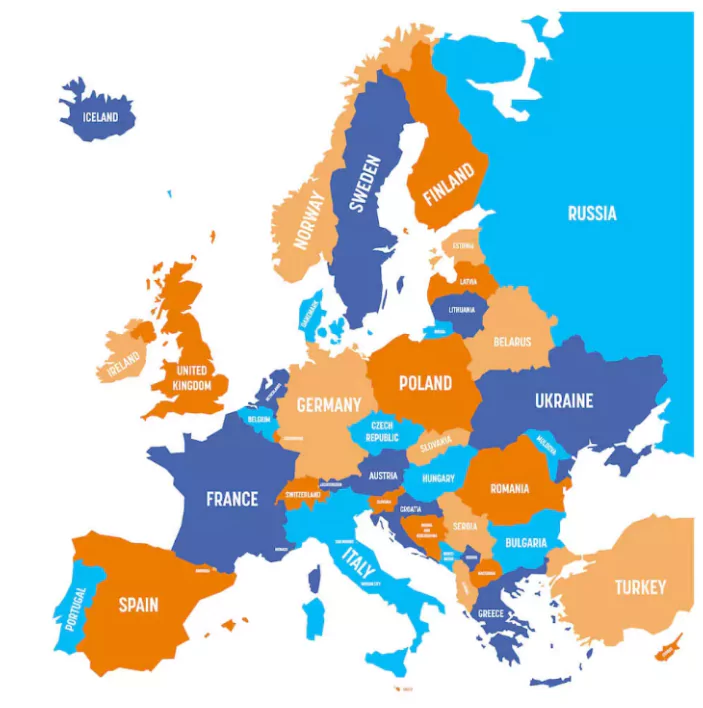
Europe Continent Map
Emerging as the sixth continent in the lineup of seven, we direct our attention to Australia, a unique “island continent” entirely enveloped by oceanic waters. Officially designated the Commonwealth of Australia, this compact landmass stands as the world’s smallest continent. Owing to its distinct geographical position, Australia is colloquially referred to as “down under.” Its nomenclature derives from the Latin term ‘australis,’ signifying “southern.”
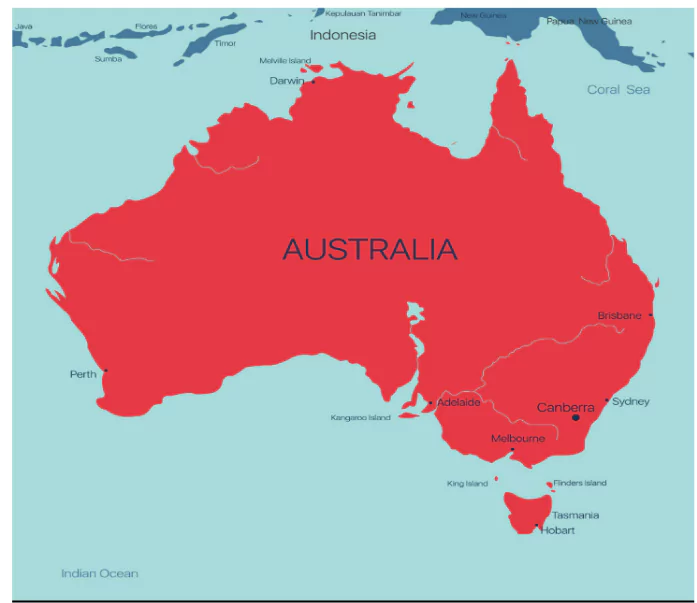
Australia Continent Map
A captivating facet of Australia is its exceptional wool production and import, attributed to a remarkable sheep population, surpassing its human populace by a factor of 14.
| Continent | Australia |
| Area | Approximately 8.6 million square kilometers |
| Population | Around 40 million |
| Countries | Consists of a single country: Australia |
| Highest Point | Mount Kosciuszko (2,228 meters) |
| Longest River | Murray-Darling River (2,508 kilometers) |
| Largest Lake | Lake Eyre (when filled, covering 9,500 square kilometers) |
| Largest City | Sydney, Australia |
| Dominant Language(s) | English |
| Main Biomes | Outback, Rainforests, Great Barrier Reef |
| Economic Activities | Mining, agriculture, tourism, manufacturing |
Securing the seventh and final place among the seven continents, we delve into the sprawling expanse of Asia, a colossal landmass revered for its sheer size and population. Encompassing a third of the Earth’s surface, Asia emerges as the largest continent, boasting 30% of the planet’s land area and accommodating a remarkable 60% of its inhabitants.
