UPSC IFS Agriculture optional Mains Exam syllabus, detailed insights, tips, and resources to excel in your preparation are provided here.

UPSC IFS Agriculture Optional Paper: The UPSC IFS Mains Examination consists of six papers with a total weightage of 1400 marks. It includes two compulsory papers: English and General Knowledge, each carrying 300 marks. The remaining four papers—Papers I, II, III, and IV—are based on optional subjects chosen by candidates during the application process. Out of these, Paper I and II account for 300 marks each, while the remaining 800 marks are determined by the optional subjects.
For candidates opting for Agriculture as their optional subject, it becomes vital to understand the syllabus, analyze the pattern, and practice Previous Year Question (PYQ) papers. Agriculture, as an optional subject, offers a comprehensive syllabus and the potential for high scoring if approached with the right strategy. Below, we’ll dive into the importance, weightage, and detailed analysis of Agriculture as an optional subject for IFS.
In the UPSC IFS Mains exam, the Agriculture Question Paper subject consists of two papers, specifically Paper I and Paper II. Each of these papers carries a weightage of 200 marks, summing up to a total of 400 marks for this optional subject. Among the various optional subjects offered by UPSC in IFS, the Agriculture Question Paper is one of the 14 optional subjects available to candidates.
What does the IFS Mains Exam Agriculture Optional syllabus include?
| Agriculture | Syllabus |
| Paper I | Ecology and its relevance to man, natural resources, their sustainable management and conservation. Physical and social environment as factors of crop distribution and production. Climatic elements as factors of crop growth, the impact of changing the environment on cropping patterns as indicators of environments. Environmental pollution and associated hazards to crops, animals, and humans.
Cropping pattern in different agro-climatic zones of the country. Impact of high-yielding and short-duration varieties on shifts in cropping pattern. Concepts of multiple cropping, multistorey, relay, and intercropping, and their importance in relation to food production. Package of practices for the production of important cereals, pulses, oil seeds, fibers, sugar, commercial, and fodder crops grown during Kharif and Rabi seasons in different regions of the country. Important features, scope, and propagation of various types of forestry plantations such as extension, social forestry, agroforestry, and natural forests. Weeds, their characteristics, dissemination, and association with various crops; their multiplication; cultural, biological, and chemical control of weeds. Soil-physical, chemical, and biological properties. Processes and factors of soil formation. Modern classification of Indian soils, Mineral and organic constituents of soils and their role in maintaining soil productivity. Essential plant nutrients and other beneficial elements in soils and plants. Principles of soil fertility and its evaluation for judicious fertilizer use, integrated nutrient management. Losses of nitrogen in soil, nitrogen-use efficiency in submerged rice soils, and nitrogen fixation in soils. Fixation of phosphorus and potassium in soils and the scope for their efficient use. Problem soils and their reclamation methods. Soil conservation planning on a watershed basis. Erosion and run-off management in hilly, foot hills, and valley lands; processes and factors affecting them. Dry land agriculture and its problems. The technology of stabilizing agriculture production in rain-fed agriculture areas. Water-use efficiency in relation to crop production, criteria for scheduling irrigations, ways and means of reducing run-off losses of irrigation water. Drip and sprinkler irrigation. Drainage of water-logged soils, quality of irrigation water, the effect of industrial effluents on soil and water pollution. Farm management, scope, importance, and characteristics, farm planning. Optimum resources use and budgeting. Economics of different types of farming systems. Marketing and pricing of agricultural inputs and outputs, price fluctuations and their cost; role of cooperatives in agricultural economy; types and systems of farming and factors affecting them. Agricultural extension, its importance, and role, methods of evaluation of extension programmes, socio-economic survey and status of big, small, and marginal farmers and landless agricultural laborers; farm mechanization and its role in agricultural production and rural employment. Training programmes for extension workers; lab to land programmes. |
| Paper II | Cell Theory, cell structure, cell organelles and their function, cell division, nucleic acids-structure and function, gene structure, and function. Laws of heredity, and their significance in plant breeding. Chromosome structure, chromosomal aberrations, linkage and cross-over, and their significance in recombination breeding. Polyploidy, euploid, and an euploids. Mutation-micro and macro-and their role in crop improvement. Variation, components of variation. Heritability, sterility and incompatibility, classification and their application in crop improvement. Cytoplasmic inheritance, sex-linked, sex-influenced, and sex-limited characters.
