Context:
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra officially launched ‘Urea Gold’ fertilizer.
About Urea Gold:
- It is basically urea fortified with Sulphur.
- Developed by: The state-owned Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd (RCF)
- Composition: Urea Gold contains 37% nitrogen (N) and 17% Sulphur, differing from regular urea’s 46% nitrogen composition.
- Objectives:
- Addressing Sulphur (S) deficiency in Indian soils, especially crucial for oilseeds and pulses.
- Enhancing the nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of urea through a gradual release of nitrogen. Coating of S over urea ensures a more gradual release of N.
- Commercial Aspects:
- Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd (RCF) has yet to launch Urea Gold commercially and disclose pricing details.
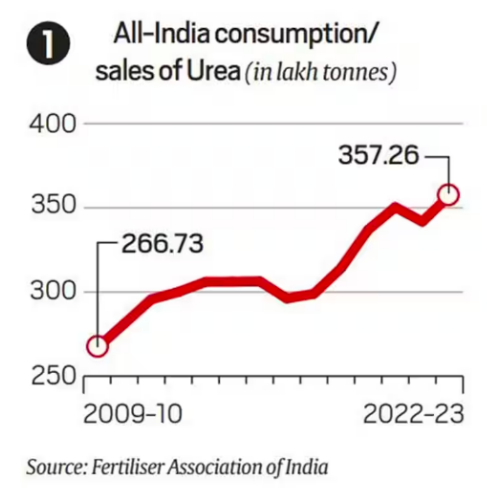
Concerns Over Rising Urea Consumption:
- Consumption of Urea: Consumption/Sales rising from 26.7 million tonnes (mt) to 35.7 mt between 2009-10 and 2022-23.
- Imports: In the previous fiscal year, 7.6 million tonnes (mt) of the total 35.7 mt of urea sold were imported.
- Domestic Feedstock: Even domestically-produced urea relies on imported natural gas as its primary feedstock.
 Comparison with China: India’s annual urea consumption of nearly 36 mt ranks second only to China’s 51 mt, which primarily relies on coal-based production.
Comparison with China: India’s annual urea consumption of nearly 36 mt ranks second only to China’s 51 mt, which primarily relies on coal-based production.
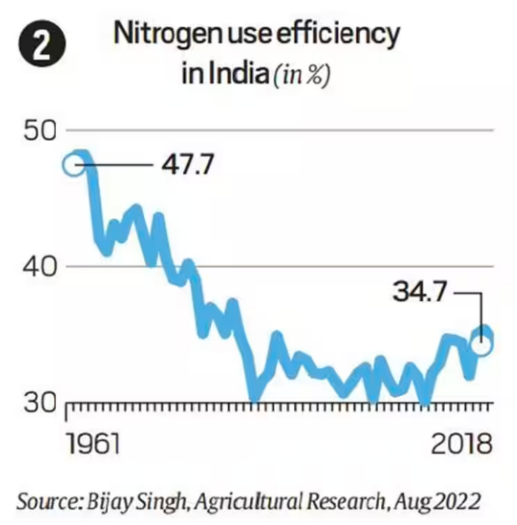
- Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) Issue:
- Utilization: Merely about 35% of the nitrogen (N) applied through urea is effectively used by crops to generate harvest yields.
- Losses: Approximately 65% of the nitrogen remains inaccessible to plants. This portion is either released as ammonia gas into the atmosphere or leaches into the ground as nitrate.
- Impact on Farming: The decreasing NUE, which was around 48% in the early 1960s, has resulted in farmers needing to apply larger quantities of fertilizer to achieve the same yield.
Way Forward:
- Fortification Approach
- Proposed approach involves coating fertilizers for improved efficacy.
- Primary nutrient fertilizers should be coated with secondary nutrients (S, calcium, magnesium) and micronutrients (zinc, boron, manganese, molybdenum, iron, copper, nickel).
- Benefits of Coating:
- Coated fertilizers serve as effective “carrier products” to deliver additional nutrients to crops.
- Coating enhances N and P use efficiency through controlled release and synergistic effects.
- Losses in fertilizers like urea due to ammonia volatilization and nitrate leaching are reduced.
News Source: The Indian Express
![]() 14 Aug 2023
14 Aug 2023

 Comparison with China: India’s annual urea consumption of nearly 36 mt ranks second only to China’s 51 mt, which primarily relies on coal-based production.
Comparison with China: India’s annual urea consumption of nearly 36 mt ranks second only to China’s 51 mt, which primarily relies on coal-based production.