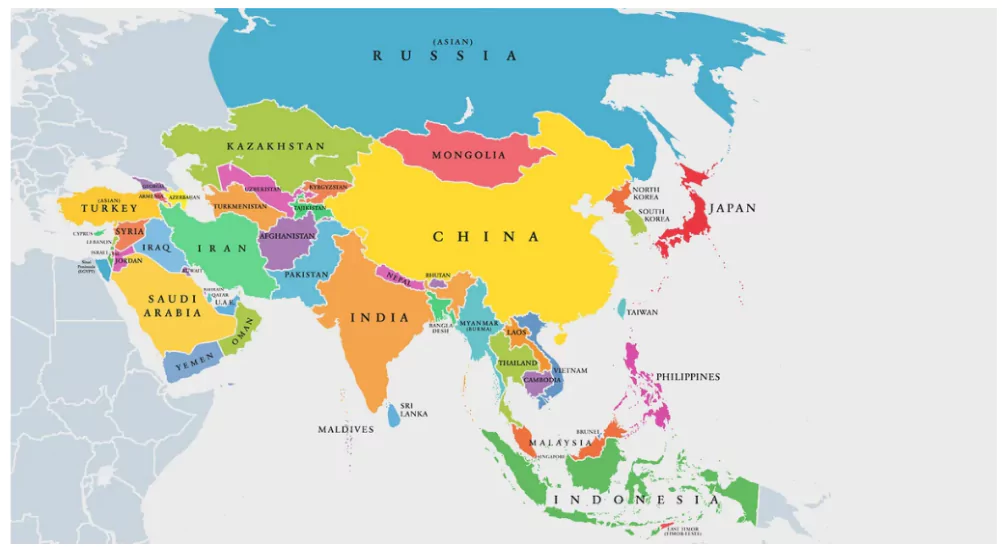
Asia Continent Map
The stature of Asia is amplified by its hosting of notable nations, including Russia, the world’s largest country, and China and India, the two most populous countries globally. The towering Mount Everest, with its peak soaring to 29,028 feet (8,848 meters), stands as a testament to Asia’s remarkable geography. Moreover, the continent is home to ten of the world’s tallest peaks.
| Continent | Asia |
| Area (sq km) | 44,579,000 |
| Population (approx.) | 4.64 billion |
| Countries | 49 |
| Highest Point | Mount Everest (Nepal/China) |
| Longest River | Yangtze River (6,300 km) |
| Largest Lake | Caspian Sea |
| Largest City | Tokyo, Japan |
| Dominant Language(s) | Mandarin, Hindi, Arabic |
| Main Biomes | Taiga, Gobi Desert, Himalayas, Rainforests |
| Economic Activities | Agriculture, manufacturing, technology |
The Great Wall of China, a marvel of human engineering, is the sole man-made structure visible from space. A cradle of civilization, Asia witnessed the emergence of two colossal ancient civilizations, namely the Harappan civilization and the Chinese civilization. As the birthplace of several major religions, including Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, and Christianity, Asia resonates with spiritual significance.
The Earth, our blue planet, is a magnificent tapestry of diverse landforms and water bodies that shape its breathtaking beauty and ecological harmony. Comprising of seven expansive continents and five vast oceans, our world is a fascinating mosaic of geographical wonders.