History of plant breeding. Modes of reproduction, selfing, and crossing techniques. Origin and evolution of crop plants, centre of origin, the law of homologous series, crop genetic resources-conservation and utilization. Application of principles of plant breeding to the improvement of major field crops. Pure-line selection, pedigree, mass and recurrent selections, combining ability, and its significance in plant breeding. Hybrid vigour and its exploitation, backcross method of breeding, breeding for disease and 20 pest resistance, role of inter-specific and inter-generic hybridization. Role of biotechnology in plant breeding. Improved varieties, hybrids, and composites of various crop plants. Seed technology, its importance. Different kinds of seeds and their seed production and processing techniques. Role of public and private sectors in seed production, processing, and marketing in India. Physiology and its significance in agriculture. Imbibitions, surface tension, diffusion and osmosis. Absorption and translocation of water, transpiration, and water economy. Enzymes and plant pigments; photosynthesis-modern concepts and factors affecting the process, aerobic and non-aerobic respiration; C, C and CAM mechanisms. Carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. Growth and development; photoperiodism and vernalization. Auxins, hormones, and other plant regulators and their mechanism of action and importance in agriculture. Physiology of seed development and germination; dormancy. Climatic requirements and cultivation of major fruits, plants, vegetable crops, and flower plants; the package of practices and their scientific basis. Handling and marketing problems of fruit and vegetables. Principal methods of preservation of important fruits and vegetable products, processing techniques, and equipment. Role of fruits and vegetables in human nutrition. Raising of ornamental plants, and design and layout of lawns and gardens. Diseases and pests of field vegetables, orchards, and plantation crops of India. Causes and classification of plant pests and diseases. Principles of control of plant pests and diseases Biological control of pests and diseases. Integrated pest and disease management. Epidemiology and forecasting. Pesticides, their formulations, and modes of action. Compatibility with rhizobial inoculants. Microbial toxins. Storage pests and diseases of cereals and pulses, and their control. Food production and consumption trends in India. National and international food policies. Production, procurement, distribution, and processing constraints. Relation of food production to national dietary pattern, major deficiencies of calorie and protein. |
UPSC Agriculture Optional Question Papers from 2018 to 2023 are readily available for aspirants seeking to enhance their preparation. We provided access to the UPSC IFS Agriculture optional question papers in PDF format, an invaluable resource for your preparation.
| Year | Paper |
| UPSC IFS Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2018 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2019 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2020 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2021 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2022 | Download Paper I |
| UPSC IFS Agriculture Optional Question Paper 2023 | Download Paper-01 |
Candidates appearing for the UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) IFS examination must make a thoughtful decision while selecting their optional subject, as it holds substantial weightage in the evaluation process. With a total of 800 marks allotted, the optional subject carries approximately 48% of the combined marks for both the written exam and the personality test (interview).
