UPSC IFS Civil Engineering Optional 2026 covers detailed syllabus for Papers I and II, exam pattern, previous year question papers, trends, success rate, advantages, disadvantages, and recommended books to help engineering aspirants prepare strategically for the Indian Forest Service Mains exam.

UPSC IFS Civil Engineering Optional Paper: The Civil Engineering optional paper for the UPSC IFS Mains 2026 is a highly specialized subject that appeals to candidates with an engineering background. With a structured syllabus covering core topics like structural analysis, hydraulics, and environmental engineering, this optional subject demands in-depth technical knowledge and conceptual clarity. Analyzing trends from previous years can help candidates identify high-weightage topics and strategize their preparation effectively.
In the UPSC IFoS Mains exam, the Civil Engineering optional subject consists of two papers, specifically Paper I and Paper II. Each of these papers carries a weightage of 200 marks, summing up to a total of 400 marks for this optional subject. Among the various optional subjects offered by UPSC in IFoS, Civil Engineering is one of the 14 optional subjects available to candidates.
| Paper I of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | Part A of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | STRENGTH OF MATERIALS AND STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS.
ENGINEERING MECHANICS- Units and Dimensions, SI Units, Vectors, Concept of Force, Concept of particle and rigid body. Concurrent, Non Concurrent, and parallel forces in a plane, moment of force and Varignon’s theorem, free body diagram, conditions of equilibrium, Principle of virtual work, equivalent force system. First and Second Moment of area, Mass moment of Inertia. Static Friction, Inclined Plane, and bearings. Kinematics and Kinetics- Kinematics in Cartesian and Polar Coordinates, motion under uniform and nonuniform acceleration, motion under gravity. Kinetics of particle: Momentum and Energy principles, D’ Alembert’s Principle, Collision of elastic bodies, rotation of rigid bodies, simple harmonic motion, Flywheel. STRENGTH OF MATERIALS- Simple Stress and Strain, Elastic constants, axially loaded compression members, Shear force and bending moment, theory of simple bending, Shear Stress distribution across cross sections, Beams of uniform strength, Leaf spring. Strain Energy in direct stress, bending & shear. Deflection of beams : Mecaulay’s method, Mohr’s Moment area method, Conjugate beam method, unit load method. Torsion of Shafts, Transmission of power, close coiled helical springs, Elastic stability of columns, Euler’s Rankine’s and Secant formula. Principal Stresses and Strains in two dimensions, Mohr’s Circle, Theories of Elastic Failure, Thin and Thick cylinder :Stresses due to internal and external pressure-Lame’s equations. STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS : Castiglianio’s theorems I and II, unit load method, method of consistent deformation applied to beams and pin jointed trusses. Slope-deflection, moment distribution, Kani’s method of analysis and column Analogy method applied to indeterminate beams and rigid frames. Rolling loads and Influences lines : Influences lines for Shear Force and Bending moment at a section of a beam. Criteria for maximum shear force and bending Moment in beams traversed by a system of moving loads. Influences lines for simply supported plane pin jointed trusses. Arches : Three hinged, two hinged and fixed arches, rib shortening and temperature effects, influence lines in arches. Matrix methods of analysis : Force method and displacement method of analysis of indeterminate beams and rigid frames. Plastic Analysis of beams and frames : Theory of plastic bending, plastic analysis, statical method, Mechanism method. Unsymmetrical bending : Moment of inertia, product of inertia position of Neutral Axis and Principal axes, calculation of bending stresses. |
| Part B of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | DESIGN OF STRUCTURES : STEEL, CONCRETE AND MASONRY STRUCTURES.