The Earth is home to five vast oceans that together cover over 70% of its surface, playing a crucial role in regulating the planet’s climate and supporting an huge diversity of marine life. Each of these oceans has unique characteristics and ecological significance. From the largest, the Pacific Ocean, to the smallest, the Arctic Ocean, these bodies of water connect continents and influence weather patterns, trade routes, and global ecosystems. Here is a detailed overview of the world’s five oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (or Antarctic), and Arctic. Here is the list of 5 oceans of the world are:
The Pacific Ocean stands as the planet’s largest and deepest body of water. Holding the record for the Earth’s greatest depth, the Mariana Trench is situated within the Pacific Ocean. Encompassing about 46% of the Earth’s water surface, the Pacific Ocean is vast. In terms of surface area, the Pacific Ocean’s expanse surpasses that of the entire land surface of the planet.
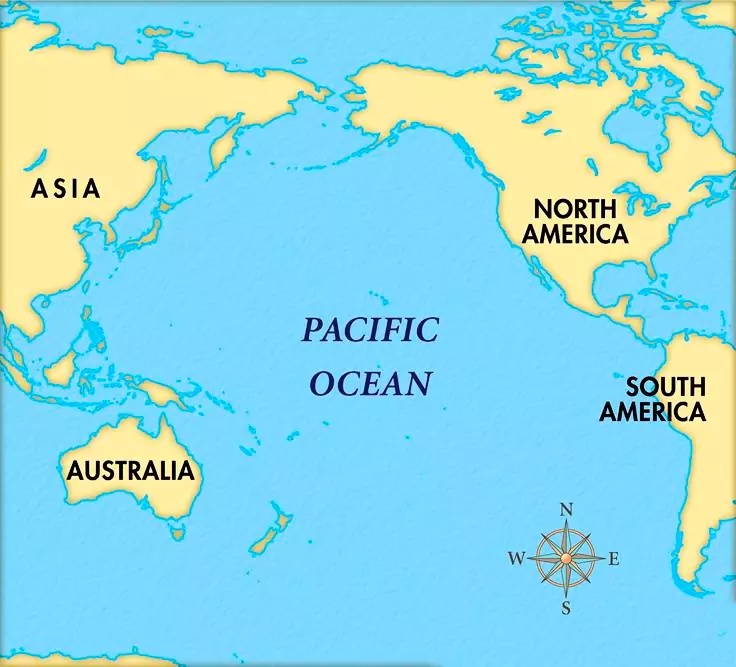
Pacific Ocean Map
| Some Characteristics of Pacific Ocean | |
| Characteristic | Description |
| Area | Approximately 168 million square kilometers |
| Average Depth | Around 4,280 meters |
| Deepest Point | Mariana Trench (Challenger Deep), about 10,994 meters |
| Location | Bounded by Asia and Australia to the west, the Americas to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Southern Ocean to the south |
| Major Currents | North Pacific Gyre, South Pacific Gyre, Kuroshio Current, California Current, Humboldt Current, and the Equatorial Currents |
| Climate Influence | Significant impact on global climate patterns, including El Niño and La Niña phenomena |
| Marine Biodiversity | Home to a diverse range of marine life, including coral reefs, fish, mammals, and numerous other species |
