Context:
- A steeplechaser and a sprinter at the Delhi Athletics Championship fled dope testers, highlighting the deep-rooted doping menace in Indian athletics.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Ethics in Sports, Indian Athletics Championship, Olympic, National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA), and World Anti-Doping Agency’s (WADA’s).
Relevancy for Mains: What is doping, Sports Ethics, The World Anti-Doping Code, Cheating In Sports Ingrained?, and case related doping. |
Doping Shadows- A Call for Anti-Doping Reform In Sports
- The rot runs so deep that syringes lying in the washrooms (viral Images and videos) during even school and university events are a common sight in the country.
- At the core of this corruption is the encouragement of coaches and parents for quick fixes, and the lethargy of India’s anti-doping machinery.
- The National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) has been ineffective in preventing doping, with competitions in remote corners of India taking place without anti-doping officials present.
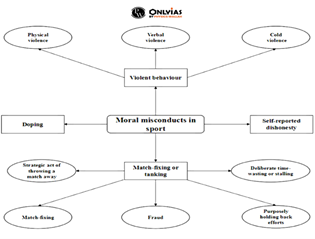
What is Sports Ethics?
- Sports ethics is a positive concept that guides human action in sports.
- It is defined as the code of conduct for promoting and ensuring healthy sporting practices.
- Sports ethics signifies not just a certain form of behavior but also a particular way of thinking
|
What are the ethics in Sports?
The World Anti-Doping Code states that there is an intrinsic value in sports that is the celebration of the human spirit, body, and mind, and is reflected in values other than winning or being the first in any sports game.
- The spirit of sports includes ethics, fair play and honesty. Anti-doping practices are based on this ethical ground and are supported all through the world.
- Sports can teach values such as fairness, team building, equality, discipline, inclusion, perseverance and respect.
- Sport has the power to provide a universal framework for learning values, thus contributing to the development of soft skills needed for responsible citizenship.
WADA report on anti-doping violations
- India is already one of the top-tier anti-doping violators in the world.
- A World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) report published in December 2022 revealed that India, with 59 instances, comes behind the perennial chart-topper, Russia, which has 135 cases in 2020.
What is Doping?
- The use of substances prohibited by the anti-doping agencies in order to gain a competitive advantage is called Doping.
- Narcotics and analgesics, anabolic steroids, hormones, and selective androgen receptor modulators are among the most frequently utilized substances.
- For example: SARMs (Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators) are getting more and more popular in India.
|
What are the reasons for moral misconduct?
- Attraction of Sports:Young people are attracted to sport for a variety of reasons including quests for excitement, participation, health, competition, acknowledgment, prestige, and profit.
- What differentiates elite athletes from their non-elite counterparts is their ability/talent, and their desire to compare and contest this against other elites.
- Pressure for performance enhancement: Depending on the sport practiced and the physical attributes it requires, the athletes will look for one or more of the following benefits of doping: recovering from an injury, increasing body recovery capacity after training, increasing muscle mass and strength, decreasing fat tissue, and increasing endurance.
- Excessive Wealth and Fame: Today sports mean sponsors, advertising contracts and money and for that some believe that any risk is worth taking.
- sports are no longer just sports; as sports become an industry, a business, and a reason for political or national pride, these facts can only lead to breaking any rules to win.
- Advancement in Technology:
- Although anti-doping controls are becoming more rigorous, doping and, very importantly, masking doping methods are also advancing, and these are usually one step ahead of doping detection techniques.
| Case Study
Lance Armstrong was a professional cyclist and cancer survivor.
- He was accused of doping for years, and in 2012, the United States Anti-Doping Agency released evidence that verified his doping activities.
- Armstrong was stripped of his seven Tour de France titles and banned from Olympic sports for life.
- In 2013, he admitted to doping for the first time, saying that he did it to remain competitive because other cyclists were also doping.
|
Doping Cases in India
- Sanamacha Chanu (WEIGHTLIFTING)
- In September 2010, she tested positive for a banned substance, her second offense after being caught at the 2004 Athens Olympics. Monika Devi (WEIGHTLIFTING)
- India’s lone weightlifting entry at the 2008 Beijing Olympics, tested positive for an anabolic salt.
- Narsingh Yadav (WRESTLING)
- Days before heading to Rio de Janeiro for the 2016 Olympics, tested positive for methandienone, a banned anabolic steroid.
- Renjith Maheshwary (ATHLETICS)
- The Kerala triple-jumper was suspended for three months in 2008. He had tested positive for ephedrine.
|
Implication
Since sports play an important role in physical and mental education and in promoting international understanding and cooperation, the widespread use of doping products and methods has consequences not only on the health of the athletes but also on the image of the sport.
Way forward
- Clean Sports Concept:
- Conceptualizing doping as a sports integrity issue, we need to move away from the archaic and delimiting view of clean sport as a drug-free sport.
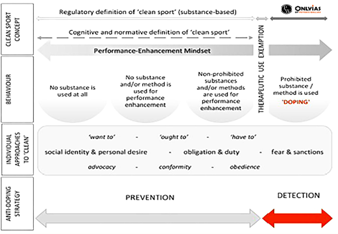
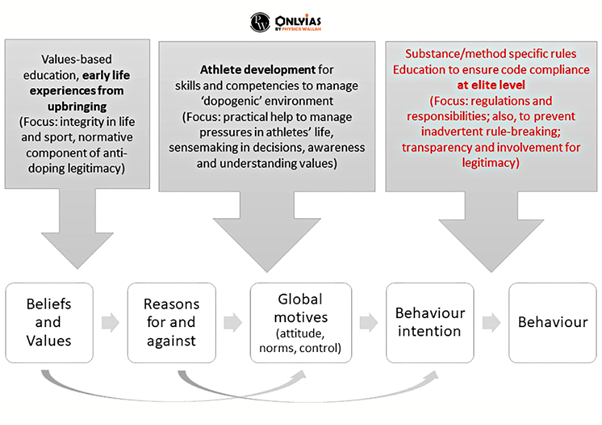
- Behavioral Approaches:
- Reconciliation of values-based education, awareness raising and anti-doping education within the broader scope of integrity, to support informed decision-making and personal agency.
- The focus here should be on developing life skills that help to cope with stress and pressure without resorting to unethical means necessary to establish and maintain correct attitudes and behaviors.
- Anti-doping Strategy in Sports:
- NADA must keep athletes in the Registered Testing Pool (RTP) and regular testing, more out of competition than during competition.
- Strict Legislation and Regulation:
- Stricter legislation with the involvement of authorities is required to prevent the spread, marketing and use of such substances.
Conclusion:
“If excellence is achieved in the form of execution and performance, winning will frequently follow.”
![]() 28 Sep 2023
28 Sep 2023