STRUCTURAL STEEL DESIGN : Structural Steel : Factors of safety and load factors. Rivetted, bolted and welded joints and connections. Design of tension and compression members, beams of built up section, riveted and welded plate girders, gantry girders, stanchions with battens and lacings, slab and gusseted column bases. Design of highway and railway bridges : Through and deck type plate girder, Warren girder, Pratt truss. DESIGN OF CONCRETE AND MASONRY STRUCTURES : Concept of mix design. Reinforced Concrete : Working Stress and Limit State method of design-Recommendations of I.S. codes design of one way and two way slabs, staircase slabs, simple and continuous beams of rectangular, T and L sections. Compression members under direct load with or without eccentricity, Isolated and combined footings.Cantilever and Counterfort type retaining walls. Water tanks : Design requirements for Rectangular and circular tanks resting on ground. Prestressed concrete : Methods and systems of prestressing, anchorages, Analysis and design of sections for flexure based on working stress, loss of prestress. Design of brick masonry as per I.S. Codes, Design of masonry retaining walls. |
|
| Part C of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | FLUID MECHANICS, OPEN CHANNEL FLOW AND HYDRAULIC MACHINES
Fluid Mechanics : Fluid properties and their role in fluid motion, fluid statics including forces acting on plane and curved surfaces. Kinematics and Dynamics of Fluid flow : Velocity and accelerations, stream lines, equation of continuity, irrotational and rotational flow, velocity potential and stream functions, flownet, methods of drawing flownet, sources and sinks, flow separation, free and forced vortices. Control volume equation, continuity, momentum, energy and moment of momentum equations from control volume equation, Navier-Stokes equation, Euler’s equation of motion, application to fluid flow problems, pipe flow, plane, curved, stationary and moving vanes, sluice gates, weirs, orifice meters and Venturi meters. Dimensional Analysis and Similitude: Buckingham’s Pi-theorem, dimensionless parameters, similitude theory, model laws, undistorted and distorted models. Laminar Flow : Laminar flow between parallel, stationary and moving plates, flow through the tube. Boundary layer : Laminar and turbulent boundary layer on a flat plate, laminar sublayer, smooth and rough boundaries, drag and lift. Turbulent flow through pipes : Characteristics of turbulent flow, velocity distribution and variation of pipe friction factor, hydraulic grade line and total energy line, siphons, expansion and contractions in pipes, pipe networks, water hammer in pipes and surge tanks. Open channel flow : Uniform and non-uniform flows, momentum and energy correction factors, specific energy and specific force, critical depth, resistance equations and variation of roughness coefficient, rapidly varied flow, flow in contractions, flow at sudden drop, hydraulic jump and its applications surges and waves, gradually varied flow, classification of surface profiles, control section, step method of integration of varied flow equations, moving surges and hydraulic bore. HYDRAULIC MACHINES AND HYDROPOWER : Centrifugal pumps-Types, characteristics, Net Positive Suction Height (NPSH), specific speed. Pumps in parallel. Reciprocating pumps, Airvessels, Hydraulic ram, efficiency parameters, Rotary and positive displacement pumps, diaphragm and jet pumps. Hydraulic turbines, types classification, Choice of turbines, performance parameters, controls, characteristics, specific speed. Principles of hydropower development. Type, layouts and Component works. Surge tanks, types and choice. Flow duration curves and dependable flow. Storage an pondage. Pumped storage plants. Special features of mini, micro-hydel plants. |
|
| Part D of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
Types of soil, phase relationships, consistency limits particles size distribution, classifications of soil, structure and clay mineralogy. Capillary water and structural water, effective stress and pore water pressure, Darcy’s Law, factors affecting permeability, determination of permeability, permeability of stratified soil deposits. Seepage pressure, quick sand condition, compressibility and consolidation, Terzaghi’s theory of one dimensional consolidation, consolidation test. Compaction of soil, field control of compaction. Total stress and effective stress parameters, pore pressure coefficients. Shear strength of soils, Mohr Coulomb failure theory, Shear tests. Earth pressure at rest, active and passive pressures, Rankine’s theory, Coulomb’s wedge theory, earth pressure on retaining wall, sheet pile walls, Braced excavation. Bearing capacity, Terzaghi and other important theories, net and gross bearing Pressure. Immediate and consolidation settlement. Stability of slope, Total Stress and Effective Stress methods, Conventional methods of slices, stability number. Subsurface exploration, methods of boring, sampling, penetration tests, pressure meter tests. Essential features of foundation, types of foundation, design criteria, choice of type of foundation, stress distribution in soils, Boussinessq’s theory, Newmarks’s chart, pressure bulb, contact pressure, applicability of different bearing capacity theories, evaluation of bearing capacity from field tests, allowable bearing capacity, Settlement analysis, allowable settlement. Proportioning of footing, isolated and combined footings, rafts, buoyancy rafts, Pile foundation, types of piles, pile capacity, static and dynamic analysis, design of pile groups, pile load test, settlement of piles, lateral capacity. Foundation for Bridges. Ground improvement techniques-preloading, sand drains, stone column, grouting, soil stabilization. |
|
| Paper II of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | Part A of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | CONSTRUCTION TECHNOLOGY, EQUIPMENT, PLANNING AND MANAGEMENT