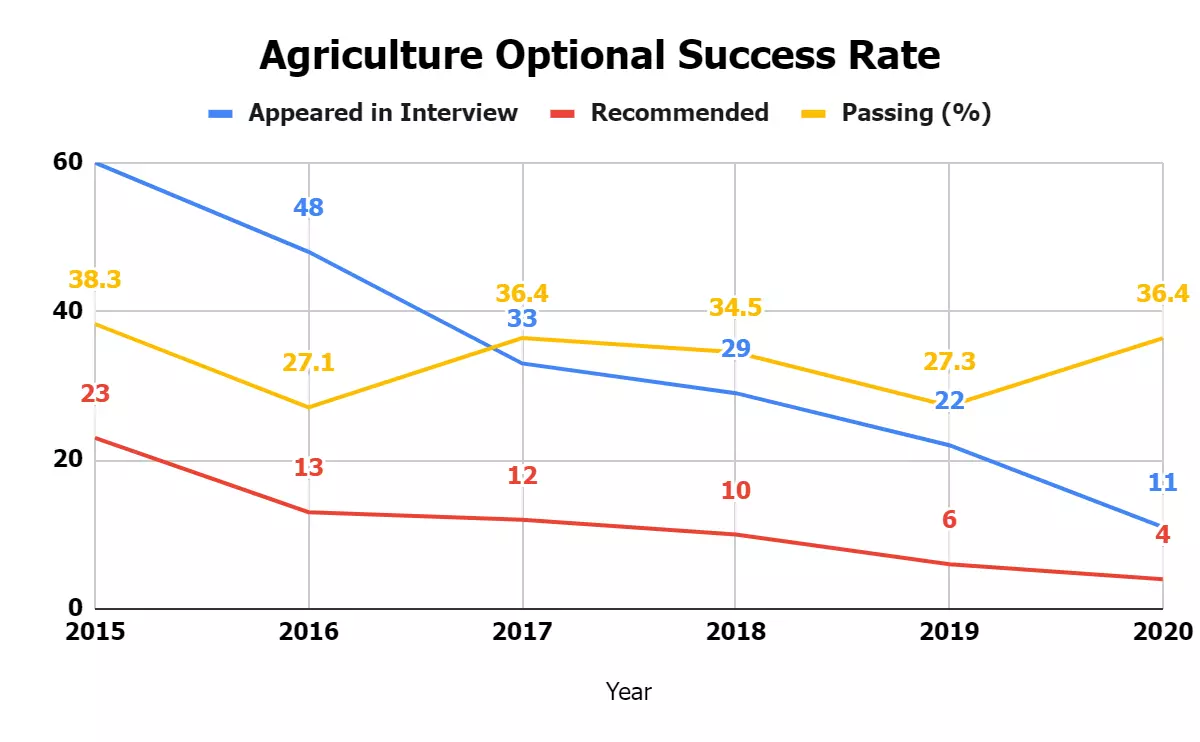
The table below offers a comprehensive overview of the success rate achieved by candidates who opted for Agriculture Optional as their optional.
| Year |
Number of Candidates |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Appeared in Interview | Recommended | Passing (%) | |
| 2015 | 60 | 23 | 38.3 |
| 2016 | 48 | 13 | 27.1 |
| 2017 | 33 | 12 | 36.4 |
| 2018 | 29 | 10 | 34.5 |
| 2019 | 22 | 6 | 27.3 |
| 2020 | 11 | 4 | 36.4 |
By examining the past papers of the Agriculture Optional, we can identify a trend in the types of questions asked. There is also a noticeable shift in the themes of the questions. Understanding the UPSC IFS Agriculture Question Paper Trend Analysis is advantageous, as it allows candidates to streamline their preparation effectively and enhance their performance in this optional subject.
Exploring the Advantages of Agriculture Optional as an Optional Subject for the UPSC IFS Mains Exam
Challenges: Cons of Choosing Agriculture Optional as Your UPSC IFS Optional Subject
Please note that before selecting Agriculture Paper as your optional subject, carefully weigh these disadvantages against the advantages and consider your own background, interests, and the time you can dedicate to preparation.
Booklist for Agriculture Optional Paper
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
No, both subjects are different and have different applications.
The Agriculture Optional Subject in the UPSC IFS Mains exam has two papers: Paper-I and Paper-II, each worth 250 marks for a total of 500 marks.
No, you can choose certain combination of subjects, which are: Agriculture and Agricultural Engg. Agriculture and Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Science. Agriculture and Forestry.
Agriculture Optional syllabus include Ecology and its relevance to man, Weeds, their characteristics, Soil conservation, Cell Theory, cell structure, History of plant breeding. Modes of reproduction, Seed technology, its importance, etc.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>