The Atlantic Ocean, the world’s second-largest ocean, spans approximately 85 million square kilometers. It is flanked by the Americas to the west and Europe and Africa to the east, with the Arctic Ocean to its north and the Southern Ocean to its south. Known for its significant depth, averaging around 3,646 meters, its deepest point is the Puerto Rico Trench, plunging to about 8,376 meters.The Atlantic Ocean
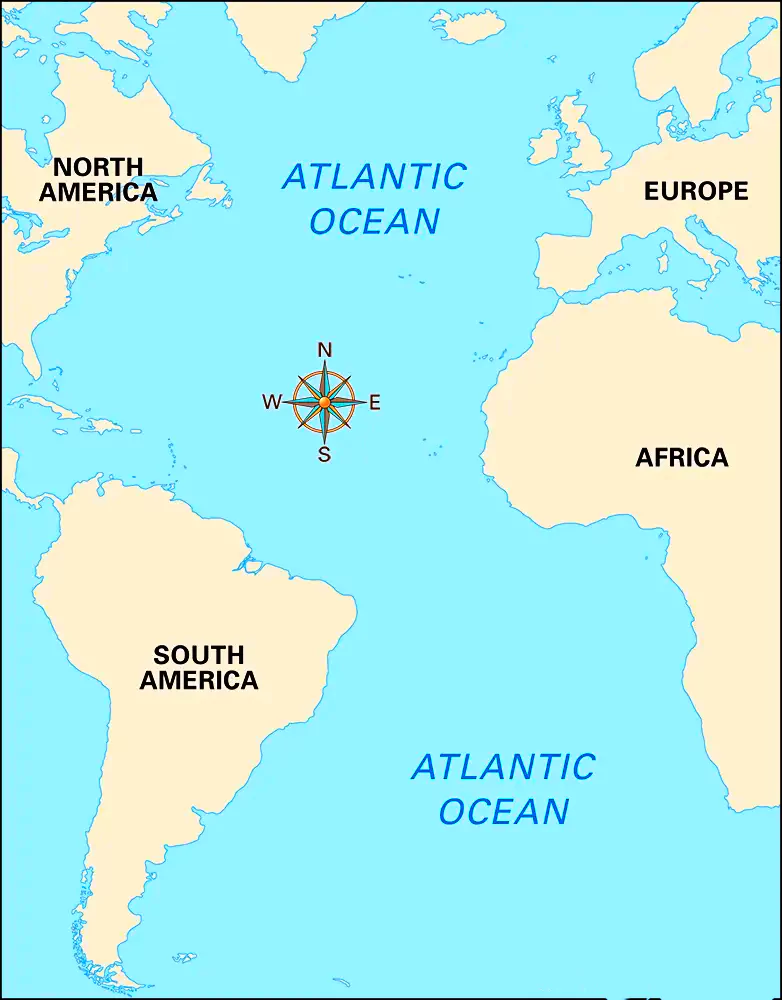
Atlantic Ocean Map
plays a crucial role in global climate systems, influencing weather patterns through phenomena such as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) and the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO).
| Ocean | Atlantic |
| Area | Approximately 85 million square kilometers |
| Average Depth | Around 3,646 meters |
| Deepest Point | Puerto Rico Trench (Milwaukee Deep), about 8,376 meters |
| Location | Bounded by the Americas to the west, Europe and Africa to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Southern Ocean to the south |
| Major Currents | Gulf Stream, North Atlantic Drift, Canary Current, Brazil Current, Benguela Current, and the South Equatorial Current |
| Climate Influence | Influences weather patterns, including the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) and the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) |
| Marine Biodiversity | Home to diverse marine life including fish, whales, dolphins, and important breeding grounds for many species |
| Economic Importance | Crucial for international shipping routes, fishing industries, and natural resources such as oil and gas |
| Islands | Includes islands and archipelagos such as the Caribbean islands, the Azores, Canary Islands, Cape Verde, and the British Isles |
Occupying the third largest position among the oceans is the Indian Ocean. Comprising about 20% of the Earth’s water surface, the Indian Ocean is substantial. Bound by Australia to its East, Africa to its West, and Asia to its North, the Indian Ocean’s limits are well-defined. Stretching southward from the Indian Ocean is the Antarctic Ocean.