Construction Technology- Physical properties of construction materials : Stones, Bricks and Tiles; Lime, Cement and Surkhi Mortars; Lime Concrete and Cement Concrete, Properties of freshly mixed and hardened concrete, Flooring Tiles, use of ferrocement, fiber-reinforced and polymer concrete, high strength concrete and lightweight concrete. Timber- Properties and uses; defects in timber; seasoning and preservation of timber. Plastics, rubber and damp-proofing materials, termite proofing, Materials, for Low cost housing. Construction : Building components and their functions; Brick masonry : Bonds, jointing. Stone masonry. Design of Brick masonry walls as per I.S. codes, factors of safety, serviceability and strength requirements; plastering, pointing. Types of Floors & Roofs. Ventilators, Repairs in buildings. Functional planning of building : Building orientation, circulation, grouping of areas, privacy concept and design of energy efficient building; provisions of National Building Code. Building estimates and specifications; Cost of works; valuation. Construction Equipment- Standard and special types of equipment, Preventive maintenance and repair, factors affecting the selection of equipment, economical life, time and motion study, capital and maintenance cost. Concreting equipments- Weigh batcher, mixer, vibration, batching plant, Concrete Pump. Earth-work equipment : Power shovel hoe, bulldozer, dumper, trailers, and tractors, rollers, sheep foot roller. Construction Planning and Management- Construction activity, schedules, job layout, bar charts, organization of contracting firms, project control and supervision. Cost reduction measures. New-work analysis- CPM and PERT analysis, Float Times, cashing of activities, contraction of network for cost optimization, updating, Cost analysis and resource Allocation. Elements of Engineering of Engineering Economics, methods of appraisal, present worth, annual cost, benefit-cost, incremental analysis. Economy of scale and size. Choosing between alternatives including levels of investments. Project profitability. |
| Part B of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | SURVEY AND TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING Survey : Common methods of distance and angle measurements, plane table survey, leveling traverse survey, triangulation survey, corrections, and adjustments, contouring, topographical map. Surveying instruments for above purposes. Tacheometry. Circular and transition curves. Principles of photo-grammetry. Railways : Permanent way, sleepers, rail fastenings, ballast, points and crossings, design of turnouts, stations and yards, turntables, signals, and interlocking, level crossing. Construction and maintenance of permanent ways : Super-elevation, creep of rail, ruling gradient, track resistance, tractive effort, relaying of track. Highway Engineering : Principles of highway planning, Highway alignments. Geometrical design : Cross section, camber, super-elevation, horizontal and vertical curves. Classification of roads : low cost roads, flexible pavements, rigid pavements. Design of pavements and their construction, evaluation of pavement failure and strengthening. Drainage of roads : Surface and sub-surface drainage. Traffic Engineering : Forecasting techniques origin and destination survey, highway capacity. Channelised and unchannelized intersections, rotary design elements, markings, sign, signals, street lighting; Traffic surveys. Principle of highway financing. | |
| Part C of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | HYDROLOGY, WATER RESOURCES AND ENGINEERING
Hydrology- Hydrological cycle, precipitation, evaporation, transpiration, depression storage, infiltration, overland flow, hydrograph, flood frequency analysis, flood estimation, flood routing through a reservoir, channel flow routing-Muskingum method. Ground water flow : Specific yield, storage coefficient, coefficient of permeability, confined and unconfined aquifers, aquitards, radial flow into a well under confined and unconfined conditions, tube wells, pumping and recuperation tests, ground water potential. WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING- Ground and surface water resource, single and multipurpose projects, storage capacity of reservoirs, reservoir losses, reservoir sedimentation, economics of water resources projects. IRRIGATION ENGINEERING- Water requirements of crops : consumptive use, quality of water for irrigation, duty and delta, irrigation methods and their efficiencies. Canals : Distribution systems for canal irrigation, canal capacity, canal losses, alignment of main and distributary canals, most efficient section, lined canals, their design, regime theory, critical shear stress, bed load, local and suspended load transport, cost analysis of lined and unlined canals, drainage behind lining. Water logging : causes and control, drainage system design, salinity. |
|
| Part D of Upsc civil engineering optional paper | ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING Water Supply- Estimation of surface and subsurface water resources, predicting demand for water, impurities, of water and their significance, physical, chemical and bacteriological analysis, waterborne diseases, standards for potable water. Intake of water : pumping and gravity schemes.
Water treatment- principles of coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation; slow-; rapid-, pressure-, filters; chlorination, softening, removal of taste, odour and salinity. Water storage and distribution : storage and balancing reservoirs : types, location and capacity. Distribution system- layout, hydraulics of pipe lines, pipe fittings, valves including check and pressure reducing valves, meters, analysis of distribution systems, leak detection, maintenance of distribution systems, pumping stations and their operations. Sewage systems- Domestic and industrial wastes, storm sewage-separate and combined systems, flow through sewers, design of sewers, sewer appurtenances, manholes, inlets, junctions, siphon. Plumbing in public buildings. Sewage characterization- BOD, COD, solids, dissolved oxygen, nitrogen and TOC. Standards of disposal in normal water course and on land. Sewage treatment : Working principles, units, chambers, sedimentation tanks, trickling filters, oxidation ponds, activated sludge process, septic tank, disposal of sludge, recycling of waste water. Solid waste- collection and disposal in rural and urban contexts, management of long-term ill-effects. Environmental pollution- Sustainable development. Radioactive wastes and disposal. Environmental impact assessment for thermal power plants, mines, river valley projects. Air pollution. Pollution control acts. |
The IFoS Civil Engineering Optional Syllabus PDF offers a clear and detailed overview of Paper I and Paper II topics prescribed by UPSC. It helps candidates understand the complete syllabus, prioritize important areas, plan structured preparation, and align their study strategy with the latest Indian Forest Service Mains examination pattern.
