Context:
Recently, scientists from the Nigerian Centre for Disease Control applied metagenomic sequencing for pathogen surveillance and detection in three cohorts of patients.
More on News:
| Metagenomic sequencing is a sequencing method whereby billions of nucleic acid fragments can be simultaneously and independently sequenced. |
- The first cohort represented population-level surveillance of individuals presenting with symptoms consistent with Lassa fever.
- Lassa fever is a viral haemorrhagic fever caused by the Lassa virus endemic to West African countries.
- The second cohort consisted of people from outbreaks with suspected infectious aetiologies.
- The third cohort consisted of people with clinically challenging but undiagnosed conditions.
About Genome:
- The genome is the blueprint of life, a collection of all the genes and the regions between the genes contained in our 23 pairs of chromosomes.
- Each chromosome is a contiguous stretch of DNA string. In other words, our genome consists of 23 different strings, each composed of millions of individual building blocks called nucleotides or bases.
Genome sequencing:
- Genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome.
- The DNA consists of a double-stranded molecule built up by four bases – adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
- The process of deciphering the order of base pairs, to decode the genetic fingerprint of a human is called genome sequencing.
Impact of COVID-19 on Genomic Surveillance:
- Initial Breakthrough in Identification: A crucial breakthrough in identifying SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19, came from unbiased genome sequencing of patient samples.
- Traditional microbiology was bypassed in favor of direct genome sequencing and bioinformatic analysis, enabling swift virus identification.
- Emergence of Metagenomics: A novel approach called metagenomics emerged, allowing rapid and direct application to patient samples.
- Metagenomics played a key role in quickly identifying SARS-CoV-2 and became a revolutionary tool in pathogen identification.
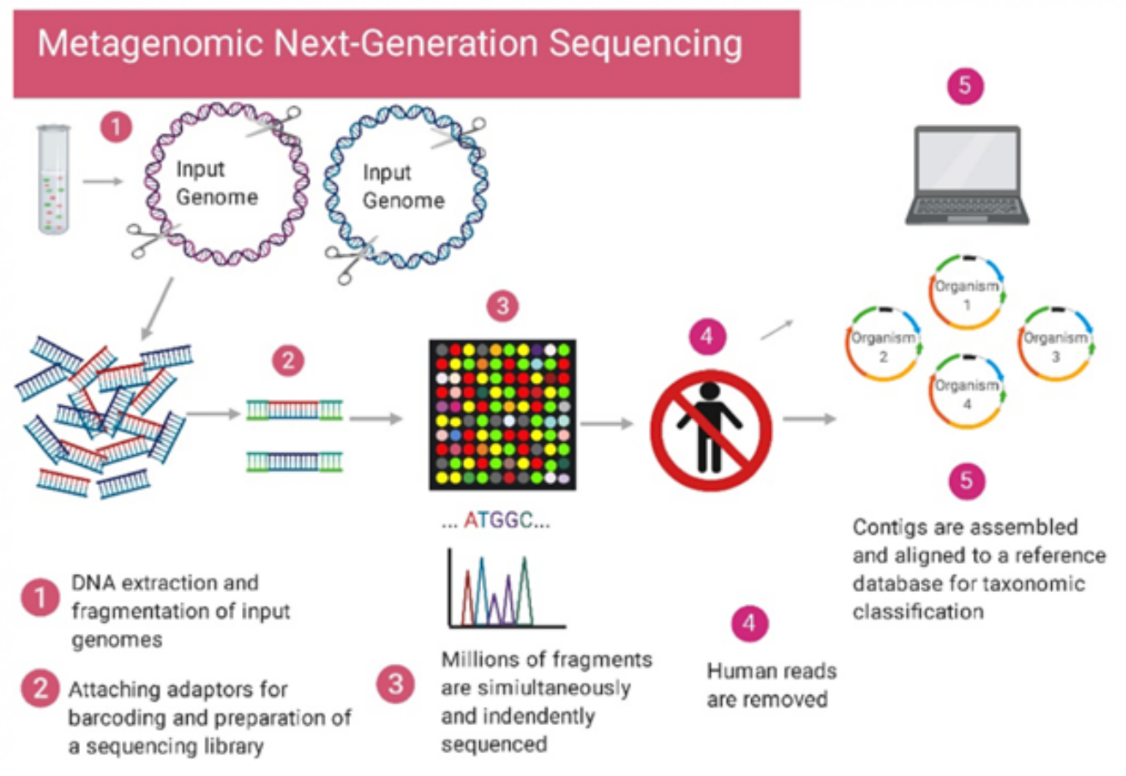 Image Source: American Society for Microbiology
Image Source: American Society for Microbiology
Transformative Technologies and Applications:
- Genome-Based Technologies: Genome sequencing technologies developed post-COVID-19, like the CovidSeq assay, drove various SARS-CoV-2 genome surveillance initiatives.
- India initiated a national SARS-CoV-2 genome-sequencing and surveillance program, supported by state governments and private initiatives.
Advantages and Future Prospects:
- Faster identification: Genome surveillance furnishes crucial information for early response strategies, identifying emerging strains, and monitoring key species.
- Future Ready: Genomic technologies are poised to become essential tools in combating future pathogenic challenges.
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 14 Aug 2023
14 Aug 2023
 Image Source: American Society for Microbiology
Image Source: American Society for Microbiology