Context:
- The Central Government is looking at offering SOPs (Standard Operating Procedure) along the lines of a production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for manufacturing Small Modular Reactors (SMR), aiming to increase the share of nuclear power in India’s energy basket.
India’s Nuclear Power Capacity
- Currently, India’s installed nuclear power capacity stands at 7.48 GW and is expected to reach 22.28 GW by 2031.
- The push for nuclear power, which is considered to be a cleaner fuel or non-fossil fuel, comes in the backdrop of India’s ambitious net zero goals ( India has pledged to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2070).
- A NITI Aayog report says that given the nascent nature of the technology and investor perceptions of business and regulatory risks, collaborative involvement of government and private sectors is critical to de-risk projects and accelerate commercialization.
- India is having bilateral talks with France, Russia, South Korea, and the US for the required technologies and investments.
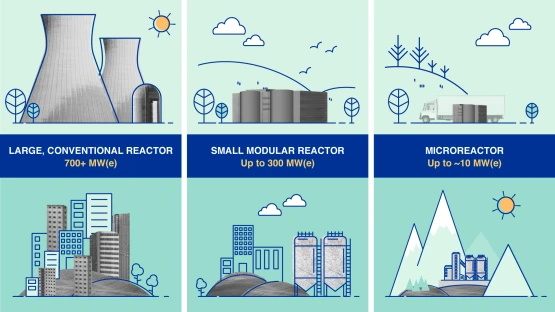
What are the Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)?
Small modular reactors (SMRs) are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors. Small modular reactors, which can produce a large amount of low-carbon electricity, are:
- Small – physically a fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor.
- Modular – making it possible for systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation.
- Reactors – harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)- Types
| Land-based water-cooled SMRs |
This includes the water-cooled Small Modular Reactor designs having different configurations of Light Water Reactor (LWR) and Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) technologies for on-land applications. |
| Marine-based water-cooled SMRs |
This includes the water-cooled Small modular reactor designs for deployment in a marine environment. This can be achieved by floating units installed on barges or ships.
- Russia’s Akademik Lomonosov, the world’s first floating nuclear power plant that began commercial operation in May 2020, is producing energy from two 35 MW(e) Small modular reactors.
|
| High-temperature gas-cooled SMRs (HTGRs) |
This can provide very high-temperature heat of more than 7500C and thereby higher efficiency in electricity generation.
Application: Industry and Co-geneneration. |
| Liquid metal-cooled fast neutron spectrum SMRs (LMFRs) |
This includes designs based on fast neutron technology with different coolant options including helium gas and liquid metal coolants like sodium, lead, and lead-bismuth. |
| Molten salt reactor SMRs (MSRs) |
This is based on molten fluoride or chloride salt in the role of coolant. MSR designs for both thermal neutron and fast neutron spectrums are under development. These technologies can sustain long fuel cycles of several years, and have an option for online refueling in which fresh fuel can be introduced in molten form, and cleaning of fission products can also be performed online. |
| Microreactors (MRs) |
MRs are very small SMRs designed to generate electrical power typically up to 10 MW(e). Different types of coolants, including light water, helium, molten salt, and liquid metal are adopted by microreactors. |
Advantages of SMRs: Many of the benefits of Small modular reactors (SMRs) are inherently linked to the nature of their design – small and modular.
- Low Cost: Prefabricated units of Small modular reactors can be manufactured and then shipped and installed on-site, making them more affordable to build than large power reactors, which are often custom-designed for a particular location, sometimes leading to construction delays.
- Accessibility: In areas lacking sufficient lines of transmission and grid capacity, SMRs can be installed into an existing grid or remotely off-grid, as a function of its smaller electrical output, providing low-carbon power for industry and the population.
- Emergency Backup: Small modular reactors can serve as a backup power supply in emergency situations or replace power generators that are often fuelled by diesel, for example, in rural communities or remote businesses.
- Safety and Nuclear Waste: Compared to existing reactors, proposed SMR designs are generally simpler, and the safety concept for Small modular reactors often relies more on passive systems (no human intervention or external power or force is required to shut down systems).
- Reduced fuel Requirements: Power plants based on Small modular reactors may require less frequent refueling, every 3 to 7 years, in comparison to between 1 and 2 years for conventional plants.
- Green Transition: The SMRs can accelerate the energy transition by facilitating greater penetration of nuclear energy.
What are the challenges associated with Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)?
- Range of Capacity: Since, Small modular reactors have a very wide range of capacity sizes ranging from less than 30 MW(e) to 300+ MW(e), which are too many for sustained growth of the SMR industry.
- Regulatory Challenge: A large number of technologies, if adopted for deployment at the same time, could not only create regulatory challenges for the nuclear industry but also take away some degree of cost optimization.
- Nascent Technology: The Small modular reactor industry is yet to realize a fully developed operational fabrication facility for large scale serial manufacturing of SMR components.
- Capital: Technology developers have challenges in mobilizing finance for technology development, licensing, and construction of prototype plants.
Source: Live Mint
![]() 4 Nov 2023
4 Nov 2023