UPSC Civil Engineering Optional Question Papers from 2018 to 2025 are readily available for aspirants seeking to enhance their preparation. We provided access to the UPSC IFS Civil Engineering optional question papers in PDF format, an invaluable resource for your preparation.
| Year | Paper of Upsc civil engineering optional paper |
| UPSC IFoS Civil Engineering Question Paper 2018 | Paper I |
| UPSC IFoS Civil Engineering Question Paper 2019 | Paper I |
| UPSC IFoS Civil Engineering Question Paper 2020 | Paper I |
| UPSC IFoS Civil Engineering Question Paper 2021 | Paper I |
| UPSC IFoS Civil Engineering Question Paper 2022 | Paper I |
| UPSC IFoS Civil Engineering Question Paper 2023 | Paper I |
| UPSC IFoS Civil Engineering Question Paper 2024 | Paper I |
| UPSC IFoS Civil Engineering Question Paper 2025 | Paper I |
Candidates appearing for the UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) IFS examination must make a thoughtful choice when selecting their optional subject, as it holds substantial weightage in the evaluation process. With a total of 800 marks allotted, the optional subject constitutes approximately 48% of the combined marks for both the written exam and the personality test.
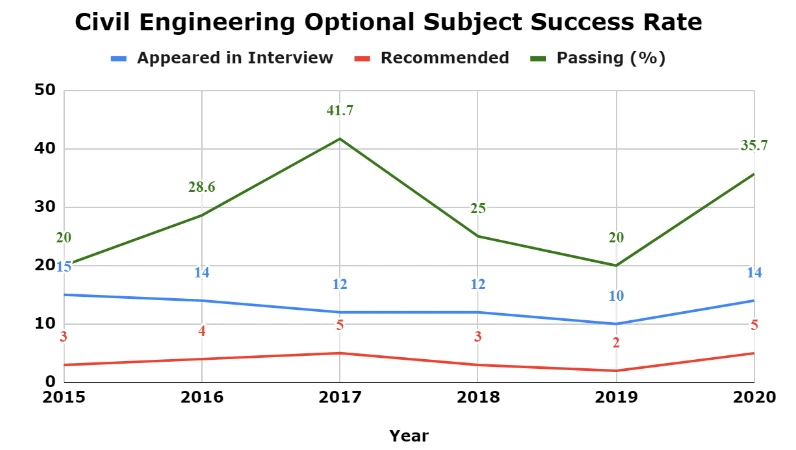
The table below offers a comprehensive overview of the success rate achieved by candidates who opted for Civil Engineering as their optional.
| Year | Number of Candidates for Civil Engineering Optional Paper | ||
| Appeared in Interview | Recommended | Passing (%) | |
| 2015 | 15 | 3 | 20 |
| 2016 | 14 | 4 | 28.6 |
| 2017 | 12 | 5 | 41.7 |
| 2018 | 12 | 3 | 25 |
| 2019 | 10 | 2 | 20 |
| 2020 | 14 | 5 | 35.7 |
By examining the past papers of the Civil Engineering Optional, we can identify a trend in the types of questions asked. There is also a noticeable shift in the themes of the questions. Understanding the UPSC IFS Civil Engineering Question Paper Trend Analysis is advantageous, as it allows candidates to streamline their preparation effectively and enhance their performance in this optional subject.
Please note that before selecting Civil Engineering as your optional subject, carefully weigh these disadvantages against the advantages and consider your own background, interests, and the time you can dedicate to preparation.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series |
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
The UPSC Civil Engineering Optional Paper is a part of the UPSC IFS Main Examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). It is one of the optional subjects that candidates can choose for one of the papers in the mains exam.
The syllabus for the UPSC IFS Civil Engineering optional includes topics like structural analysis, geotechnical engineering, hydraulics, environmental engineering, and construction management.
The UPSC IFS Civil Engineering Optional consists of two descriptive papers—Paper I and Paper II, each carrying 200 marks, making a total of 400 marks in the IFS Mains examination.
Yes, Civil Engineering is a good optional for candidates with an engineering background. It offers a well-defined syllabus, scoring potential, and overlap with IES and IAS exams, but requires strong technical fundamentals and consistent practice.
There are two papers of optional subjects Paper III, Paper IV, Paper V, Paper VI.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>