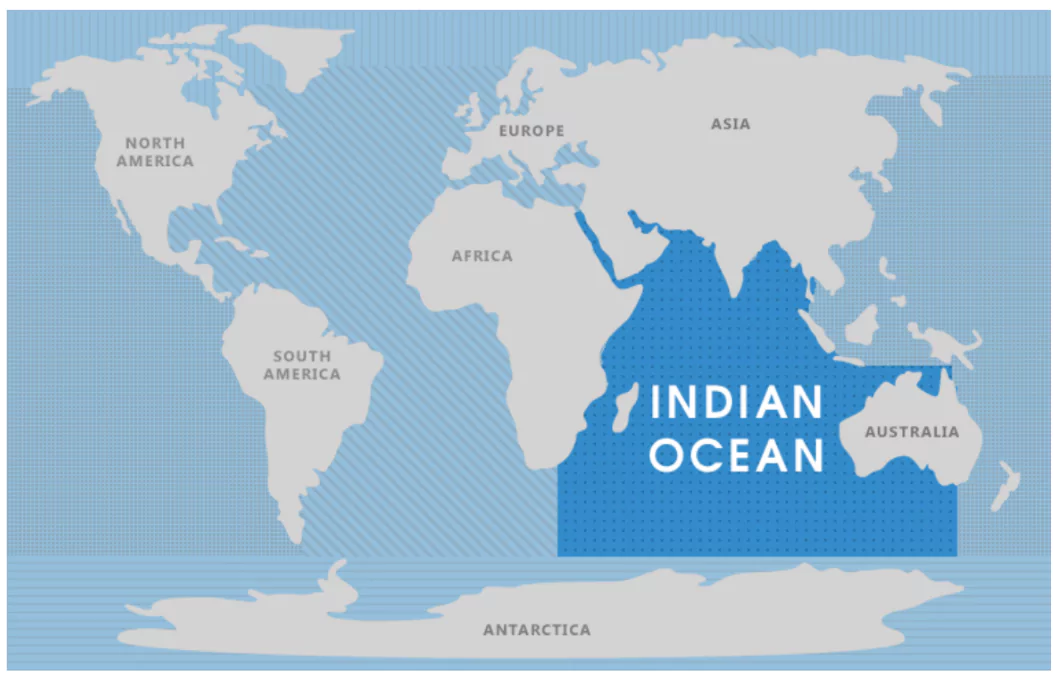
Indian Ocean Map
| Characteristic | Description |
| Area | Approximately 70 million square kilometers |
| Average Depth | Around 3,741 meters |
| Deepest Point | Java Trench (Sunda Trench), about 7,258 meters |
| Location | Bounded by Africa to the west, Asia to the north, Australia to the east, and the Southern Ocean to the south |
| Major Currents | Indian Monsoon Current, Agulhas Current, Somali Current, and the South Equatorial Current |
| Climate Influence | Influences the monsoon weather patterns, critical for agriculture in surrounding regions |
| Marine Biodiversity | Rich in marine life including coral reefs, diverse fish species, marine mammals, and unique ecosystems |
| Economic Importance | Key shipping routes connecting the Middle East, Africa, and East Asia, with significant oil and gas resources and fisheries |
| Islands | Includes islands and archipelagos such as Madagascar, the Maldives, Seychelles, Sri Lanka, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
The Antarctic Ocean also known as the Southern Ocean, surrounds the southernmost continent of Antarctica. It is known for its icy landscapes and extreme conditions, it plays a crucial role in shaping Earth’s climate and oceanic currents. Despite its harsh environment, the Antarctic Ocean supports a rich variety of marine life, adapted to its unique conditions. From towering icebergs to diverse ecosystems beneath the surface, this oceanic realm offers valuable insights into the complexities of our planet’s southernmost waters.
