Learn about One Nation One Election, its history, significance, benefits, challenges, and recent developments, including constitutional amendments needed for simultaneous elections in India.

One Nation One Election: The One Nation, One Election proposal, recently approved by the Indian government, aims to hold simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha, state legislative assemblies, and local bodies across the nation. This action seeks to streamline the election process, reduce costs, and improve governance by limiting the frequency of election-related disruptions. A high-level committee chaired by former President Ram Nath Kovind has been set up to explore the feasibility of this ambitious plan. The proposal has created widespread debate which highlights the potential benefits such as cost savings and consistent governance, but also raises concerns about its logistical and constitutional challenges. In this guide, we will provide an overview of why this proposal is in the spotlight, the key recommendations of the committee, and the history of the proposal.
Recent Update on One Nation One Election
The One Nation One Election initiative has garnered renewed attention, with government sources indicating that the earliest possible date for synchronized Lok Sabha and State Assembly elections would be 2034, provided the Bills cleared by the Cabinet are passed by Parliament without amendments.
On Wednesday, September 18, 2024, the Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, has accepted the recommendations of the High-Level Committee on Simultaneous Elections under the chairmanship of former President Shri Ram Nath Kovind. It proposed simultaneous elections to the Lok Sabha and State Assemblies as the first step, and municipal and panchayat polls within 100 days of the general election in the next phase.
The objective of this report is to reduce electoral fatigue, improve governance, and minimize public expenditure.
Some sources indicate that the bill for conducting these simultaneous elections is expected to be introduced during the upcoming winter session of Parliament.
One nation one election, also known as simultaneous elections, refers to the practice of holding elections to Lok Sabha, all the state assemblies, and local bodies – municipalities and panchayats, together.
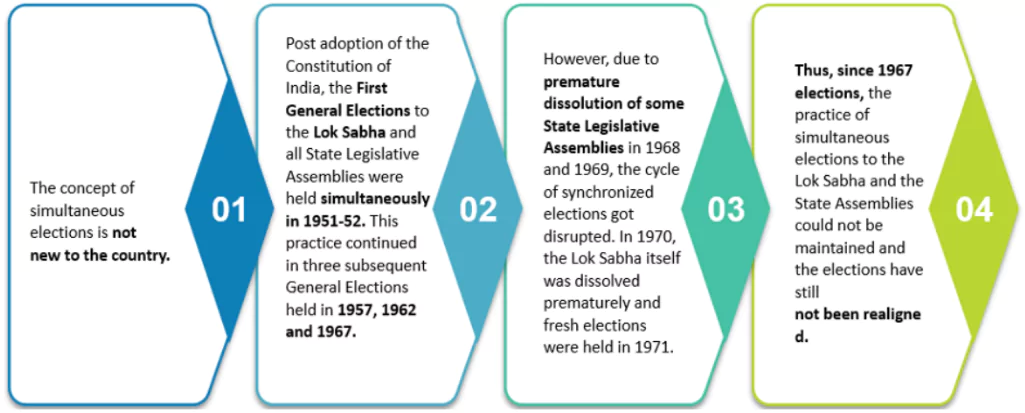
The concept of One Nation, One Election dates back to India’s early years of independence when simultaneous elections were held for both the Lok Sabha and state assemblies in 1951-52, 1957, 1962, and 1967. However, the cycle was disrupted after 1967 due to the premature dissolution of some state assemblies and the Lok Sabha itself in 1970. Since then, elections have been held separately, leading to increased costs and administrative challenges. The idea was revived in recent years as a potential reform to streamline India’s electoral process.
| Advantages of One Nation One Election |
|
| Disadvantages of One Nation One Election |
|
The policy of One Nation One Election is not possible in the current framework of the constitution, so we require some essential amendments in the constitution to implement this policy:
| South Africa |
|
| Sweden |
|
| Belgium |
|
| For the Lok Sabha |
|
| For Legislative Assemblies |
|
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Election Commission Of India | Lok Sabha Election Results 2024 |
| Election System In India | Panchayati Raj In India |
| Electoral Bonds Scheme | ARTICLE 370 OF INDIAN CONSTITUTION |
"One Nation One Election" refers to the practice of holding simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha (national) and state assemblies at the same time.
Simultaneous elections can lead to cost savings, long-term governance focus, increased voter turnout, and efficient use of resources like security forces.
Amendments to Articles 83, 85, 172, and 174 of the Indian Constitution are required to enable simultaneous elections.
Yes, challenges include synchronization difficulties, potential impact on federalism, voter behavior complexities, and implications for regional parties.
Some countries like South Africa, Sweden, and Belgium have elections for different levels of government synchronized at various intervals.
One proposed approach is to conduct elections in two phases, syncing state elections with Lok Sabha elections, and avoiding premature dissolution through specific recommendations.
Yes, smaller parties may compete more effectively with larger ones due to reduced overall election expenses, creating a more level playing field.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>