![]() 12 Dec 2023
12 Dec 2023
Non-renewable resources have a limited stock. Once the stocks are exhausted it may take thousands of years to be renewed or replenished. Minerals and fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas are examples of non-renewable sources of energy. Mineral fuels are essential for generation of power, required by agriculture, industry, transport and other sectors of the economy.
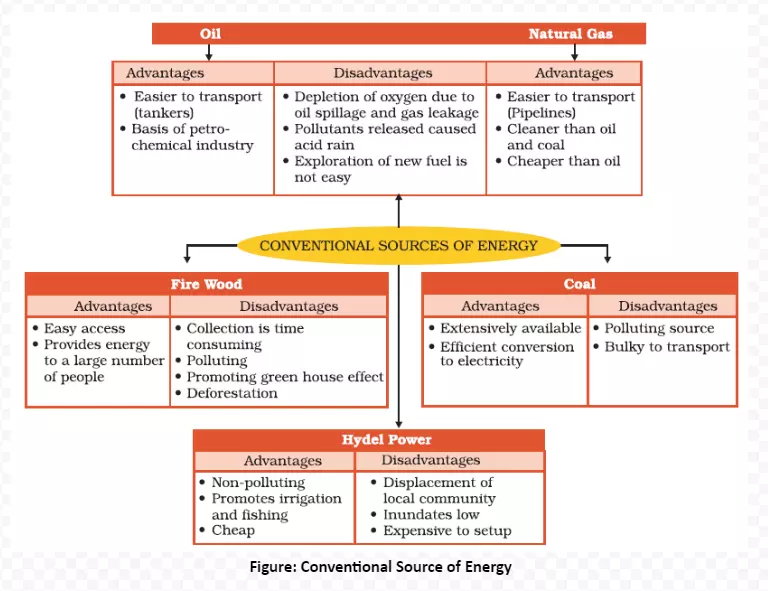
Fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas, firewood, cattle dung cake, nuclear energy minerals, electricity (both hydel and thermal) are the conventional source of energy and are exhaustible resources (Refer below Figure ).
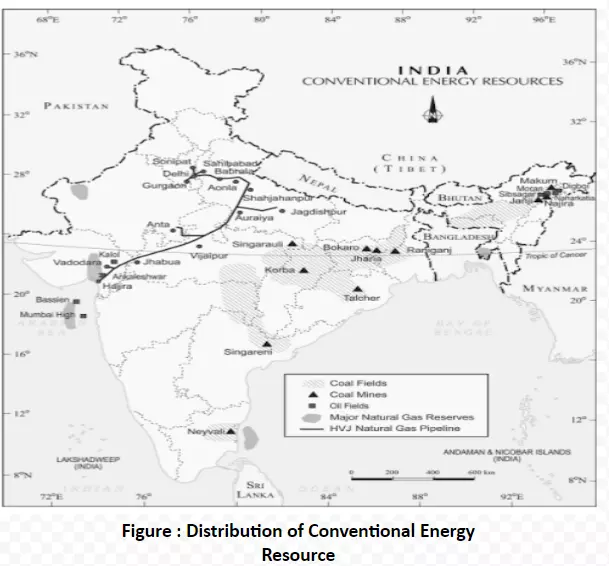
Marked absence of coal in the African Continent that falls within the tropical region with Evergreen forest is contrasted with rich coal fields of Applachians (North America) and Pennines (Europe) that fall in the mid latitude region. Can you establish the link between the distribution of coal resources and theories of Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics, shaping the geological history of these strategic source of energy?
In summary, diverse sources of energy, from fossil fuels like coal to natural gas, are crucial for powering our world. Understanding their distribution and characteristics is vital for sustainable energy planning, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach to ensure a resilient and efficient energy future.
Also Read: Conventional Sources of Energy in India: Wealth, Challenges, Sustainable Future
<div class="new-fform">
</div>