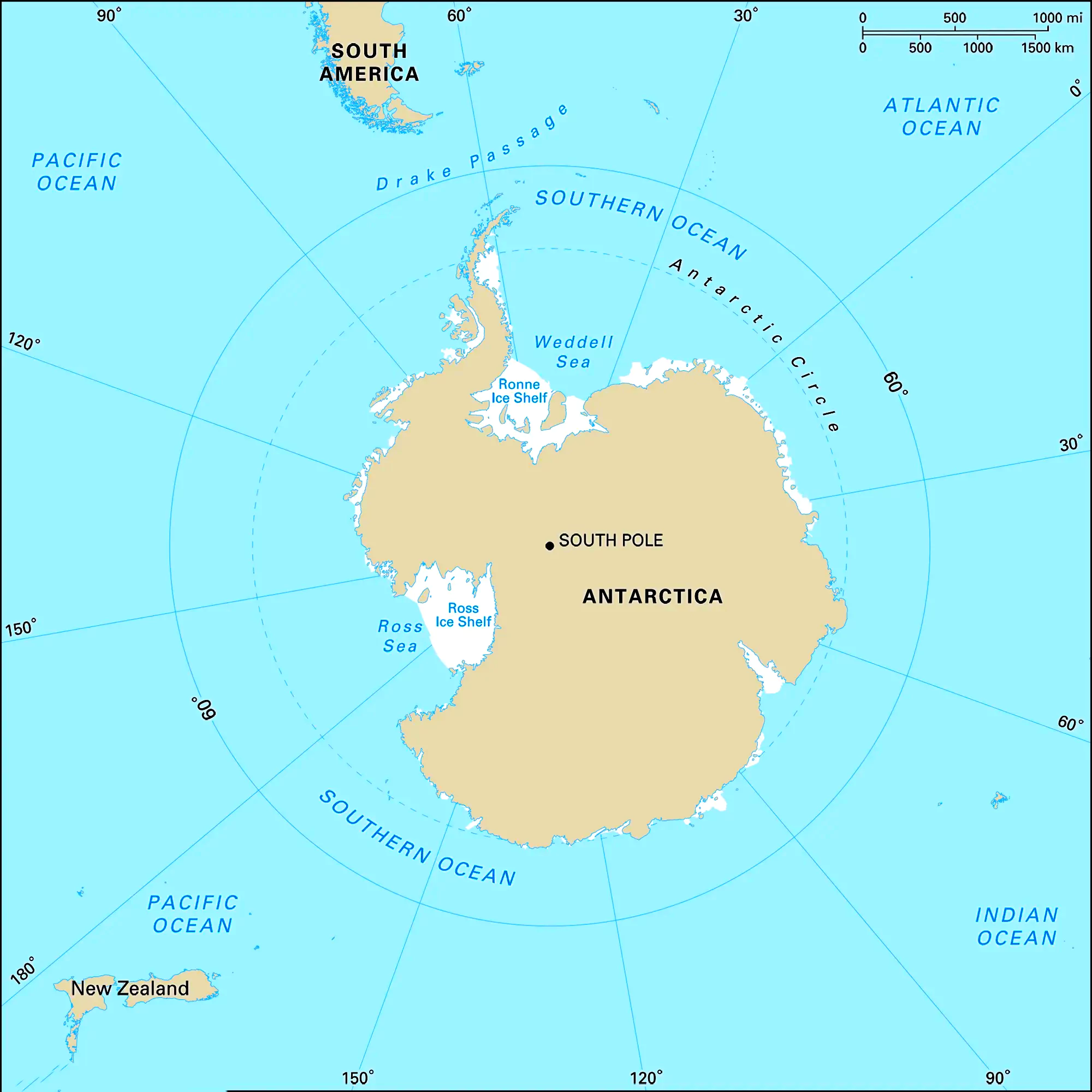
Antarctica Ocean Map
| Name | Antarctic Ocean (Southern Ocean) |
| Area | Approximately 20 million square kilometers |
| Average Depth | Around 3,000 to 4,000 meters |
| Deepest Point | Unknown |
| Location | Surrounds Antarctica |
| Major Currents | Antarctic Circumpolar Current |
| Climate Influence | Plays a significant role in global climate regulation and oceanic circulation |
| Marine Biodiversity | Supports diverse marine life adapted to extreme cold, including fish, seals, and whales |
The Arctic Ocean, Earth’s smallest and shallowest major ocean, lies at the top of the world. Amidst its icy expanse, climate change is rapidly melting ice, affecting sea levels and ecosystems. Home to polar bears and seals, this delicate region’s changes demand global attention for understanding and conservation.
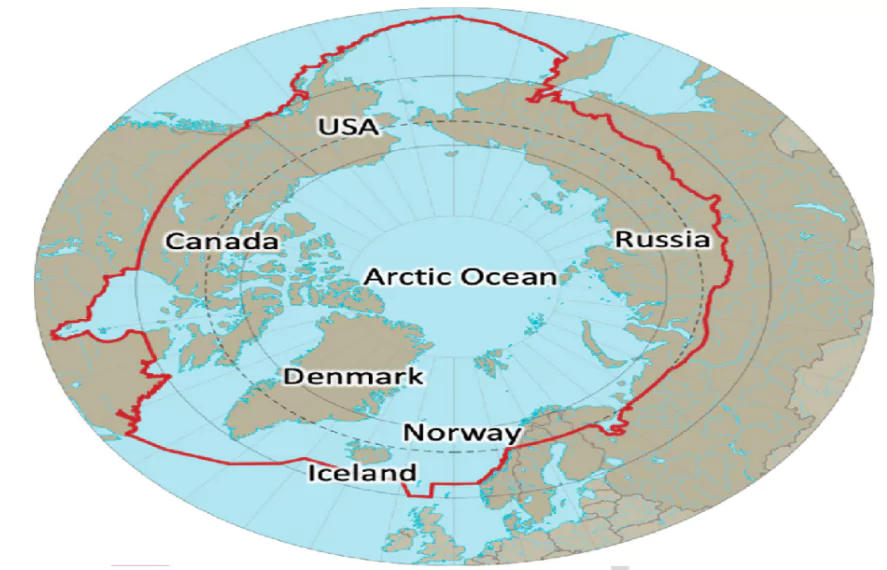
Arctic Ocean Map
| Name | Arctic Ocean |
| Area | Approximately 14 million square kilometers |
| Average Depth | Around 1,200 meters |
| Deepest Point | Fram Strait (around 5,450 meters) |
| Location | Centered around the North Pole |
| Major Currents | Transpolar Drift, Beaufort Gyre, East Greenland Current |
| Climate Influence | Plays a crucial role in regulating global climate, especially affecting polar regions |
| Marine Biodiversity | Supports unique marine life adapted to cold conditions, including polar bears and seals |
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series |
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
While a significant portion of Russia's landmass lies in Asia, it's important to note that Russia is also a part of Europe. This is due to the fact that the capital of Russia is situated within the European region.
Seven continents (namely, North America, South America, Europe, Africa, Asia, Australia, and Antarctica), the five oceans (including the Pacific, Atlantic, Arctic, Indian, and Southern oceans), as well as the cardinal directions (North, South, East, West).
The arrangement of the five oceans, ranging from the tiniest to the most expansive, goes as follows: the Arctic Ocean, the Southern Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Pacific Ocean.
There are seven continents in the world such as Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia (or Oceania).
The 7 continents are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. The 5 oceans are: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (or Antarctic), and Arctic.
The 7 continents of the world are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.
The largest continent in the world is Asia.
The smallest continent in the world is Australia.
The 7 continents from largest to smallest are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.
The oldest continent, in geological terms, is often considered to be Africa, particularly the East African region.
The 5 oceans of the world are: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (or Antarctic), and Arctic.
The largest ocean in the world is the Pacific Ocean.
The smallest ocean is the Arctic Ocean.
The total area of the 7 continents is approximately 148.94 million square kilometers.
Australia is a continent because it is a large landmass that sits on its own tectonic plate, distinct from other landmasses, and has unique flora and fauna.
Antarctica is considered a continent because it is a large, continuous landmass entirely covered by ice and surrounded by the Southern Ocean. Greenland, although large, is considered part of the continent of North America.
Antarctica is a continent because it is a large, continuous landmass. The Arctic is not considered a continent because it is mostly composed of ice-covered ocean and does not have a central landmass.
The order of the world's five primary oceans, based on their dimensions, includes the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean holds the title of the most extensive ocean, covering more than a third of the Earth's surface.
The seven oceans are the Arctic, North Atlantic, South Atlantic, North Pacific, South Pacific, Indian, and Southern Oceans.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
